
Dermoscopy of Keratoacanthoma: “Jellyfish Tentacles” Appearance
*Corresponding Author(s):
Patil DeenaDepartment Of Dermatology, M S Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Email:patildeena13@gmail.com
Introduction
Keratoacanthoma is characterized by a nodule with central crater like appearance. The dermoscopy of the lateral wall of nodule shows white areas and is known to correspond to keratinous crater with acanthosis [1]. We are here reporting a case of keratoacanthoma showing a patterned white area on the lateral wall of the nodule.
Case Report
A 50-year-old male, complaints of a slowly growing asymptomatic skin lesion on right hand since 8 months. On examination there was a small nodule measuring around 3x2 cm with crusted plaque on the top (Figure 1a). On palpation it was non tender with mild indurated base. Clinically the differential diagnosis considered were keratoacanthoma, nodular basal cell carcinoma, dermatofibroma, and ruptured sebaceous cyst. On dermoscopy, there was a central concentric ring-shaped crust with a few haemorrhagic spots. On the lateral walls of the nodule there were a regular wavy patterned whitish structure on dark background giving an appearance of “jelly fish tentacles” (Figure 1b). After dermoscopy, dermatofibroma and sebaceous cyst were ruled out due to absence of central white area, pigmentary network, and ivory white background respectively. Excision biopsy was performed, and histopathology depicts a crater -like imagination of the epidermis, filled with keratinous material (Figure 2a). The wall of the crater is formed by acanthotic epidermis at places showing enlarged keratinocytes suggestive of keratoacanthoma (Figure 2b).
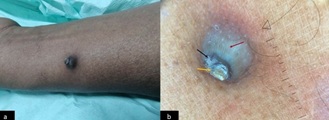 Figure 1a) A solitary nodule with central crust present on the flexor aspect of right hand; b)Dermoscopy (Heine Delta 30: Polarized view, 10× magnification) showing central concentric scales (yellow arrow) with haemorrhage(black arrow). Lateral walls of the nodule showing patterned whitish areas giving a jelly fish tentacle appearance (red arrow).
Figure 1a) A solitary nodule with central crust present on the flexor aspect of right hand; b)Dermoscopy (Heine Delta 30: Polarized view, 10× magnification) showing central concentric scales (yellow arrow) with haemorrhage(black arrow). Lateral walls of the nodule showing patterned whitish areas giving a jelly fish tentacle appearance (red arrow).
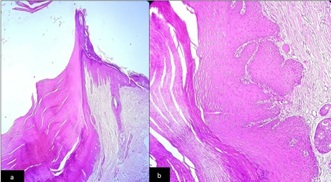 Figure 2: a) (H&E Stain) 10X: Section showing a crater -like imagination of the epidermis, filled with keratinous material. b) (H&E Stain) 40X: Section showing the wall of the crater formed by acanthotic epidermis at places showing enlarged keratinocytes.
Figure 2: a) (H&E Stain) 10X: Section showing a crater -like imagination of the epidermis, filled with keratinous material. b) (H&E Stain) 40X: Section showing the wall of the crater formed by acanthotic epidermis at places showing enlarged keratinocytes.
Discussion
Keratoacanthoma is a self-limiting skin tumour. It is postulated that keratoacanthoma is derived from follicular infundibulum as the expression of K17 exceeds K 16in the tumour [2]. In 1940, it was Freudenthal of Wroclaw who coined the term “keratoacanthoma” as histology showed excessive acanthosis in the epidermis [3] Dermoscopy is helpful to differentiate various nodular lesions such as keratoacanthoma, nodular basal cell carcinoma, dermatofibroma, and sebaceous cyst [4]. The central concentric rings of heaped up keratin in the centre with haemorrhage may be seen in both keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma [1]. The peripheral arrangement of vascular structures is more prominent in squamous cell carcinoma, where as in keratoacanthoma linear irregular vascular dots and haemorrhage is seen. In nodular basal cell carcinoma, there is presence of arborizing vessels with white structure less areas and less commonly blue grey globules [5]. The white areas seen on the lateral surface of the nodule indicate the keratin deposition in the crater and extensive acanthosis seen in histopathology of keratoacanthoma [5]. The dermoscopy features of lateral wall of keratoacanthoma lesion is less described in literature. The white areas in the periphery showed an appearance of jelly fish tentacles on Dermoscopy as seen in our index case. However histopathological examination gives a definitive confirmatory diagnosis.
Conclusion
We conclude that, in keratoacanthoma apart from centre concentric rings of scales with haemorrhage, the white structures on the lateral walls resembling “jelly fish tentacles” indicate presence of central crater and acanthosis. This case highlights that this dermoscopy feature on the peripheral walls of keratoacanthoma might help in identifying lesion as against the white irregular structure less areas seen in squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinomas.
Declaration of Patient Consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given her consent for her images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patient understands that her names and initials will not be published, and due efforts will be made to conceal her identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
The Authors declares that there is no conflict of interest
References
- Sgouros D, Theofili M, Damaskou V, Theotokoglou S, Theodoropoulos K, et al. (2021) Dermoscopy as a Tool in Differentiating Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Its Variants. Dermatol Pract Concept 11: 2021050.
- Yoshikawa K, Katagata Y, Kondo S (1995) Relative amounts of keratin 17 are higher than those of keratin 16 in hair-follicle-derived tumors in comparison with nonfollicular epithelial skin tumors. J Invest Dermatol Page no: 104:396.
- Karaa A, Khachemoune A (2007) Keratoacanthoma: a tumor in search of a classification. Int J Dermatol 4: 671-678.
- Kuonen F, Durack A, Gaide O (2016) Clues in DeRmoscopy: Dermoscopy of keratoacanthoma. Eur J Dermatol 26: 419-420.
- Álvarez-Salafranca M, Ara M, Zaballos P (2021) Dermoscopy in Basal Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Edn) 112: 330-338.
Citation: Deena P, Rithvik KRG, Santosh KV, Sumathy TK (2023) Dermoscopy of Keratoacanthoma: “Jellyfish Tentacles” Appearance. J Clin Dermatol Ther 9: 0111.
Copyright: © 2023 Patil Deena, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

