
Effectiveness of Muscle Relaxatnt Terapy in the Treatment of Tmj Dysfunction
*Corresponding Author(s):
Tetiana KostiukDepartment Of Orthodontic And Prosthetic Dentistry, Faculty Of Med Dent, Bogomolets National Medical University Kiev, Ukraine
Email:k-tm@ukr.net
Abstract
Our study allowed us to trace and analyze changes in the chewing muscles of patients that occur during the treatment of Tempoal-Mandibular Joint dysfunction (TMJ) and indicate its effectiveness. In patients with TMJ dysfunction, qualitative and quantitative indicators of electromyography closely correlate with the stages of development of pathology and correspond to its clinical manifestations. In this study, for the first time, the relationship between changes in the parameters of the frequency of muscle contractions and the subjective sensation of pain in the area of the specified chewing muscle in patients was analyzed. The purpose of this study is to study and comparative analysis of the nature and degree of changes in electromyographic activity of the main and auxiliary chewing muscles in patients with TMJ dysfunction before and after the use of myorelaxing spleen. Materials and methods of research. A five-year study of patients with TMJ dysfunction (109 people). The general analysis provided 1024 electromyograms before and at the stages of treatment of patients. The results of the analysis of the effectiveness of the use of myorelaxation tires in the treatment of TMJ dysfunction can improve the quality of treatment of this pathology in patients. The results obtained after 12 months indicate that the effectiveness of treatment of patients with KG I (with the lowest intensity of symptoms of TMJ dysfunction) reached 89.1 ± 1.3%; KG II – up to 78.3 ± 1.3%.
Keywords
Bioelectric rest; Bioelectrical activity; Chewing muscles; Dysfuction; Electromyography; Facial muscles; Splin; Temporomate-mandibular joint, Visual-analog pain scale (VAS)
Introduction
The problem of effective diagnosis and treatment of TMJ dysfunction was and, unfortunately, remains one of the main problems of modern dentistry. Analysis of the sharp increase in annual patient appeals and its general high prevalence is due to the variety of complaints and clinical manifestations of this pathology. Diagnosis and treatment of TMJ dysfunction have a multidisciplinary, fundamental and individualized approach [1]. 80% of adults and almost 25% of children and adolescents have clinical manifestations that meet the criteria for the diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction [2,3]. The number of patients with TMJ dysfunction is increasing every year [4]. A sharp increase in the prevalence of the disease is due to the peculiarities of the etiopathogenesis of TMJ dysfunctions: the initial stages are asymptomatic and the primary organic changes cannot be controlled [4,5].
Diagnosis and treatment of TMJ dysfunctions is complicated by the fact that 95.7–98% of such patients have complications in the form of pain burden [5]. The pain that accompanies this pathology is chronic and differs from other types of pain. Structural and functional neuroplastic changes in the brain, which occur in patients with TMJ pain dysfunction, are caused by the processes of peripheral and central sensitization. It is possible to stop such pain only if it is possible to activate the process of reversible development of already formed structural and functional changes. Functional changes in various departments of the central nervous system consist in damage to the processes of transmission of nerve impulses. As a result of these injuries: neuroplastic changes in these departments. It is this fact that explains what we observe in patients with TMJ dysfunction: the patient feels pain even after the cessation of the triggering stimulus. In these cases, the phenomenon of pain loses its protective function and turns from a symptom of primary signaling value into a formed independent disease [5]. When researching the etiopathogenetic mechanisms of the development of TMJ dysfunction, neuromyogenic factors are dominant. The paradigm of symptoms is the main basis for existing traditional methods of treatment of TMJ muscle and joint dysfunction [5]. That is why the priorities in the treatment of painful TMJ dysfunction are myorelaxation and drug therapy to relieve pain symptoms in patients.
The transformation of the usual myotatic reflex should be carried out using therapeutic splints. To adjust the load in the chewing and facial muscles, we use myorelaxing splints made with the help of "EXOCAD" digital technology. echanism of action of the splint: a planned artificial occlusal space is created, which replaces the usual occlusal relationships, promotes stretching of the fibers of the masticatory muscles and triggers the transformation of the load inside the masticatory muscle. It is necessary to use such a medical splint for at least 16-18 hours a day. It is necessary to adjust the occlusal surface of the splint every 3-4 weeks of its regular use.
The aim of this study is to study and compare the nature and degree of changes in the electromyographic activity of the main and auxiliary masticatory muscles in patients with temporomandibular joint dysfunction before and after treatment with myorelaxing splints.
- The object of the study
The representative contingent of patients included 109 people, of which 74 (67.9%) patients were female, 35 (32.1%) patients were female. In total, 1024 electromyograms were analyzed at different stages of patient management. For five years (2017-2021), we conducted examination and treatment of TMJ dysfunction on the basis of the Dental Medical Center of the National Medical University named after O.O. Bogomolets
- Methods of the research
Electromyographic research of the main and auxiliary masticatory muscles, as well as facial muscles, was carried out with the help of a modern computer complex ioEMG III (BioRESEARCH Associates, Inc., USA). To date, this is the only system for electromyography of the maxillofacial area, which allows you to determine the parameters both at rest and during clenching and chewing in one recording, without a phase shift. To conduct the research, we chose the technique of surface functional EMG [5]. To record bioelectric potentials, we used standard skin disposable surface bipolar electrodes from BioResearch (VioFLEH, USA). The electromyographic study of masticatory muscles began with the physical determination of the motor point of the studied muscle. It is a dense formation, to identify which we ask the patient to squeeze the teeth with force. The skin in the projection above the motor point was degreased with ethyl alcohol and electrodes with a self-adhesive surface were fixed. The grounding electrode was placed on the patient's right wrist.
All patients had clinically diagnosed TMJ dysfunction, and according to clinical manifestations and the degree of manifestation of dysfunctional changes, they were divided into two studied Clinical Groups (CG). According to the degree of damage to the TMJ, the Helkimo index ranges from 5 to 25:
- The first clinical group (CG I) - 98 people (89.9%) - treatment was carried out according to the proposed method with the use of muscle relaxation splints;
- The second clinical group (CG II) - 11 people (10.1%) - was treated according to the traditional algorithm.
The following samples were subject to analysis and study: resting state of the patient's muscles, voluntary chewing, volitional compression of the chewing muscles and prescribed one-sided chewing, swallowing, free opening of the mouth. The study was given the following periods: the state before the application of splint therapy, six months after the start of treatment (Figure 1). In the same time intervals, the patient's subjective complaints were analyzed based on the visual analog pain scale and axiography data.
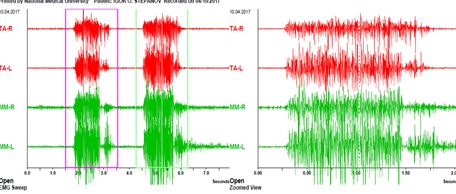 Figure 1: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles before treatment.
Figure 1: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles before treatment.
Ualitative and quantitative parameters of electromyography, axiography, and pain screening were subject to analysis. Pain analysis was performed using a modified 10-point FPS-R Bayers scale (recommended by the World Association for the Study of Pain (IASP).
Research Results And Their Discussion
The parameters of the norm of the state of rest, under the conditions of the absence of the impact of the load on the dental and jaw apparatus or the influence of other irritating factors, as well as in the absence of pathological changes in the structure of the muscle itself, are the registration of a uniform clear isoline on the monitor. The norm of the volitional compression test of the masticatory muscles is the registration of a masticatory wave with a uniform build-up of ascending and descending action potentials. The parameters of the maximum amplitude and average amplitude of action potentials of the masticatory cycle were subject to analysis and comparison (Tables 1 & 2).
|
parameter
|
Me (QI – QIII) |
certainty, P |
|
|
CG I, |
CG I, After (n=70) |
||
|
BC_TA_R_A_max |
108,6 (108,6-110,8) |
101,7 (97,9-111,1) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_TA_L_A_max |
117,9 (113,7-117,9) |
101,8 (98,3-110,9) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_TA_R_A_mean |
89,5 (85,9-89,5) |
85,9 (78,9-89,4) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_TA_L_A_mean |
82,8 (82,8-83,9) |
82,45 (79,1-82,9) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_MM_R_A_max |
177,9 (176,8-178,3) |
164,45 (157,3-175,8) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_MM_L_A_max |
176,9 (175,9-178,4) |
165,55 (158,3-176,9) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_MM_R_A_mean |
59,5 (57,2-60,8) |
56,89 (54,8-60,2) |
<0,001 |
|
BC_MM_L_A_mean |
60,5 (57,4-61,9) |
55,85 (53,8-61,1) |
<0,001 |
Table 1: The value of the indicators of volitional compression in the main masticatory muscles of patients of KG I before and after treatment by the proposed method.
|
parameter
|
Me (QI – QIII) |
p |
|
|
CG II, |
CG II, |
||
|
BC_TA_R_A_max |
110,8 (108,6-124,45) |
108,6 (108,075-110,8) |
0,219 |
|
BC_TA_L_A_max |
117,9 (113,025-121,5) |
108,9 (108,6-110,8) |
0,019 |
|
BC_TA_R_A_mean |
89,5 (86,8-106,675) |
89,5 (86,8-89,5) |
0,188 |
|
BC_TA_L_A_mean |
82,8 (82,8-99,25) |
82,8 (82,8-89,3) |
0,188 |
|
BC_MM_R_A_max |
160,6 (158,3-162,7) |
160,6 (158,30-160,6) |
>0,999 |
|
BC_MM_L_A_max |
176,9 (175,9-178,4) |
162,7 (158,875-173,05) |
0,004 |
|
BC_MM_R_A_mean |
54,3 (53,375-58,05) |
63,4 (57,925-65,175) |
0,027 |
|
BC_MM_L_A_mean |
61,6 (59,85-63,2) |
63,9 (57,45-66,675) |
0,301 |
Table 2: The value of indicators of volitional compression of the main masticatory muscles of CG II before and after treatment with the traditional method.
Note: Wilcoxon t-test for paired samples was used for pre- and post-treatment comparisons.
All, without exception, patients of the studied clinical groups (100%) had impaired muscle activity before treatment (Figures 2-4).
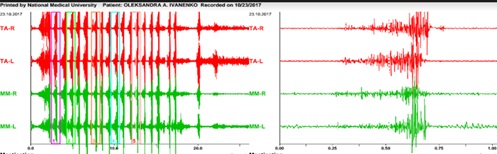 Figure 2: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with traditional methods.
Figure 2: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with traditional methods.
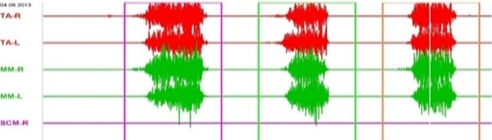 Figure 3: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with the use of a myorelaxant splint.
Figure 3: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with the use of a myorelaxant splint.
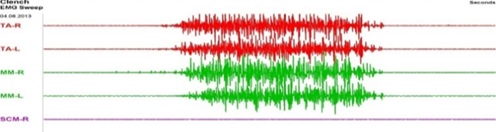 Figure 4: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with the use of a myorelaxant splint (inversion).
Figure 4: EMG of volitional compression of the patient's masticatory muscles after treatment with the use of a myorelaxant splint (inversion).
The results obtained and analyzed after 6 months indicate the normalization of the structure of the chewing cycle: qualitative and quantitative components. Comparing the obtained results of the effectiveness of treatment with the results of the effectiveness of treatment of TMJ dysfunction by traditional methods, a significant difference in quantitative data was observed.
We also noted that the effectiveness of treatment of patients of the studied clinical group reached 89.1 ± 1.3%, compared to the fact that the usual analog parameter of traditional treatment schemes does not exceed 55.4 ± 1.3%.
Conclusion
This reseach made it possible to analyze and combine the interdependence of the value of the subjective parameter of pain and the objective parameters of the bioelectrical changes of the masticatory muscles both before and after the treatment of patients with TMJ dysfunction. The results of the conducted statistical analysis of the effectiveness of myorelaxation splints in the treatment of TMJ dysfunction allow to improve the quality of treatment of this pathology in patients. The results obtained after 6 months indicate that the effectiveness of treatment of patients of the studied clinical group reached 89.1 ± 1.3%, compared to the fact that the usual analogue parameter of traditional treatment schemes does not exceed 55.4 ± 1.3%.
References
- Kostiuk T, Chrol N (2017) Substantion of relaxing splint used on patient with the para function of chewing musles. Likars’ka sprava 130-134.
- Kostiuk T, Kaniura A, Lytovchenko N (2020) Analysis efficiency of the temporo-mandibular disorders treatment. Medical Science of Ukraine 1: 48-51.
- Kostiuk TM, Kaniura A, Shinchukovskiy I, Tsyzh A, Medvinska N (2020) Reseach of the chewing muscles in dysfunction disorders of TMG. Neurophisiology 1: 50-53.
- Kostiuk T, Lytovchenko N (2020) The use of occlusal splints manufactured with “EXOCAD” software in the treatment of temporo-mandibular disfunction. International Journal of Medical Dentistry 24: 66-70.
- Malanchuk VO, Timoshchenko NM (2015) Diagnostics of position of the motor and trigger points: Of the chewing muscles for zygomatic complex fractures. Likars' ka sprava 109-115.
Citation: Kostiuk T, Proshchenko N, Syroishko M (2023) Effectiveness of Muscle Relaxatnt Terapy in the Treatment of Tmj Dysfunction. J Phys Med Rehabil Disabil 9: 81.
Copyright: © 2023 Tetiana Kostiuk, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

