
A Study to Find the Prevalence of Breast Engorgement among Lactating Mothers
*Corresponding Author(s):
Indrani DDepartment Of Urology And Obstetrics Physiotherapy, Saveetha College Of Physiotherapy, Saveetha Institute Of Medical And Technical Sciences, Tamil Nadu, India
Tel:+91 7731852852,
Email:indranidasarapu@gmail.com
Abstract
Breast engorgement problem was common in early days and also after weeks of breast feeding. This frequent problem can happen to lactating mother who don’t or can’t breast feed as well as those who do. It is usually caused by an imbalance between milk supply and infant demand, if engorgement left untreated it can lead to potentially serious issues including painful blebs, plugged milk ducts or mastitis.
Aim
The study aimed to find out the prevalence of breast engorgement among lactating mothers with vaginal delivery, lower segmental caesarean section.
Materials and Methods
A total of 90 women were selected from Saveetha Hospital and Saveetha Rural Health Centre, based on the inclusion criteria Saveetha Hospital and Saveetha Rural Health Centre, based on the inclusion criteria of Lactating mothers with Breast Engorgement and pain for atleast 2-3days who underwent vaginal delivery or lower segmental caesarean section. Exclusion criteria were lactating mothers with soft breast and non lactating mothers and other breast problems. After getting the consent from mothers and after explaining the Six Point Self-rated Engorgement Scale (SPES) and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). They were asked to rate their level of engorgement and pain. The materials used were VAS and SPES.
Results
The study showed that the prevalence of breast engorgement among lactating mothers was 65%-75%.
Conclusion
The study concluded that the prevalence of breast engorgement among lactating mothers was 65%-75%. Breast engorgement is a major issue in the lactating mothers can leads to many problems like blocked milk ducts, feeding difficulties, a depressed milk ejection reflex, infection, inflammation of the breast and sore/cracked nipples.
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Engorgement was assessed using 6-Point Self Rated Engorgement Scale from 1 to 6 (Figure 1)
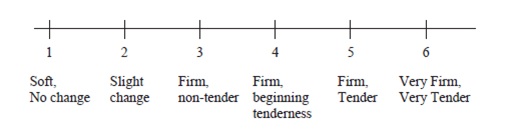
1- being soft, no change
2- being slight change
3- being firm, non-tender
4- being firm, beginning tenderness
5- being firm, tender
6- being very firm, very tender, [Any measure of 3- firm, no tender or more after baseline was the threshold for this subjective rating]
Pain was assessed subjectively by using the visual analogue scale, a subjective measure of self-rated pain on a numerical scale of 1-10 (Figure 2)
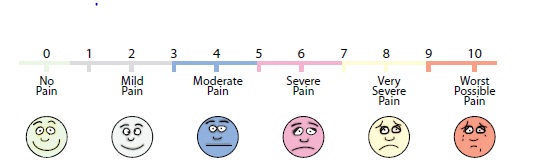
0- Being no pain
1-3 being mild pain
3-5 being moderate pain
5-7 being sever pain
7-9 being very severe pain
9-10 being worst possible pain [10 being the worst possible pain, 5 moderate pain, 0 no pain]. The threshold for pain was having atleast one subsequent pain measure 3points or more above baseline.
The participants in this study belongs to lower socio economic status and had no idea about breast feeding positions, breast care, breast engorgement and problems related to breast.
RESULTS
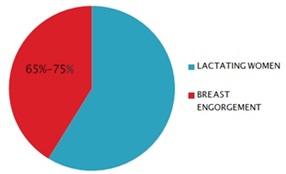 Figure 3: Percentage of breast engorgement among lactating mothers.
Figure 3: Percentage of breast engorgement among lactating mothers.|
S. NO |
Name |
Age |
6-Point Self Rated Engorgement Scale |
Visual Analogue Scale |
|
1 |
Kamachi |
28 |
4 |
5 |
|
2 |
Meenakshi |
25 |
5 |
7 |
|
3 |
Rani |
27 |
5 |
7 |
|
4 |
Roja |
20 |
6 |
8 |
|
5 |
Sasikala |
27 |
3 |
2 |
|
6 |
Thagan |
31 |
1 |
0 |
|
7 |
Srigitha |
35 |
1 |
0 |
|
8 |
Archana |
31 |
2 |
2 |
|
9 |
Sumitra |
23 |
5 |
4 |
|
10 |
Kamaaktchi |
31 |
3 |
3 |
|
11 |
Monisha |
23 |
5 |
6 |
|
12 |
Jenifer |
23 |
6 |
7 |
|
13 |
Anuradha |
35 |
1 |
0 |
|
14 |
Mahizmadhi |
25 |
1 |
0 |
|
15 |
Manionmani |
36 |
1 |
0 |
|
16 |
Poongothai |
29 |
4 |
8 |
|
17 |
Sindhiya |
32 |
1 |
0 |
|
18 |
M. Shanthi |
40 |
1 |
0 |
|
19 |
Ramya |
28 |
3 |
2 |
|
20 |
Priyanka |
24 |
4 |
6 |
|
21 |
Rosemitha |
23 |
5 |
8 |
|
22 |
Selvi |
24 |
3 |
4 |
|
23 |
Methilda |
39 |
1 |
0 |
|
24 |
Indra |
29 |
4 |
5 |
|
25 |
M. Gowri |
26 |
6 |
9 |
|
26 |
Meenakshi |
44 |
1 |
0 |
|
27 |
Vaishali |
23 |
3 |
4 |
|
28 |
Umarani |
36 |
4 |
3 |
|
29 |
Joly |
34 |
4 |
3 |
|
30 |
Kavitha |
38 |
1 |
0 |
|
31 |
Rajarajeshwai |
38 |
1 |
0 |
|
32 |
Ishwarya |
27 |
4 |
7 |
|
33 |
Prathisha |
26 |
5 |
8 |
|
34 |
Mahalakshmi |
30 |
1 |
0 |
|
35 |
Joshibha |
38 |
1 |
0 |
|
36 |
Radhika |
37 |
1 |
0 |
|
37 |
Danalakshmi |
34 |
5 |
6 |
|
38 |
Madhu |
21 |
6 |
5 |
|
39 |
Rohini |
40 |
4 |
5 |
|
40 |
Sujitha |
38 |
5 |
4 |
|
41 |
Hema |
31 |
4 |
3 |
|
42 |
Kousalya |
39 |
3 |
8 |
|
43 |
Lakshmi |
35 |
4 |
6 |
|
44 |
Rohini. M |
24 |
4 |
6 |
|
45 |
Fazilath |
24 |
4 |
6 |
|
46 |
Devi |
37 |
6 |
8 |
|
47 |
Sylvia |
38 |
5 |
9 |
|
48 |
Babisha |
24 |
4 |
7 |
|
49 |
Heena |
32 |
3 |
6 |
|
50 |
Murrugammal |
32 |
6 |
7 |
|
51 |
Yosodha |
23 |
3 |
5 |
|
52 |
Vijayalakshmi |
28 |
4 |
4 |
|
53 |
Janaki |
25 |
3 |
5 |
|
54 |
Amulya |
28 |
3 |
5 |
|
55 |
Malliga |
33 |
2 |
1 |
|
56 |
Anjali |
24 |
5 |
4 |
|
57 |
Ramya |
33 |
6 |
9 |
|
58 |
Rani |
34 |
1 |
0 |
|
59 |
Kamatchi |
22 |
4 |
5 |
|
60 |
Sumathi |
38 |
3 |
2 |
|
61 |
Lakshmi |
31 |
4 |
2 |
|
62 |
Malliga |
22 |
5 |
3 |
|
63 |
Devika |
30 |
1 |
0 |
|
64 |
Uma |
29 |
6 |
8 |
|
65 |
Komalatha |
33 |
4 |
7 |
|
66 |
Sarojini |
36 |
1 |
0 |
|
67 |
Girija |
35 |
1 |
2 |
|
68 |
Padma |
33 |
2 |
0 |
|
69 |
Bommi |
36 |
2 |
1 |
|
70 |
Yasodha |
28 |
3 |
4 |
|
71 |
Bavani |
34 |
1 |
0 |
|
72 |
Vanithamani |
40 |
2 |
0 |
|
73 |
Padmavathi |
42 |
2 |
0 |
|
74 |
Chandrakumari |
27 |
3 |
6 |
|
75 |
Vijayalakshmi |
26 |
4 |
8 |
|
76 |
Sujitha |
26 |
3 |
4 |
|
77 |
Christina |
23 |
4 |
6 |
|
78 |
Mallisharani |
35 |
1 |
1 |
|
79 |
Kanchana |
28 |
4 |
7 |
|
80 |
Revathi |
25 |
5 |
8 |
|
81 |
Kalaivani |
32 |
1 |
0 |
|
82 |
Elilarsi |
28 |
6 |
9 |
|
83 |
Bharathy |
21 |
3 |
4 |
|
84 |
Kaniyammal |
33 |
1 |
0 |
|
85 |
Meena |
27 |
4 |
5 |
|
86 |
Panchavarnam |
24 |
3 |
4 |
|
87 |
Sesikala |
30 |
1 |
0 |
|
88 |
Premalatha |
28 |
5 |
8 |
|
89 |
Pavithra |
24 |
6 |
7 |
|
90 |
Valli |
22 |
4 |
8 |
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- Godhia ML, Patel N (2013) Colostrum - its Composition, Benefits as a Nutraceutical - A Review. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 1: 37-47.
- Newton M, Newton NR (1951) Postpartum engorgement of the breast. American Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology 61: 664-667.
- Hill PD, Humenick SS (1994) The occurrence of breast engorgement. J Hum Lact 10: 79-86.
- Hewat RJ, Ellis DJ (1987) A comparison of the effectiveness of two methods of nipple care. Birth 14: 41-45.
- Humenick SS, Hill PD, Anderson MA (1994) Breast engorgement: Patterns and selected outcomes. J Hum Lact 10: 87-93.
- Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee, Eglash A (2010) ABM clinical protocol #8: human milk storage information for home use for full-term infants (original protocol March 2004; revision #1 March 2010). Breastfeed Med 5: 127-130.
- Lee WT, Lui SS, Chan V, Wong E, Lau J (2006) A population-based survey on infant feeding practice (0-2 years) in Hong Kong: breastfeeding rate and patterns among 3,161 infants below 6 months old. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 15: 377-387.
- Priyanka P, Basavaraj C, Ramannavar A, Kurhade G, Kurhade A, et al. (2016) Comparative effect of ultrasound therapy with conventional therapy on breast engorgement in immediate post-partum mothers: A randomized controlled trial. Integr Mol Med 3: 553-558.
- Arora S, Vatsa M, Dadhwal V (2008) A Comparison of Cabbage Leaves vs. Hot and Cold Compresses in the Treatment of Breast Engorgement. Indian J Community Med 33: 160-162.
- de Sousa L, Haddad ML, Nakano AM, Gomes FA (2012) [A non-pharmacologic treatment to relieve breast engorgement during lactation: an integrative literature review]. Rev Esc Enferm USP 46: 472-479.
- Brown D, Langdon C (2014) Does Kinesio Elastic Therapeutic Taping Decrease Breast Engorgement in Postpartum Women? Clinical Lactation (Vol 5).
- McLachlan Z, Milne EJ, Lumley J, Walker BL (1991) Ultrasound treatment for breast engorgement: A randomised double blind trial. Aust J Physiother 37: 23-28.
- Lawrence RA (1989) Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. St. Louis, Missouri, USA. Pg no: 652.
- Applebaum RM (1970) The modern management of successful breast feeding. Pediatr Clin North Am 17: 203-225.
Citation: Indrani D, Sowmya MV (2019) A Study to Find the Prevalence of Breast Engorgement among Lactating Mothers. J Reprod Med Gynecol Obstet 4: 023.
Copyright: © 2019 Indrani D, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

