
Gross, Histomorphological, Histochemical and Ultrastructural Studies of Pecten Oculi in Guinea Fowl (Numida Meleagris)
*Corresponding Author(s):
Balwant MeshramDepartment Of Veterinary Anatomy And Histology, College Of Veterinary And Animal Science, Rajasthan, India
Tel:+91 9166097570,
Email:drbmeshram@gmail.com
Abstract
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
The pecten oculi is highly vascular and pigmented structure which plays an important role in various functions of the eye such as providing nutrition to retina, maintaining retinal circulation, regulation of intraocular pressure, maintaining the pH and providing oxygen gradient to retina [3]. It functions in maintaining acid base balance and constant intraocular temperature [4,5]. Plenty of blood vessels and pigment cells were observed located in pecten oculi [6,7].
The shape of pecten oculi has been classified morphologically as Conical, Vaned and Pleated types. The conical pecten was observed in kiwi (Apteryx mantel), vaned type was observed in ostrich (Struthio camelus) and rhea (Rhea americana) and pleated type of pecten was observed in other bird species like quail, common buzzard, black kite, galah etc., [8-10]. The size and number of folds in pecten oculi are varied in accordance to the different type of diuranel and nocturnal birds [11,12]. The present studies are aiming towards scientific delineation of pecten oculi in Guinea fowl (Numida Meleagris) on differential parameteric characters as to histomorohological, functional and ultrastructural strictures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Initially samples of pecten oculi were collected by equatorial dissection of the apparatus of vision and it was subjected for the studies of gross structures as per [9,12]. During the dissection of eye it was observed that, while having an equatorial cut on eyeball the delicate components of pecten were getting smashed off (Figure 1). They were getting partly distributed in both the halves due to forceful movement of vitreous while getting it drained. Hence the complete enucleated eyeball is kept in the refrigerator for 1-2 minutes in an attempt to restrain the movement of vitreous and to obtain stand firm pecten with all the delicate components. In the later stage while dissecting the eyes an elliptical cut was preferred around a striped kind of scar mark identified at the outermost scleral tunic of eyeball in mediodorsal position. It was also discovered that the scar mark was due to the inside positioned optic disc. Almost immediately after the collection of pecten its gross studies were undertaken. The collected specimens of pecten oculi were studied and findings were recorded on the parameter of its location, orientation, attachment, color, number of accordion folds and their biometrical dimensions. Micrometrical observations were also recorded with help of vernier calliper viz. Digimatic Micrometer (MDC-SX) of Mitutoya Company.

After performing the gross study on collected samples, the same were processed for Routine histomorphological and histochemical studies [13]. The paraffin sections have been stained by Haematoxylin and Eosin method, Van Geison’s method were also employed for investigating the presence of collagen fibers and Azan Trichrome method was used to explore the presence of collagen and reticular fibers [13].
While performing the histochemical investigations, samples were fixed for 24 hours in chilled acetone. Dehydration was done through the chilled ascending grades of alcohol, cleared in refrigerated toluene by opting two changes for 30-60 minutes. The tissue samples were allowed for infiltration for 60 minutes while giving each change. Gomori’s Cobalt method has been used to detect the intensity of alkaline phosphatase activity and Gomori’s method for the acid phosphatase activity [13]. McManu’s method for Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) reaction was employed for identifying the presence of glycogen and used Fontana Masson Silver Method to detect the presence of melanin. Stained slides were studied under microscope for microscopical and micrometrical observations.
The transmission electron microscopical study was pursued on the procured samples of pecten oculi which were approximately 1 X 1 mm in thickness and employed routine procedure1 for the same after fixation in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and 2% Paraformaldehyde (PF). Semi thin sections of 0.5 to 1.0 μm thickness were taken on ultramicrotome with the help of glass knife for light microscopical studies as to get the quality of fixation, size and position of the cutting face for final trimming and area to be chosen for further TEM studies in ultrathin sections.
The section scrutinizing procedure was adopted under light microscope to have suitable sections. Selection was accomplished for the area to be examined under Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and again blocks were trimmed further. By using fresh glass knife the ultrathin sections of 60 to 150 nm thickness were taken and allowed to flow on the liquid of knife-boat and depending upon intrusion of colors shown by the ultrathin sections its thickness was determined. Generally the sections showed Gray, Silver and Golden coloration. The Gray colored ultrathin sections might be considered with the thickness of 60 nm, silver with 60 to 90 nm and golden color sections must have the thickness 90 to 150 nm. The golden colored sections with 90 to 150 nm thickness were considered suitable for low magnification studies, hence, it was stretched by exposing to chloroform. The sections were lifted over matted surface of grid and were allowed. Double staining method was applied by using uranyl acetate and alkaline lead citrate to achieve the suitable contrast and sections were studied at various magnifications under transmission electron microscope.
RESULTS
Gross Studies

It has shown pleural number of accordion (pectineal) folds on the tune of 13 to 17 numbers and each of them has a bilateral attachment with adjoining folds. Pectineal folds, which were started from the base, moved vertically inward and formed a cohesive structure in the form of band, which recognized as the bridge. It is to be determined as pleated type of pecten oculi, which has alternate furrow and bulging structure due to the different pleats. These pleats were observed interconnected similarly to that of intercostal muscles of the animals between different neighboring ribs. The shape of that structure which was exhibited as a sailboard shape, identified as the pecten oculi. In totality the pecten oculi occupies from base to the bridge with either side boundaries of temporal and nasal surfaces.
The maximum length of base in all the 18 numbers of pecten oculi was measured and it was in the range of 3.865 to 2.899 mm, with an average of 3.378 ± 0.061 mm. Maximum height of pecten was measured from its attachment at optic disc, from where it was initiated, to the distal end of bridge and it was found in the range of 6.339 to 5.248, with an average of 5.913 ± 0.074 mm (Table. 1).
|
Sample |
Maximum |
Maximum |
Total Length |
Maximum |
Maximum |
Maximum |
|
P1 |
3.549 |
5.731 |
298 |
82 |
11 |
8 |
|
P2 |
3.235 |
6.339 |
340 |
72 |
13 |
9 |
|
P3 |
3.485 |
5.987 |
300 |
76 |
10 |
7 |
|
P4 |
3.335 |
5.689 |
462 |
88 |
13 |
14 |
|
P5 |
2.988 |
5.248 |
346 |
46 |
11 |
6 |
|
P6 |
3.219 |
6.235 |
440 |
94 |
10 |
12 |
|
P7 |
3.458 |
5.836 |
320 |
56 |
11 |
7 |
|
P8 |
3.568 |
5.831 |
400 |
48 |
9 |
7 |
|
P9 |
3.138 |
6.289 |
328 |
60 |
10 |
8 |
|
P10 |
3.453 |
5.798 |
414 |
55 |
12 |
7 |
|
P11 |
3.325 |
6.325 |
420 |
52 |
11 |
6 |
|
P12 |
3.548 |
5.879 |
348 |
59 |
9 |
6 |
|
P13 |
3.435 |
5.746 |
298 |
60 |
13 |
12 |
|
P14 |
2.899 |
5.428 |
425 |
49 |
12 |
4 |
|
P15 |
3.126 |
5.825 |
420 |
57 |
10 |
5 |
|
P16 |
3.854 |
6.236 |
457 |
64 |
12 |
8 |
|
P17 |
3.865 |
5.758 |
387 |
58 |
13 |
8 |
|
P18 |
3.318 |
6.248 |
428 |
50 |
11 |
7 |
|
Average |
3.378 |
5.913 |
379.5 |
62.556 |
11.167 |
7.833 |
|
SD |
0.259 |
0.313 |
57.042 |
14.147 |
1.339 |
2.55 |
|
SE |
0.061 |
0.074 |
13.445 |
3.335 |
0.316 |
0.601 |
Histomorphological observations
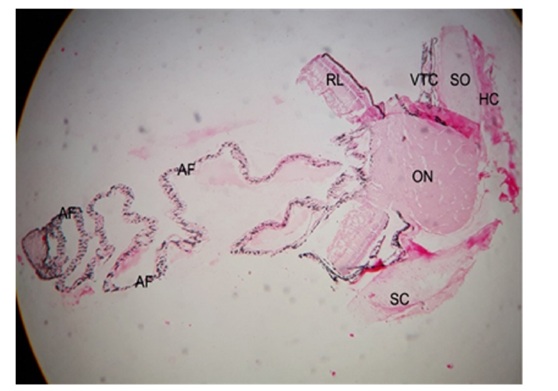 Figure 3: Photomicrograph showing the pecten oculi with its surrounding structures including Sclera Tunic(SC), Scleral Ossicles (SO), Hyaline Cartilage (HC), Vascular Tunic Choroid (VTC), Optic Nerve (ON) and Retinal Layers (RL). Haematoxylin and Eosin 5X.
Figure 3: Photomicrograph showing the pecten oculi with its surrounding structures including Sclera Tunic(SC), Scleral Ossicles (SO), Hyaline Cartilage (HC), Vascular Tunic Choroid (VTC), Optic Nerve (ON) and Retinal Layers (RL). Haematoxylin and Eosin 5X.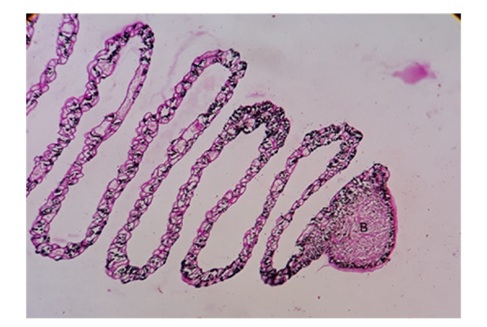 Figure 4: Photomicrograph showing the cantilever fashioned irregularly triangular shaped Bridge (B). PAS 10X.
Figure 4: Photomicrograph showing the cantilever fashioned irregularly triangular shaped Bridge (B). PAS 10X. Medium shaped choroidal blood vessels were perceived with the lining of flattened type of endothelial wall. Adventitia was also well defined and embedded in areolar connective tissue network wherein few melanocytes were observed. Though the smaller melanin granules were there but they were supportive for overall function of pecten. The complete pecten oculi from optic nerve to the distal end of bridge was tentatively divided into three equal portions as the bridge, base and middle one third (Figure 5). The middle one third has shown maximum length of the accordion folds and it was recorded between 46 to 94 μm with an average of 62.556 ± 3.335 μm.
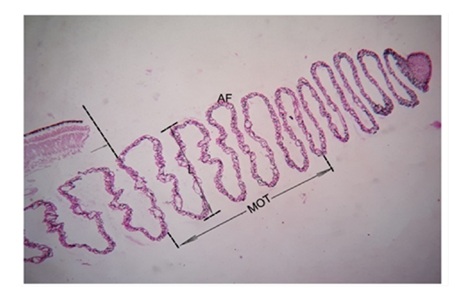 Figure 5: Photomicrograph showing the middle one third (MOT) segment of pecten with maximum Length (L) of accordion folds (AF). Arrow is showing initial point of MOT. PAS 10X.
Figure 5: Photomicrograph showing the middle one third (MOT) segment of pecten with maximum Length (L) of accordion folds (AF). Arrow is showing initial point of MOT. PAS 10X.Accordion folds also called as pectineal folds have illustrated their commencement from base and travel to hold the apex, the bridge. The course from base to bridge has exhibited the lateral undulation type of movement which observed comparable movement pattern in snakes. Each of the accordion folds was showing numbers of blood capillaries with variable size and different diameter but in most of the cases larger dimension of capillaries were only located at the middle one third of pecten and in particular the central linear component of the pecten had most largest dimension (Figure 6). These capillaries with larger dimension which were located at the middle one third of pecten oculi were recorded in the range of 4 to 14 μm with its average 7.722 ± 0.641 μm (Table 1).
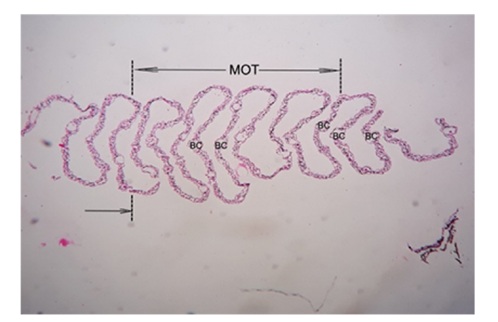
The distance between two pectineal folds were also found on higher tune at the same middle one third virtual portion of pecten which was recorded between 9 to 13 μm and its average was 11.167 ± 31 0.316 μm. The maximum luminal diameter of blood capillary among the various pectineal folds of pecten oculi was noted in between the range of 5 to 12 μm with the findings of its average 7.833 ± 0.601 μm (Table. 1). The pectineal folds have shown the complex association of blood capillaries with varied density and shape (Figures 7 & 8). It was not only showing the presence of nucleated erythrocytes but also the distinct distribution of heterophils, monocytes and thrombocytes (Figure 9). The pectineal blood capillaries had shown tight junctions at luminal surface by the endothelial cells, which has the thickest nuclear region. These vessels have also shown the thick basal lamina wherein the pericytes were found enclosed (Figure 10). The pecten oculi has shown over all dark black coloration due to the melanosomes which surfaced at luminal and abluminal component of pectineal blood capillaries. The concentration of melanin was observed highest at apex, the bridge and even in the laterally placed undulated fold components of pecten. The polymorphic melanocytes were unmistakably revealed its presence individually or in groups at inside and outside of the blood vessels, in between different blood vessels. Hyalocytes, the vitreous cells were observed in particular at the convex and concave surface of accordion folds (Figure 8).
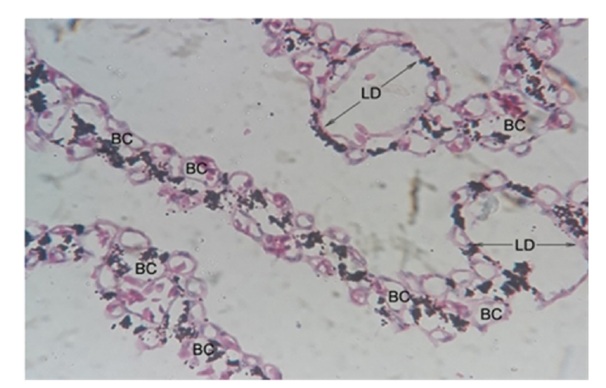 Figure 7a: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal Blood Capillaries (BC) with maximum Luminal Diameter (LD).
Figure 7a: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal Blood Capillaries (BC) with maximum Luminal Diameter (LD).Haematoxylin and Eosin 40X.
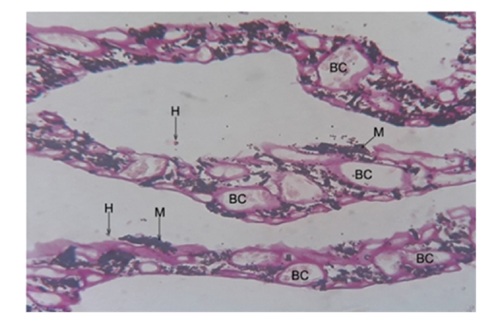 Figure 8: Photomicrograph showing pectineal blood capillaries (BC) with Hyalocyte (H) and melanocyte (M) PAS 40X.
Figure 8: Photomicrograph showing pectineal blood capillaries (BC) with Hyalocyte (H) and melanocyte (M) PAS 40X. 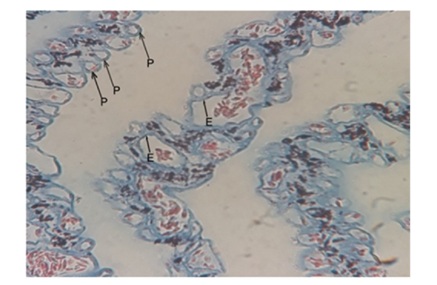 Figure 9: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal blood capillaries with Heterophils (H) and Monocyte (M). Toulidine Blue 100X.
Figure 9: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal blood capillaries with Heterophils (H) and Monocyte (M). Toulidine Blue 100X.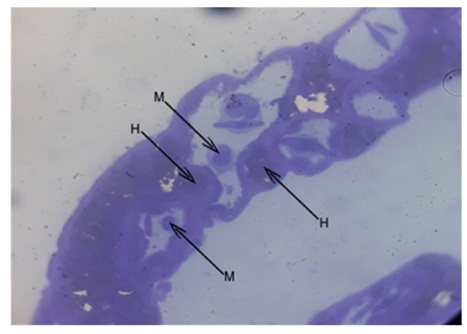 Figure 10: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal blood capillaries with Heterophils (H) and Monocyte (M). Toulidine Blue 100X.
Figure 10: Photomicrograph showing the pectineal blood capillaries with Heterophils (H) and Monocyte (M). Toulidine Blue 100X.HISTOCHEMICAL FINDINGS
Alkaline phosphatase
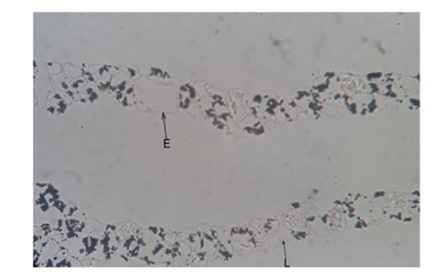 Figure 11: Photomicrograph showing basal Lamina (L) and Endothelium (E) with very weak strength of alkaline phosphatase activity. Alkaline Phosphatase 40X.
Figure 11: Photomicrograph showing basal Lamina (L) and Endothelium (E) with very weak strength of alkaline phosphatase activity. Alkaline Phosphatase 40X.Acid Phosphatase
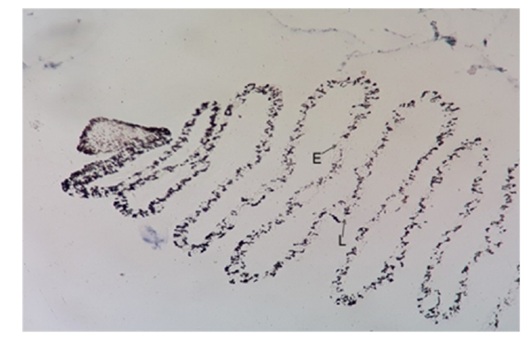 Figure 12: Photomicrograph showing very weak activity of acid phosphatase in capillary of pecten at basal Lamina (L) and Endothelium (E). Acid Phosphatase 10X.
Figure 12: Photomicrograph showing very weak activity of acid phosphatase in capillary of pecten at basal Lamina (L) and Endothelium (E). Acid Phosphatase 10X.Periodic-Acid-Schiff (PAS) for glycogen
Fontana-Masson Silver for Melanin The pecten oculi was showing the intense higher concentration of positive reaction for melanin at the capillaries which was surrounding the triangular apex, known as the bridge. The similar higher degree of reaction at pigmented epithelium of retinal layer was also observed. The reaction was also seen at laterally placed blood capillaries of undulated fold components of pecten (Figure 14).
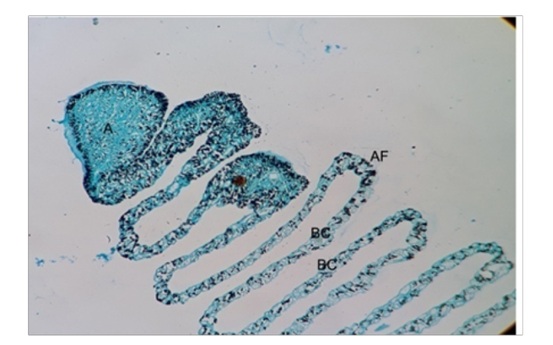 Figure 14: Photomicrograph showing the apex (A) with higher concentration as in black colour at Accordion Fold (AF) and Blood Capillaries (BC). Fontana Massons Silver 10X.
Figure 14: Photomicrograph showing the apex (A) with higher concentration as in black colour at Accordion Fold (AF) and Blood Capillaries (BC). Fontana Massons Silver 10X.Ultrastructural findings
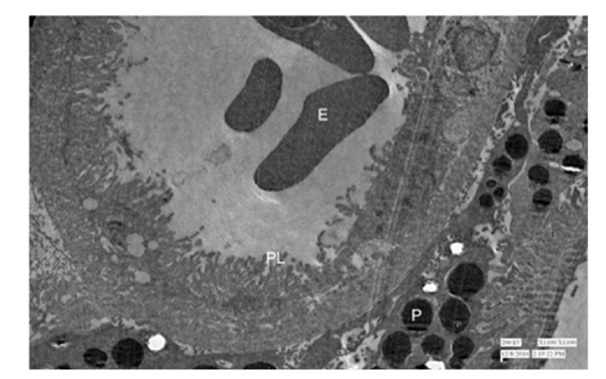 Figure 15: Showing nucleated erythrocyte (E) surrounded by Primary Lamellae (PL) and extra vascular Pigment (p) at outside the capillary. 1100X.
Figure 15: Showing nucleated erythrocyte (E) surrounded by Primary Lamellae (PL) and extra vascular Pigment (p) at outside the capillary. 1100X.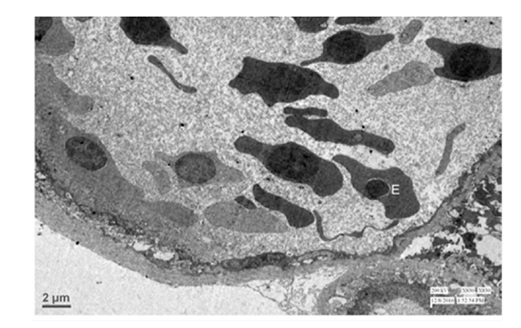 Figure 16: Transmission electron micrograph showing the lumen of pectineal capillary with nucleated Erythrocyte (E). 830X.
Figure 16: Transmission electron micrograph showing the lumen of pectineal capillary with nucleated Erythrocyte (E). 830X.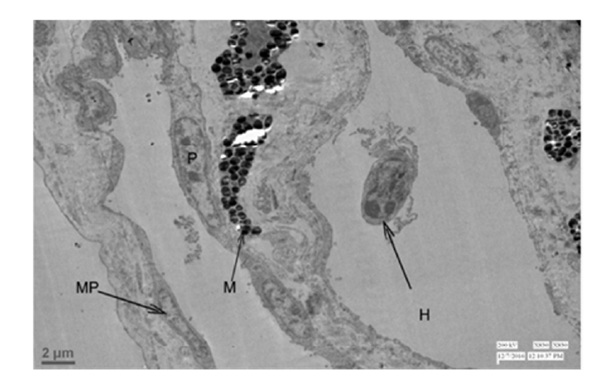 Figure 17: Transmission electron micrograph showing the pectineal capillary with Melanocyte (M), Melanocyte Process (MP), Heterophil (H) and Pericyte (P). 830X.
Figure 17: Transmission electron micrograph showing the pectineal capillary with Melanocyte (M), Melanocyte Process (MP), Heterophil (H) and Pericyte (P). 830X.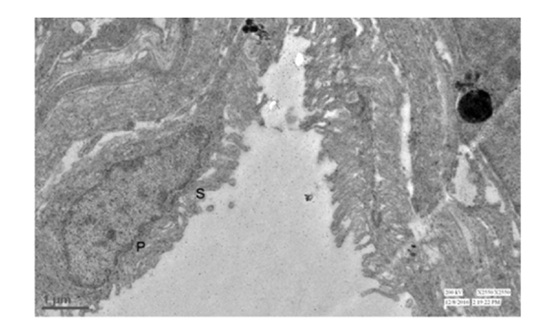 Figure 18: Transmission electron microscopy showing the Primary (P) and Secondry (S) lamellae at luminal surface of the pectineal capillary. 2550X
Figure 18: Transmission electron microscopy showing the Primary (P) and Secondry (S) lamellae at luminal surface of the pectineal capillary. 2550X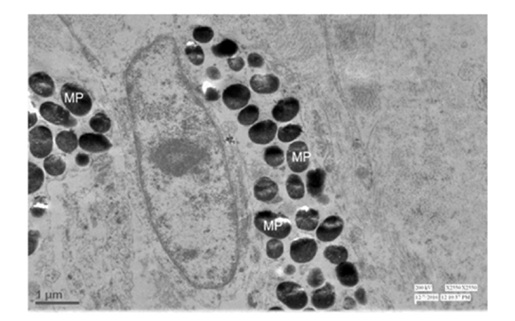 Figure 19: Transmission electron micrograph showing the melanin pigment (MP) depositing globules at secondry lamellae of luminal component of pectineal capillary. 2550X.
Figure 19: Transmission electron micrograph showing the melanin pigment (MP) depositing globules at secondry lamellae of luminal component of pectineal capillary. 2550X.DISCUSSION
All the 18 samples in the present study were endorsed the discovery of 13 to 17 number of accordion (pectineal) folds and each of them had bilateral attachment with adjoining folds as the intercostal muscles between two ribs in animals and these annotations were similar to which specified by [19]. Various studies of pecten in aves has been reported with variable number of folds [6,9]. The birds were differentiated as day active viz. diurnal, which has more than 10 pleats and night active viz. nocturnal, which has pleats within the range of 4-5 [20]. A day and night active bird has higher and decreased visual acuity respectively which was reliant upon the number of pleats possessed by pecten oculi. In view of that well said differentiation the bird Guinea fowl (Numida Meleagris) upon which present study was performed has comfortably confirmed as the diurnal bird and its habit while getting the prey was also showing the long establishment with the confirmation.
Base of the pecten had attachment dorsally to the head of stripe shaped optic disc and ventrally it moved off vertically inward by way of fundus into the vitreous humour. The different pectineal folds formed a cohesive structure in vitreous humour as the apex, in the form of band which distinguished its entity as the bridge. The observations which has been confirmed in present studies that the pecten was nothing but the pleated type of pecten and it was consented too [6,17]. In the study of diurnal and nocturnal birds of various species mentioned that pleated pecten was widespread and essentially similar in most species. This pecten oculi which left the optic disc as a base and reach at the bridge with its either boundaries of temporal and nasal area and the shape what it show off got matched in greater extent as the sailboard, the windsurfing floating unit glide on water.
The present findings has shown maximum length of base in all the pecten oculi which was in the range of 3.865 to 2.899 mm, with an average of 3.378 ± 0.061 mm while its maximum height from its initiation from optic disc to the bridge was also measured and it was in the range of 6.339 to 5.248 mm, with an average of 5.913 ± 0.074 mm. The present results against measurements of base and height of pecten oculi were in variation with the reporting of various researchers due to the species difference [9,17].
In this attempt of studies of pecten oculi, it was cited as the crown at bulging of optic nerve which was invariably brought into being centrally positioned with its either side the sclera and choroid layer. Connective tissue at the outer side of scleral tunic, scleral ossicles, hyaline cartilage, vascular tunic of choroid, retinal layers and the components of accordion folds were very well identified under microscope. This outcome of the present examination was in close confirmation with the findings [9,12,21].
Microscopically the core of optic nerve allows the pecten oculi to initiate and to pass through a vitreous humour, furthermore, at distal free end a cantilever fashioned irregularly triangular shaped structure was obtained which got acceptance in the name of bridge. These findings of the present endeavor were not different, but it was very true that the initiation and end of pecten oculi has the connectivity by laterally undulated natured pathway of accordion (pectineal) folds, the similarly fashioned movement of snake [10,16].
The total length of pecten oculi from optic disc to the distal end of bridge was ascertained between 298 to 462 μm with an average of 379.500 ± 13.445 μm. On virtual three equal splitting up of complete pecten oculi, the middle one third segments has shown the maximum length of accordion folds and it was recorded between 46 to 94 μm with an average of 62.556 ± 3.335 μm. Numbers of blood capillaries with varied diameter were noticed as the festoon of pecten oculi but in most of the cases not only the larger capillaries of remarkable dimensions were observed at the middle one third segment of pecten but the space between two pectineal folds were also observed on higher tune at this segment which was evidenced between 9 to 13 μm with an average of 11.167 ± 0.316 μm. These findings were recorded without any equality with the observations of other researchers as due to the non-availability of such micrometrical observations. Among the various positions of pectineal folds the maximum luminal diameter of their blood capillary was noted in the range of 5 to 12 μm with its average 7.833 ± 0.601 μm which has much minimized dimension in relation to the recordings noted with 30 to 40 μm [22]. Such dissimilarity might be the provenance to the species disparity.
In addition, the central linear component of the middle one third of pecten oculi has brought to light the largest most dimensions of blood capillaries which were recorded in the range of 4 to 14 μm with its average 7.722 ± 0.641 μm.
The pecten oculi in whole has exposed a structure of festoon of varied shape blood capillaries.Prominent blood capillaries were identified at the anterior end of unification of summit of pecten and optic nerve with either side retinal layers. Flattened type of endothelial wall lining was sited at the medium shaped choroidal blood vessels. Their adventitial layer was well defined and has got surrounded in areolar connective tissue network wherein few melanocytes were also observed. The smaller melanin granules were there but its presence was showing the supportiveness toward performance of overall function of the pectin [14,23-25].
The prominent mesothelial retinal epithelium was clearly marked wherein the melanin pigments were packed. It was also showing the adventitial layer as the supporting structure to epithelial layer and combinely the epithelium and adventitia functions as outer barrier for retina while supporting its function for capturing the image. Another, the retina of Guinea fowl was not observed in resemblance with mammals as it was devoid of blood vessels, which was compensated by festoon of blood capillaries as the pecten oculi. These pectineal blood capillaries have tight junctions at luminal surface by the endothelial cells where it forms another barrier at inner side between retina and pecten oculi. The blood or fluid retinal barrier from either side, as outer and inner might be attributed to the support system of retina for its normal functioning of image capture to get the visual acuity. These elucidations were in partly agreement [26], as he was studied the blood retina barrier to know the pathophysiology and therapeutics of retinal diseases but without specifying of any species of animals or birds.
Pectineal folds have been profoundly shown the varied density and shape of blood capillaries.The nucleated erythrocytes had evidence there and distinct distribution of leucocytes as to heterophils, monocytes and even thrombocyte were also been demonstrated. Erythrocytes at luminal component of pectineal capillary were commonly reported by researchers [9,23], but the other constituents of blood viz. heterophil, monocytes and thrombocyte were not reported earlier. Contrary, the present observations wherein other constituents were also reported in addition to the erythrocytes has shown the significance of pecten oculi with the function of fight off diseases and infection by heterophils, phagocytosis by monocytes and hemostasis performed by thrombocytes.
The detection of pectineal capillaries has revealed [6,23], which were in similarity with present revelations wherein the luminal surface of pectineal blood capillaries had tightly interconnected endothelial cells with its substantial prominent nuclear region. The pericytes had also shown their existence which were surrounded by the thick basal lamina.
In toto it has been observed that the pecten oculi has taken its dark black colour due to the melanosomes and it was surfaced at luminal and abluminal component of pectineal blood capillaries.The apex of the pecten oculi which also known as the bridge was observed with highest in concentration of melanin and same findings has also been shown at laterally positioned undulated fold components of pecten. In between pectineal blood vessels the polymorphic melanocytes were unquestionably revealed its presence either alone or in groups at inside and outside of the blood vessels, vitreous cells, and hyalocytes was observed at the convex and concave surfaces of accordion folds. Similar findings have been put on record in the pectin oculi in most of the species14,36,54,20,46. Principally, black body is involved into the absorption of heat. The black colored pecten oculi with its different components got black colour due to the presence of melanosomes and it identified as the organ of heat absorption and thereby the homeostasis. It was not only catalyzing the increase of metabolic reaction of pecten but also it tries to maintain the required elevated body temperature in the form of energy for birds as per the higher basal metabolic rate of the body of birds.
Ultrasructurally, the nucleated erythrocytes were witnessed at luminal area of pectineal blood capillary and the endothelial cells of capillary were elaborating tight junction between the basement membrane of it. The thick basal lamina of pectineal capillary has demonstrated pericytes and the processes of melanocytes and melanosomes. The capillary had nucleated erythrocytes in its lumen that were surrounded by primary lamellae with extra vascular pigment deposits at the capillary abluminally. Transmission electron microscopically the observations which were confirmed in the present study of pecten oculi in Guinea fowl (Numida Meleagris) were presented collaboratively with the findings [6,23] but, in the present findings lumen of pectineal capillary has shown the presence of heterophils. In respect of the heterophils [27], the similar constituent blood cells in mammal which known as the neutrophils or neurocytes were located into the pectineal capillary of Guinea fowl (Numida Meleagris) as the constituent blood cells and sufficiently given the indication that it were actively involved into the process of phagocytosis. It also means the pecten oculi has engaged into the function of immunity after its phagocytic natured heterophils.
The luminal region of pectineal capillary was showing the primary and secondary lamellae and the secondary lamellae also were on the verge to expand as to tertiary while replacing the vacant luminal place. Pigment depositing globules were not only discovered in primary lamellae but it were also found in secondary lamellae with centrally placed nuclei [12,28]. Though the different calibre of blood capillaries were seen at pecten oculi but entirely it encountered in a single cell as its outer thickness which only permit to term it as the capillary, and it were observed in the form of festoon in overall pecten oculi.
In present morphological study of the pecten oculi, macroscopically its shape was not different than the shape of sail board which was started from base and travel to apex. Microscopically the study has also revealed that its base initiated from cauda of optic nerve and travels via fundus distally into the vitreous humour and ended into irregularly triangular structure. The sail board of pecten oculi has encompassed with several pectineal folds which were vertically started from base with the connection to optic nerve and travelled in lateral undulated fashion as to snake while extending upto the apex known as bridge. Barris was revealed the engineering diagram of diving springboard with their different components (Figure 20) [29]. The microscopic make-up of pecten oculi has exhibited a very close resemblance with an architectural sculpture of diving spring board, an extreme model of speciality which used as sport device for water diving. The researcher had worked on functional principles of springboard and cited that a springboard work like a linear spring and any application of load over its tip move down in proportion to the load [30,31]. Greater of the load to the linear spring resulted into a greater degree of deflection, and, principally it acts as per the Hooke’s law of physics i.e. strain of any elastic material found directly proportional to the stress [30]. A moveable fulcrum, the device which located at the thickest region of the springboard from where the board tapered back to the hinged anchor and forward to the tip [32, 33]. Fulcrum has to place on that position between the base and tip of diving spring board as to facilitate oscillations in a regular fashion and becoming it progressively smaller [30]. Accordingly the structure, activity and place of location of fulcrum getting collaborative with the midline of initial point of middle one third segment of pecten oculi.
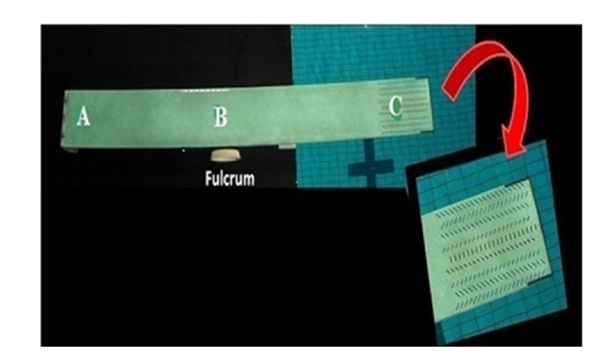
Microscopic structure of pecten oculi shown with the different accordion folds as a festoon of blood capillaries with their elastic, collagen and reticular fibers certainly might have been working as the elastic and flexible material which work as the transmitter of mechanical energy and has identical as the linear spring of diving spring board. The largest dimensioned blood vessels were observed at the central linear component of microscopical structure of pectin oculi that has also might be the encouraging towards close comparison with the functional principle of diving spring board. Tip of the diving spring board has an area of perforations while making the region more submissive than rest of the board. And, the apex, which was identified as the bridge in present study as the cantilever unit at distal end of ribbon of blood capillaries might be attributed to the similarity in functioning of tip of diving spring board as the most compliant morphological component of pecten oculi. Structurally the diving spring board has similarity not only with the microscopical structure of pecten oculi but its working principle also might have been tuned with Hooke’s law because of its histomorphological comparable composition. Therefore, movement of the eye as to find the prey must be credited to the sail board shaped pecten oculi for its working ability and the diving spring board with its cantilever, the apex known as the bridge contribute at large for support to the directional movement of the eye and also to provide the energy for its unremitting function by involving into self-oscillatory movement in vitreous humour and thereby the resulted process of diffusion. Moreover, the tip as he major inhabitant of melanin was not only preventing the apparatus of vision from ultraviolet light but it was also helping to protect same against the light toxicity [34]. Course of lateral undulated movement of snakes in water support their decent speed by propelling the water waves and retain the energy. Such movement was also recorded while having the connection of pectineal folds from base to apex. The laterally undulation pattern of accordion folds also might be the tool to retain the energy by propelling the vitreous humour wherein it occupied.
Histochemically the structural component of pectineal capillaries has demonstrated a very weak activity of alkaline phosphatase in the form of extremely faded blackish colour at the basal lamina and also at the endothelium. The festoon of blood capillaries of pecten has confirmed the extreme weak activity at the endothelium and basal lamina region. In respect to the comparison of acid and alkaline phosphatase activity, the acidic was experienced very much weak rather than the alkaline phosphatase. No alkaline phosphatase activity was observed in the pecten of dark adapted eye in chick [35]. He mentioned that darkness may make the exchange of metabolites between pecten and less active vitreous humour with the similar observations in chicken4. However in the present study, it was similar with them when the day active i.e. diurnal birds were chosen for detecting the strength of alkaline phosphatase activity in their pecten oculi, wherein it revealed a very weak activity then it was required to be noted that alkaline and acid phosphatase were those enzymes which hydrolyzes the phosphate group and act as catalyst to speed up the chemical reaction in cell at basic and acidic environment with optimum pH of 10.5 and 5.3 respectively. In present studies against both the acid and alkaline phosphatase the activities were recorded as very weak with the close resemblance to negative, which made it known that if the activity found in elevation then the organ component indicating its association with certain medical condition [36]. And, in the present study of pecten oculi in Guinea fowl where activity was near to negative for both acidic and alkaline phosphatase meant that the components of its pecten were extremely active and vigorously performing in the medium of vitreous humour.
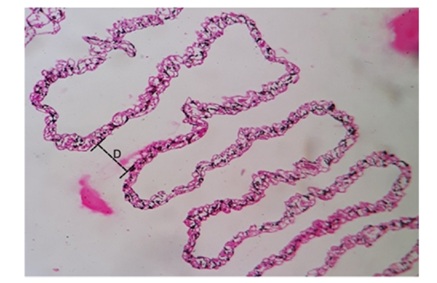
The strong activity of glycogen was noticed at optic nerve and the collagen fibers which provide potential structure of pectineal capillaries. As per the property of glycogen it has displayed the strong red purple colour of activity at both endothelial and basal lamina region of capillary. Even it has show off the strongest presence of activity at surrounding connective tissue septa of an apex, the bridge of pecten. The study of pecten oculi revealed in domestic fowl and confirmed PAS positive reaction in a whole pecten and as the secretory product they observed the glycogen in the form of mucopolysaccharide in pecten oculi [16]. In the present study of pectin oculi most of the components of it and its surroundings comprising optic nerve, collagen fibers of potential pectineal capillaries, endothelial and basal lamina region of capillaries and even the surrounding connective tissue septa of an apex, the bridge were showing PAS positive activity in greater or lesser extent and it were remained source of energy for incessant working of the pectin oculi.
The purposeful presence of melanin in pecten oculi, particularly at the pectineal capillaries and also around the surrounding of irregularly triangular apex, bridge has demonstrated intense concentration. Similarities of higher degree of reaction were also located at pigmented epithelium of retina and also at the laterally placed blood capillaries of undulated fold components of pecten. These observations were in exact similarity by other investigators who has explored different avian species [6,9,12]. The structural support and protection of ocular component, the pecten oculi from ultraviolet light and oxygen radicals might be possible by the presence of melanin there.
The documentation which was made available in different species of birds by several workers, pecten oculi perform various functions. It protects the eye from harmful effect of ultraviolet radiation created by sunlight [46]. Intraocular pressure and pH regulation, stabilization of the vitreous, reduction of intraocular glare, serving as a blood and fluid barrier for the retina and vitreous body, supplementation of nutrition, oxygen gradient supply to the retina, keeping constant intraocular temperature [21] , flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the capillaries and vitreous body, detoxification of the retina [20] , nourishment of the avascular retina and vitreous body, protecting the visual efficiency of the eye [25], ocular sextant [17] were fitting with the findings revealed during present study. But along with the mentioned a pecten oculi of Guinea fowl (Numida Meleagris), it has also been observed as the performing organ of hemostatic, work as support system to retina for its normal functioning of image capture to get the visual acuity, fight off diseases and infection, involvement into the function of immunity, absorbing unit of heat and maintaining energy to perform as per the need of higher metabolic rate of bird, work as the elastic and flexible material which carry out as the transmitter of mechanical energy while performing as the source of it for vitreous humour by way of diffusion.
REFERENCES
- . Wikivet (2017) Heterophils.
- Bonney R, Rohrbaugh JR, Ronald (2004) Handbook of Bird Biology (2nd edn.), Princeton, NJ:Princeton University Press, USA.
- Wingstrand KG, Munk O (1965) The pecten oculi of the pigeon with particular regard to its function. Bio 14: 1- 64.
- Brach V (1975): The effect of intraocular ablation of the pecten oculi of the chicken. Invest Ophthalmol 14: 166-168.
- Brach V (1977) The functional significance of the avian pecten: A review. The Condor 79: 321-327.
- Braekevelt CR (1993): Fine structure of the pecten oculi in the great horned owl (Bubo virginianus). Histol Histopathol 8: 9-15.
- Kiama SG, Maina JN, Bhattacharjee J, Weyrauch KD, Gehr P (1998) A scanning electron microscope study of the luminal surface specializations in the blood vessels of the pectin oculi in a diurnal bird, the black kite (Milvus migrans). Ann Anat 180: 455-460.
- Meyer D. B., (1977): The Avian Eye and its Adaptations. In: Crescitelli F. (eds) The Visual System in Vertebrates. Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol 7 / 5. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
- Orhan O, Ekim O, Bayraktaroglu AG (2011) Morphological investigation of the pecten oculi in quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Ankara Univ Vet Fak Derg 58: 5-10.
- Braekevelt CR (1984): Electron microscopic observations on the pecten of the nighthawk (Chordeiles minor). Ophthalmologica 189: 211-220.
- Brakevelt CR (1988) The fine structure of the pecten of the pigeon (Columbia livia). Ophthalmologica 196: 151-159.
- Dayan MO, Ozaydin T (2013) A comparative morphometrical study of the pecten oculi in different avian species. The Scientific World Journal Page no: 1-5.
- Singh UB, Sulochana (1996) Handbbok of histological and histochemical techniques, Premier pub. house, Hyderabad, India.
- Mann IC (1924) The function of the pecten. The British journal of ophthalmol, Henry George plimmer research fellow, London, UK.
- Kiama SG, Maina JN, Bhattacharjee J, Weyrauch KD (2001) Functional morphology of the pecten oculi in the nocturnal spotted eagle owl (Bubo bubo africanus), and the diurnal black kite (Milvus migrans) and domestic fowl (Gallus gallus var. domesticus): A comparative study. Journal Zool 254: 521-528.
- Braekevelt CR (1998) Fine structure of the pecten oculi of the emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Tissue cell 30: 157-165.
- Pourlis AF (2013) Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies of the Pecten Oculi in the Quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Anat Res Inter 650601: 6.
- Haller NK, Lind O, Steinlechner S, Kelber A (2014) The influence of motion on spatial contrast sensitivity in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover Pg no: 1-73.
- Tucker R (1975) The surface of the pecten oculi in the pigeon. Cell Tissue Res 157: 457-65.
- Micali A, Pisani A, Ventrici C, Puzzolo D, Roszkowska AM, et al. (2012): Morphological and Morphometrical study of the Pecten Oculi in the Budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus). Anat Rec (Hoboken) 295: 540-550.
- Jezler PCOC, Braga MBP, Perlmann E, Squarzoni R, Borella MI, et al. (2010) Histological analysis of eyeballs of the striped owl (Rhinoptynxclamator). Microscopy: Science, Technology, Applications and Education Pg no: 1048-1054.
- Gultiken ME, Yildiz D, Onuk B, Karayigit MO (2012) The morphology of the pecten oculi in the common buzzard (Buteo buteo). Vet Ophthalmol 15: 72-76.
- Bawa SR, Roy YC (1974): Structure and function of vulture pectin. Acta Anat (Basel) 89: 473-480.
- Kiama SG, Bhattacharjee J, Maina JN, Weyrauch KD (1994) A scanning electron microscope study of the pecten oculi of the black kite (Milvus migrans): Possible involvement of melanosomes in protecting the pecten against damage by ultraviolet light. Journal Anat 185: 637-642.
- Rajab JM (2012) Morphological and histological description of the pecten oculi in the sparrow hawk (Accipiter nisus). Diyala Journal of pure sci 8: 1-12.
- Cunha-vaz JG (1976): The blood-retinal barriers. Documenta opthalmol 41: 287-327.
- Wikivet (2017) Heterophils.
- Kiama SG, Maina JN, Bhattacharjee J, Mwangi DK, Macharia RG, et al. (2006): The morphology of the pecten oculi of the ostrich (Struthio camelus). 188: 519-528.
- Barris (2013) An examination of learning design in elite springboard diving. Quinsland university of technology, Brisbane, Australia.
- Miller D (2008) Springboard and platform diving. Zatsiorsky IV (Ed.), Biomechanics in Sport Pg no: 326-348.
- Sprigings E (1990) Measurement of the modeling parameters for a Maxiflex “B” Springboard. Intern. Journal of Sport Biomechanics. 6: 325-335.
- Jones I, Miller D (1996) Influence of fulcrum position on springboard response and take-off performance in the running approach. Journal of Applied Biomechanics 12: 383-408.
- Miller D, Osborne M, Jones I (1998) Springboard oscillation during hurdle flight. Journal of Sport Sci 16: 571-583.
- Peters S, Lamah T, Kokkinou D, Bartz Schmidt KU, Schraermeyer UZ, et al. (2006) Melanin protects choroidal blood vessels against light toxicity. Z Naturforsch C 61: 427-433.
- Tsugio A (1982) Electron histochemical study of alkaline phosphatase activity in the pecten oculi of the chick. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 219: 114.
- Wikipedia (2017) Elevated alkaline phosphatase.
Citation: Mishra P, Meshram B (2019) Gross, Histomorphological, Histochemical and Ultrastructural Studies of Pecten Oculi in Guinea Fowl (Numida Meleagris). Archiv Zool Stud 2: 009.
Copyright: © 2019 Pratiksha Mishra, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

