
Why are Opioids So Addictive?
*Corresponding Author(s):
Bernice La FranceDepartment Of Anesthesiology, Howard University Hospital And Howard University College Of Medicine, Washington, D.C, United States
Tel:+1 2028656100,
Email:bemore1576@gmail.com
Abstract
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
Opioids alter the functioning of the brain, which gradually becomes tolerant to the drugs. Thus, a person has to take high amounts of the drug to experience the same feeling. One becomes dependent on the drug when he/she uses the drug for a long duration, and cessation from the drug leads to withdrawal symptoms such as muscle cramps, anxiety, and diarrhea [2]. Addiction to opioids could be life-threatening as it exposes the addict to overdose which is very dangerous as it causes breathing to slow down or stop altogether, which results in the possibility of an addict becoming unconscious or dying [2]. The use of opioids has also been associated with increased sensitivity to pain, which means the probability of a sustainable trend of increasing dosage for the management of recurrent pain [3]. Dizziness, confusion, and depression, which have adverse effects of physical and mental functionalities, are other effects of opioid abuse. The class of drugs also cause vomiting, constipation, and low levels of testosterone [3]. The mortality rate due to opioid overdose is also high, with more than 46 people reported to die daily in the United States from prescription opioids [3]. The persistence of the opioid epidemic, the legality of its medicinal use that has become a health epidemic, and the effects of its use that promotes sustained reliance identify the need for a solution to the opioid addiction problem. This study seeks to identify the causes of opioid addiction for the identification of possible solutions to the problem.
METHODS
The study sought to understand the causes of opioid addiction for the development of knowledge that can lead to the identification of solutions to the harmful addiction to opioid drugs. The systematic review of the literature, which involves the collection and analysis of data from existing literature, was used. The capacity of the systematic review to realize the objective of this study, because of the existence of literature on factors to the occurrence of opioid addiction, informed its use. Rigor was also applied in the recruitment and selection of literature for the review. The EBSCO host database, ScienceDirect database, and Google search engine were used to recruit sources for the review and the following search phrases were applied.
• Causes of opioid addiction
• Reasons for opioid addiction
• Factors to opioid addiction
• Causes of opioid misuse
• Reasons for opioid misuse
• Factors to opioid misuse
Duplicates were eliminated before the articles were screened for their publication dates and articles published before the year 2014 were eliminated. A quality assessment then followed, only sources that contained relevant information to the objective of the study were selected, and med the validity criteria for quantitative studies or credibility criteria for qualitative studies were included. Figure 1 below summarizes the procedure for the selection of the studies used in the review.
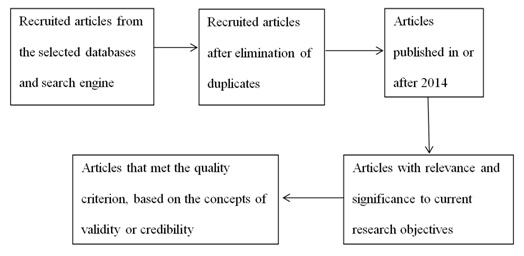
Figure 1: Procedure for selecting reviewed studies.
The relevance of the concepts, which were in a published source, to the objective of the study about the addictive nature of opioids, was one of the criteria for inclusion. A source was only included if it identified at least a reason for the incidence of opioid abuse or misuse. The quality of an article, which credibility or validity identifies, was another criterion. Publication in the year 2014 or later also informed inclusion. The failure to meet any of the criteria led to the exclusion of a source from the review.
The researcher assumed the data collection and analysis responsibility. Each selected article was examined, based on the inclusion criteria, for the selection of the articles for the review. Selected articles were synthesized for the identification of relevant themes and concepts that were then consolidated to explain the addictive nature of opioids. The study, based on its reliance on existing and publicly available literature, was not susceptible to ethical issues.
RESULTS
|
Author(s) |
Major Themes |
|
Lockwood CJ [4] |
|
|
Madhusoodanan J [5] |
|
|
Cicero TJ and Ellis MS [6] |
|
|
Han B, et al. [7] |
|
|
Levy S, et al. [8] |
|
The review identifies multiple factors that explain the opioid addiction. The need for effective pain management and the subsequent advocacy for effective management is the root cause of the opioid addiction because of its effects on the emergence of the use of opioids for pain management [4]. Effects of opioid on pleasure, relaxation, and contentment, which emerge from initial use of opioids for pain management then sustains the usage into addiction [4-7]. The lack of knowledge on the possible adverse effects of addiction [5], and the failure to balance the focus between the positive and the negative effects of opioids are other reasons for the observed abuse [6]. The misconception that the delayed release of opioids into the body could manage abuse, which instead promoted abuse, is another reason as the drug promoted intake of opioid [4,6]. The vulnerability of adolescents [4,8], misuse of illegal drugs [8], and susceptibility to influence from friends and relatives [7] are other reasons causes of opioid addiction. The reliance of opioids as alternatives to illegal drugs, effects of withdrawal symptoms, the failure to eliminate the addictive effects of opioids [6], and the failure to develop alternative strong pain management drugs to opioids [5], is other reasons for the addiction.
DISCUSSION
The review identifies multiple reasons for the addictive nature of opioids. Some of the reasons are common among more than one of the reviewed sources, and this establishes the credibility of the results [4,6,7]. For example, identify the role of the perceived benefits of opioids as the drivers of the addiction. The reliance on current publications on the reasons for opioid addiction also identifies the contemporary nature and validity of the results. The identified reasons for the addictive nature of opioid use forecast the persistence of the opioid addiction problem and establish bases for possible solutions. Research initiatives into the development of alternative pain management drugs and the management of the addictive features of opioids are some of the existing avenues to a solution. Regulatory measures that increase the cost of opioids, including the illegalization of the drugs following the development of safe alternatives, are other bases for alternatives.
CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- Miller NS, Gold MS (2015) Prescription opioids and addiction. Psychiatric Annals 45: 516-521.
- Williams TC (2017) Long read review: Drug dealer, MD: How doctors were duped, patients got hooked and why it’s so hard to stop by Anna Lembke. LSE Review of Books, Wales, UK.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017) Opioid overdose. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, USA.
- Lockwood CJ (2018) Why is there an opioid crisis? Contemporary OB/GYN, Norwalk, USA.
- Madhusoodanan J (2018) Inner workings: Safer opioids may be on the horizon, but mitigating addiction is a long shot. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115: 8229-8231.
- Cicero TJ, Ellis MS (2017) The prescription opioid epidemic: A review of qualitative studies on the progression from initial use to abuse. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 19: 259-269.
- Han B, Compton WM, Blanco C, Crane E, Lee J, et al. (2017) Prescription opioid use, misuse, and use disorders in US adults : 2015 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Ann Intern Med 167: 293-301.
- Levy S, Breen L, Lunstead J, Weitzman ER (2018) Facing addiction: A laudable, but incomplete effort. Am J Public Health 108: 153-155.
Citation: Griffith C, France BL (2018) Why are Opioids So Addictive? J Addict Addictv Disord 5: 16.
Copyright: © 2018 Bernice La France, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

