
Foodborne illness a Dynamic, Everywhere Possible Emergency Field Today
*Corresponding Author(s):
Liana Monica DeacUniversity Babes- Bolyai And Public Health Center, Cluj -Napoca, Romania
Email:liana_deac@yahoo.com
Abstract
Foodborne illness is a common, costly yet preventable public health problem. Every year in the United States, 17 % of Americans get sick, as a result of consuming contaminated foods or beverages. During 2017-2019, we have observed foodborn diseases in Transylvania region, Romania, and realized a complex epidemiological and clinical study, with the right interpretations and conclusions. Most cases appeared in adults with several chronic illnesses, in 56%, male in 68% from rural side in 57%. The pathology was relevant for family events as wedding, birthday party etc., when food contamination occurred probably at any point, from: production, processing, distribution, or any meals preparation with eggs, milk and meat products, as even from less hand washing or hygiene protective uses. There were several forms from simple one, in 70%, middle one, in 22% to severe who arrived in totality to 8 % and needed almost several days of hospitalization. These foodborn infections have had the etiology of: Salmonella spp in 67%, mostly Salmonella enteritidis in 29 %. Other 14% were determined by Staphylococcus aureus and in 19% forms, we could not put in evidence any microbiological determinant germs.
To protect people from such disease there is needed to survive correct each chain of food production, processing, transportation, handling, and all preparation steps as to use a correct hand washing activity in food uses.
Keywords
Chronic illnesses; Foodborne disease; Food production
INTRODUCTION
Food-borne illness has a large economic impact across the nation, representing millions of dollars in lost income, lost revenue and healthcare-associated costs. It was estimate in CDC studies that 1 in 6 Americans get sick from contaminated foods or beverages each year, and 3,000 die. It was also determined then anyone in this world, can get sick from eating contaminated food [1] That for, WHO publish annual summaries of domestic food borne disease outbreaks, based on reports provided by state, local, and territorial health departments [2]. These summaries help public health practitioners better understand the: germs, foods, settings, and contributing factors, involved in these outbreaks. They also can help identify emerging food borne disease threats and even can present what hat to be used to shape and assess outbreak prevention right measures. The food we eat and the beverages we drink (including water), can become contaminated by: bacteria, viruses, parasites that can cause food-borne diseases. A case definition includes criteria for: person, place, time, and clinical features.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
During 2017-2019, it was observed the pathology of Food born diseases in Transylvania region from Romania (Figure 1).
 Figure 1: Transylvania geographical region.
Figure 1: Transylvania geographical region.
We got foodborn infection data for 145 such diseases in several sub regions (Figure 2). It was possible to appreciate so: the clinical medical situation and with, it was a good reason, to determine a complex epidemiological and clinical study, even with some pertinent interpretations and prevention conclusions.
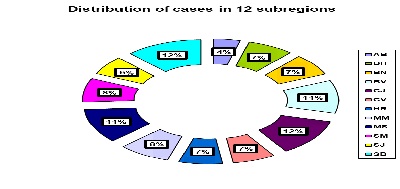 Figure 2: Cases of Food born Infection in Transylvania - Romania
Figure 2: Cases of Food born Infection in Transylvania - Romania
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Data were accumulate in the Sanitary District Polices, for each of the 145 Food born cases. Most of them appeared during the summer seasons in each year, from May to September (Figure 3).
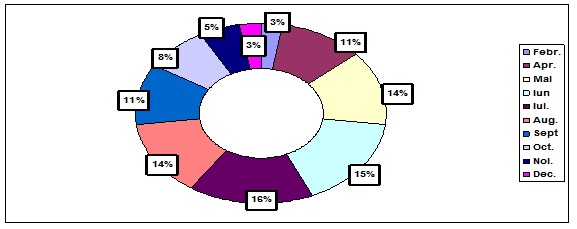
Figure 3: Seasonality for foodborn infection.
It was observed more one in July, at 16%, but we have had in each month some pathology with cases here. It had also to be mentioned that it was an increase of 5% cases, in the hot summer time of the year 2018, in the last 2 weeks from August, a month then with very high temperatures in our region. Always, when a food born disease outbreak is detected, public health and regulatory officials, work quickly to collect as much information for to find out what is causing it and the most important reason is to can take the right action for to prevent more people from getting sick. A contamination can happen anywhere along the chain of food production, processing, transportation, handling, and preparation. More, if contaminated food stays on store shelves, in restaurant kitchens, or in home pantries, more people may get sick as CCFH figured out [3]. An outbreak is over when the number of new illnesses drops back to what investigators normally expect [4]. In our situations it is interesting to show out that: food contamination occurred at any point, during: production, processing, distribution, or preparation. Some foods were contaminated before they reached into the kitchen, even by the food handlers, who did not washed correct their hands. That for outbreaks we have determined, in Urban and in Rural places, when hygiene activities were not well respected In our region, most of them appeared in Rural places- 52%, where hygiene was almost not right well respected (Figure 4).
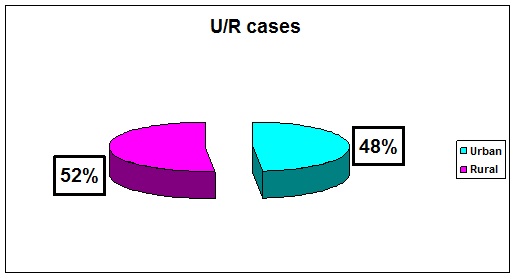 Figure 4: Sick cases in Urban and Rural regions.
Figure 4: Sick cases in Urban and Rural regions.
Also, it can even appear food born infection, either in family, or in collectivity situations. We have had most outbreaks in family situation- 57% as weddings, birthday parties or other parties, where some sanitary orders for preparing several food, were not well used or comprehensive understood, as even the choose for the meals products were not correct from hygienically point of view determined out (Figure 5).
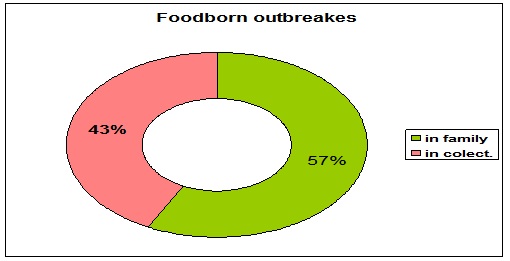 Figure 5: Family and collectivity outbreaks.
Figure 5: Family and collectivity outbreaks.
Gender has almost nothing to do with foodborn diseases, because it can in general happen either at male or female. In our cases, more male 68% have had the disease as female 32% and there is no proper other explanation for the situation happened on that time (Figure 6).
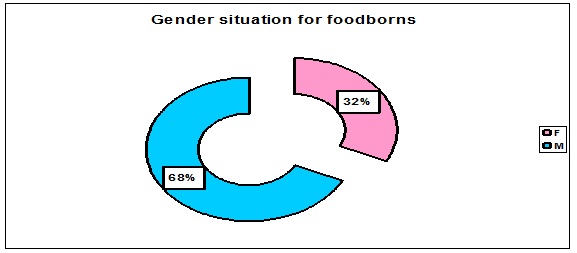 Figure 6: Food-born up to gender situation.
Figure 6: Food-born up to gender situation.
CDC report the risk for food-born diseases for: elderly people; children younger than 5 years; people with weakened immune systems; pregnant women who were 10 times more likely to get such infection [1,5]. Most such disease appeared in our region, in adults with several chronic illnesses, in 56%, followed by the elderly one and children in lower percents each 20-24% (Figure 7). Our reality is that not many children or elderly people can participate at many festive occasions from restaurants, as even in family events parties here today.
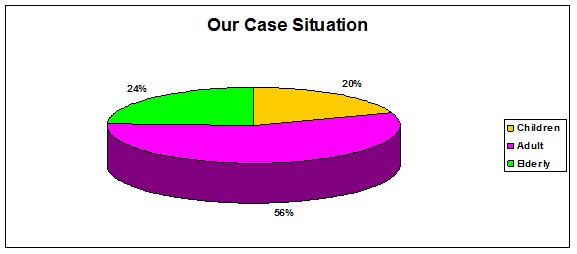 Figure7: Our foodborn cases.
Figure7: Our foodborn cases.
The common known symptoms of foodborne disease are: nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, diarrhea and sometimes fever. However, symptoms may differ among the different types of food borne illness, which can take several forms from simple one , 70%, middle one- 22% to severe who arrived in totality to 8 % and needed almost several days of hospitalization (Figure 8). No death cases have been reported in our study.
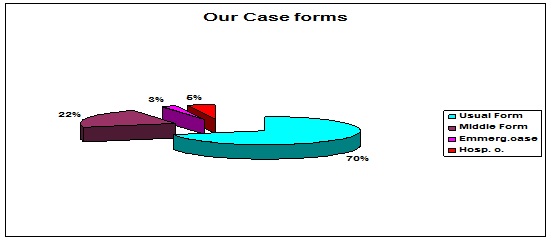 Figure 8: Clinical foodborn cases.
Figure 8: Clinical foodborn cases.
Typically, food-borne disease only lasts a few days. It depend almost even of the Microbiological origin of the food infection. The top five germs that cause illnesses from food eaten, in the United States are: Norovirus, Salmonella, Clostridium perfringens, Campylobacter, Staphylococcus aureus [5]. Most their toxins may be in the food we eat even for longer time and may be produced by: bacteria growing on food that has not been handled properly; may result from chemicals, heavy metals and other substances in food; or because of fish, shellfish or other animals which have concentrated toxins in their flesh from their feeding habits and environment [6]. At present in Romania We can still have, food- born infection almost with: Salmonella spp, Campylobacter, Staphylococcus aureus and suddenly with Norovirus and Clostridium perfringens. In our cases, the etiology was because of: Salmonella spp 67%, mostly Salmonella enteritidis in 29 %. 14% of the food-born diseases were determined by Staphylococcus aureus and in 19% forms; we could not put in evidence any microbiological determinant (Figure 9).
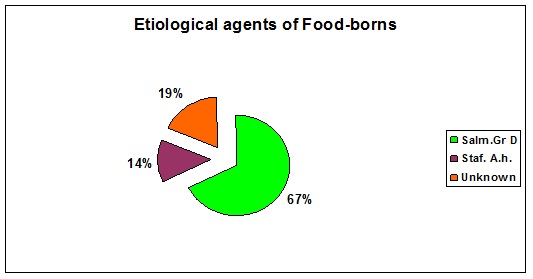 Figure 9: Microbiological origin of foodborns.
Figure 9: Microbiological origin of foodborns.
Many pathogens can exist in much of the food we eat, such as meat and poultry. Usually, these pathogens are destroyed when the food is cooked. However, if the food is eaten undercooked or raw, or the food is handled improperly during preparation or storage, the risk for transmitting pathogens to humans increases. We figured out contamination for Eggs in 28%, contaminated milk products in 23% and meat products in 19%, which caused most of the food-born in our regions. In rest only few cases have appeared because of other food products, as seafood or some unwashed fruits, etc (Figure 10).
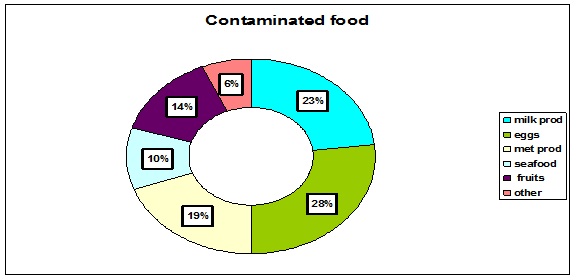 Figure 10: Suspect food products.
Figure 10: Suspect food products.
CONCLUSION
Every country around the world, get medical social and economical sufferings from foodborne illnesses, which became a possible active today medical emergency everywhere who must be prevent.
To protect people from such disease there is needed to survive correct each chain of food production, processing, transportation, handling, and all preparation steps.
Also necessary is the correct washing of hands and surfaces, as often possible.
The population must be educated for good Hygiene uses, which are grateful prevention of these illnesses
A useful prevents and control activity in Food born infection, is to be put together: epidemiologists, environmental health specialists, laboratory specialists, clinicians as all other specialists with possible enteric disease outbreak connections and therapy responsibilities.
REFERENCES
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2010) Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks - United States, 2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 59: 973-979.
- World Health Organization (2008) WHO initiative to estimate the global burden of foodborne diseases. World Health Organization, Switzerland.
- Codex Committee on Food Hygiene (CCFH) (2015) European Commission.
- D’Souza RM, Becker NG, Hall G, Moodie KBA (2004) does ambient temperature affect foodborne disease? Epidemiology 15: 86-92.
- Tirado C, Schmidt K (2001) WHO surveillance programmes for control of foodborne infections and intoxications: preliminary results and trends across greater Europe. J Infect 43: 80-84.
- Scallan E, Griffin PM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Hoekstra RM (2011) Foodborne illness acquired in the United States unspecified agents. Emerg Infect Dis 17: 16-22.
Citation: Deac LM (2020) Foodborne illness a Dynamic, Everywhere Possible Emergency Field Today. J Clin Stud Med Case Rep 7: 100104.
Copyright: © 2020 Liana Monica Deac, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

