
Increasing employee understanding of disease risks associated with excess sugar consumption by engaging digital mobile technology
*Corresponding Author(s):
George A GellertEvidence-Based Solutions, United States
Email:ggellert33@gmail.com
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the impact of an on demand, digital mobile application deployed via smartphone on the disease risk understanding of excess daily sugar consumption among employees within a large multinational banking enterprise.
Methods: A daily sugar consumption education program was implemented using a smartphone application with the employee population of a large multinational digital bank in Asia, spanning 12 nations of East, South and Southeast Asia, Australia and the USA. Participating employees were challenged to record and reduce their daily added sugar intake over a 7-day period. Personal smartphones were employed to educate and encourage employees to engage the program and provided easy to assimilate, timely education on the importance of reducing excess daily sugar consumption to lessen risk of associated diseases such as diabetes and obesity. Daily sugar consumption risk education imparted specific practical educational content and reinforced motivational messaging and support. Awards and incentives were deployed to increase program compliance and completion. Participants’ sugar consumption, understanding of the health risks posed by excess sugar consumption, attitudes and future commitment toward reducing individual daily added sugar consumption were captured by serial surveys.
Results: There were 295 employee participants who engaged the sugar intake reduce program across 12 nations, or 43% of eligible participants. Seventy-four percent of participants achieved a modest reduction in their daily added sugar consumption during the program. While the volume magnitude of daily added sugar reduction was modest, a large majority of participants stated that the digital engagement program made them more aware of the need to reduce sugar intake in the prevention of diabetes and related diseases (97.5%), indicated that what they learned in the program will influence their future selection of supermarket foods (98.3%) and food choices in restaurants (89.9%). Almost 90% responded that they would be more likely in the future to select beverages, snacks and other food items that have substituted added sugar with healthier artificial sweeteners when available. When asked if they will continue to practice sugar reduction behaviors in the future, 97.6% stated that they would do so.
Conclusion: The digital employee engagement program evaluated in this study delivered an increased employee understanding of the risk of excess sugar consumption in the origin of metabolic disease such as diabetes and obesity, as well as enhanced motivation to reduce added daily sugar intake that participants will take forward in better managing their dietary risks. The automation and rules-driven customization enabled by web-based digital media such as smartphones can improve population sugar consumption risk understanding and attitudes at scale across large employee enterprise populations in multinational settings. These results and the impact achieved after a single 7-day risk reduction and education program across a complex multicultural employee setting are indicative of the power and value that digital mobile wellness engagement can deliver to employees.
Keywords
Diabetes risk; Employee wellness; Mobile digital engagement; Obesity risk; Sugar consumption
Introduction
Enhancing Employee Understanding of How Dietary Sug-ar Consumption Increases Risk for Metabolic Diseases
The impact of sugar intake on disease risk and overall health has been well documented. Studies have produced evidence demonstrating that regularly consuming high levels of sugar in one’s diet elevates individual risk of weight gain and obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemias, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases [1]. Dietary sugars are also a leading cause of tooth decay [2]. In addition to negatively impacting physical health, there is evidence that increased dietary sugar intake can affect an individual’s mental health as well, with foods and beverages high in sugar content increasing risk for development of mood disorders like depression [3].
As a result of the negative impact of high intake of dietary sugar on both physical and mental health, and the disease risk associated with high sugar consumption, measures to help employees decrease their daily sugar consumption should be of interest to employers when implementing workplace health and wellness initiatives for their enterprise workforce. The prevalence of chronic diseases caused by metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and contributed to by high sugar intake are associated with a multinational set of occupational health challenges to reduce morbidity and avoidable care utilization and costs, and to mitigate lowered workplace productivity and absenteeism associated with metabolic disease [4]. Additionally, the workplace provides a uniquely effective setting for supporting health promotion at the individual level, with workplace health interventions demonstrated as being both practical and effective [4-6].
This study examines how the digital mobile platform of smartphone technology can enable solutions for effective engagement, education and motivation of employees to reduce their sugar intake. We assess whether there are meaningful changes and improvement in participant understanding of and inclination to reduce unnecessary sugar intake beyond the program period.
Methods
Intervention objectives and technology deployed
An on demand, digital interactive mobile application was deployed via smartphone to engage, educate, socially connect and motivate employees in a program to reduce consumption of excess daily sugar. The application and platform used to deliver the intervention suite and to capture impact data was a white label of the Wellteq smartphone application (iHealth Well Version 1.1.5). Willis Towers Watson provided consultancy across the deployment of the program with a particular focus on client insights. The program objective was to drive specific improvements in understanding of and commitment to reduce excess daily intake and consumption of added sugar, and then observe any impact in reduced sugar consumption that might commence during the brief 1-week wellness and health promotion program.
The most frequently used vehicle engaged by participants to receive communications, respond to survey questions and share their data was their personal smartphones. Figure 1 show several of the primary and most frequently used functionalities through which participating employees were engaged for conveying education and motivation to reduce excess daily sugar consumption.
 Figure 1: Mobility of Engagement, Content Delivery, Functionality and Impact Measurement
Figure 1: Mobility of Engagement, Content Delivery, Functionality and Impact Measurement
Study setting
The dietary improvement program, or employee Sugar Reduce Challenge, was implemented in December 2021 within the employee population of one of the largest digital or electronic banking systems in East, South and Southeast Asia.
Study participants and selection/eligibility
There were 295 employee participants who engaged in the sugar reduction challenge in 13 nations and 8 enterprise markets across the Asian-Oceanic region. The countries/markets where participants were located include Australia, China, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, U.S.A., and Vietnam. Eligible participants included those recording at least five nutrition ratings within the digital application during the sugar reduce program period.
Intervention content
The Sugar Reduce challenge was designed based on peer reviewed scientific evidence of behavioural responsiveness and sustained behavioural uptake and included various metrics including attitudinal/perception and knowledge-based indices and reported sugar consumption. Participating employees were challenged to record and reduce their added daily sugar reduction over a 7-day period. Awards and modest incentives were deployed to increase program compliance and completion, including a chance to win prizes such as gift cards and similar financial incentives. Participants’ daily added sugar consumption was self-reported within the mobile digital application.
The intervention method employed to encourage employees to engage and participate over the course of the sugar reduction week long challenge included providing easy to assimilate, timely education on the importance of reducing added daily sugar consumption, and conveyed reinforcing and supportive motivational messaging at critical junctures. Straightforward messages imparted specific, personalized practical health educational content, tips, and resources around the chronic disease risk mitigation value of reducing added daily sugar intake.
These resources were conveyed to participants via email and in-application notifications within the mobile application. Select notifications were delivered as a push-notification, keeping the sugar reduction challenge front of mind and supporting behavior change with reminders, accountability, and support. Research shows that using push notifications is highly effective in encouraging user engagement in mental health and wellbeing digital applications [7]. The sugar reduction challenge thus combined provision of motivation and support via push notifications to participants’ mobile phones.
Different types and frequency of program outreach, guidance and messaging, and frequency of data capture can be defined and implemented within the mobile application’s platform according to specific enterprise objectives, as illustrated in Figure 2. These are mobile phone screenshots of messaging that was actually deployed during the sugar reduction program.
Outcomes metrics captured
The outcomes measured included self-reported knowledge, perceptions and attitudes toward added dietary sugar consumption as captured by surveys implemented through the smartphone digital engagement application. In addition, self-reported actual daily consumption of added sugar was gathered. All employee participant ratings needed to be saved in the digital application by 11:59 am SGT December 21, 2021. The metric of added sugar used was number of sugary drinks or teaspoons of sugar (Figure 2).
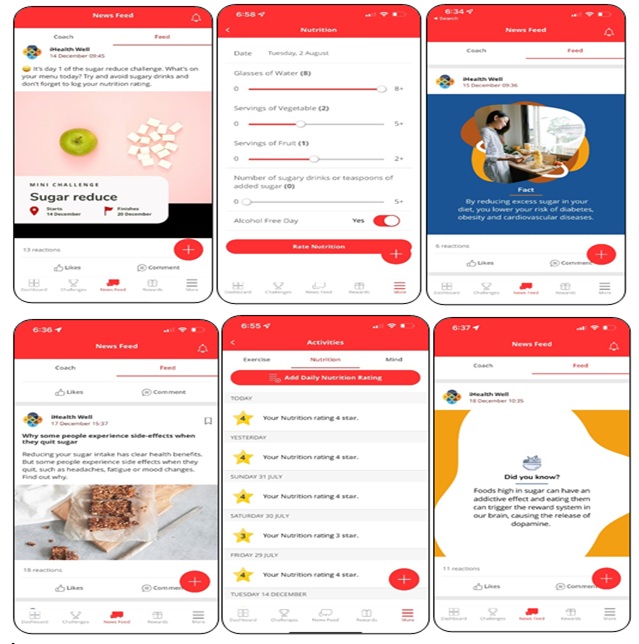 Figure 2: Sample Smartphone Screens of Sugar Intake Reduction
Figure 2: Sample Smartphone Screens of Sugar Intake Reduction
Results
Forty-three percent of eligible participants completed the sugar reduction program, where completions are defined as application users who recorded at least five nutrition ratings in the digital application during the program period of December 14-20, 2021. Eligible participants were those who met the incentives terms and conditions associated with the challenge, and 30% of participants met the eligibility criteria.
As shown in Figure 3, China had the highest percentage of eligible participants complete the sugar intake reduction challenge (58%) (“excludes” participants without data). Among participants with a history of pre-diabetes or diabetes, 62% (13) completed the challenge, a completion rate 19% above the average overall completion rate of 43%.
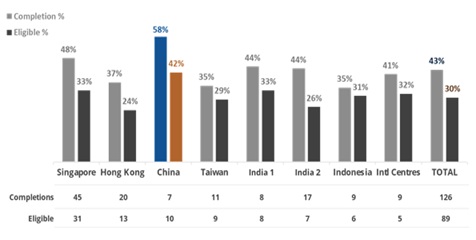 Figure 3: Engagement of Digital Sugar Intake Reduction Program
Figure 3: Engagement of Digital Sugar Intake Reduction Program
Seventy-four percent of participants achieved a reduction in their daily added sugar consumption during the program (Figure 4). Across all eight markets and all 12 participating nations the sugar intake reduction program delivered a mean reduction in daily sugar consumption of 0.4 teaspoon (excludes 13 participants without data). While the volume magnitude of daily added sugar reduction was modest, it is still notable given the short one-week duration of the program (India 1 and 2 are regional markets in India; International Centres include the markets of Australia, Japan, Malaysia, South Korea, Thailand, U.S.A. and Vietnam). Participants in India reduced their daily added sugar consumption by the largest proportion. With respect to preferred format or medium for receiving educational content about reducing sugar intake, 73% found written articles to be the most helpful content medium, and 44% of respondents stated their preferred medium was video.
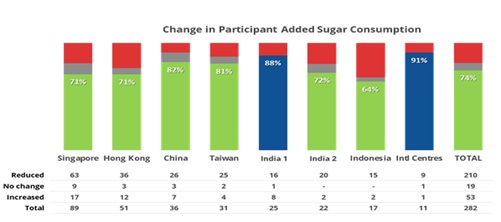 Figure 4: Change in Participant Added Daily Sugar Consumption
Figure 4: Change in Participant Added Daily Sugar Consumption
In terms of participant attitudinal change, 93% of participants stated that they will continue to practice sugar reduction behaviors in the months and years ahead. Of respondents with a history of pre-diabetes or diabetes, 100% (13) indicated that they will progress their reduction in sugar intake in the future. A post-program survey was administered to assess the level of participant sugar consumption risk knowledge and associated attitudes, with 119 participants completing the survey (Table 1). Of these, a very large majority of participants stated that the digital engagement program made them more aware of the need to reduce sugar intake in the prevention of diabetes and related diseases (97.5%), and indicated that what they learned in the program will influence their future selection of supermarket foods (98.3%) and food choices in restaurants (89.9%). Almost 90% responded that they would be more likely in the future to select beverages, snacks and other food items that have substituted added sugar with healthier artificial sweeteners when available. When asked if they will continue to practice sugar reduction behaviors in the future, 97.6% stated that they would do so.
|
Sugar Consumption Awareness and Attitudes Survey Question |
Percent of Participants Agreeing (N = 119) |
|
Did program make you more aware of the need to reduce your sugar intake to prevent diabetes and related diseases? |
97.5 % (116) |
|
Will your future choices of supermarket food purchases be influenced by what you learned about the harm added sugar and sugary foods in your diet can cause? |
98.3 % (117) |
|
Will your restaurant food choices be informed by what you learned in the sugar intake reduction challenge? |
89.9 % (107) |
|
Will you be more likely to select beverages, snacks and other food items that have substituted added sugar with healthier artificial sweeteners when they are available? |
89.9 % (107) |
|
Will you continue to practice sugar reduction behaviors in the weeks and months ahead? |
97.6 % (116) |
Table 1: Post-Program Survey on Sugar Consumption Knowledge
Discussion
Deploying mobile digital engagement technology to sugar intake risk knowledge and attitudes
The digital mobile employee engagement and program implementation evaluated in this study showed minor improvement in actual sugar intake or consumption during the one-week study period, but realized a clinically meaningful improvement in comprehension of the health risks of excess sugar consumption as well as increased motivation to reduce such intake in the future. A one-week intervention period is likely too little time to achieve – or to observe – an impact in sugar consumption behavior. However, participant knowledge, perceptions and understanding of the need to reduce dietary sugar consumption, and motivational commitment to do so following program completion, indicate the potential impact a longer digital or virtual engagement program could achieve, and are highly promising.
The findings indicate that automation and rules-driven customization enabled by web-based digital media such as smartphone programs can improve employee sugar consumption behavioral change readiness, and can be deployed rapidly and cost-effectively at scale across large employee/enterprise populations in multinational settings. These results and program impact on knowledge, perceptions and attitudes toward sugar consumption, achieved after a single 7-day sugar intake reduction challenge, are indicative of the power and value that digital mobile wellness engagement can deliver to employees. The findings illustrate how high value programs deploying this technology can deliver targeted health promotion focused on chronic illness prevention, and specifically metabolic disease risk reduction, which can in turn potentially reduce associated avoidable health care utilization and enterprise costs.
Conclusion
Demonstrated improvement in sugar risk understanding, attitudes and intent
The digital mobile employee engagement and program implementation evaluated in this study delivered an increased understanding of the risk of excess sugar consumption in the origin of metabolic disease such as diabetes and obesity, as well as knowledge and personal motivation to reduce sugar intake that participants will take forward in better managing their dietary risks. This study compellingly demonstrates the impact, utility and value of digital mobility deployed against a difficult to modify behavior such as dietary sugar consumption.
The automation and rules-driven customization enabled by web-based digital media such as smartphones can improve population sugar consumption risk perception and understanding at scale across large employee/enterprise populations in multinational settings. These results and impact achieved after a single education and risk reduction program across a complex multinational and multicultural employee and enterprise setting are indicative of the power and value that digital mobile wellness engagement can deliver to employees.
References
- Yang Q, Zhang Z, Gregg EW, Flanders WD, Merritt R, et al. (2014) Added sugar intake and cardiovascular diseases mortality among US adults. JAMA Intern Med 17: 516-524.
- Kmietowicz Z (2014) Reduce sugar intake to 3% to protect against tooth decay say researchers. BMJ 349: g5622.
- Knüppel A, Shipley MJ, Llewellyn CH, Brunner E (2017) Sugar intake from sweet food and beverages, common mental disorders and depression: Prospective findings from the Whitehall II study. Science Reports 7.
- Proper KI, van Oostrom SH (2019) The effectiveness of workplace health promotion interventions on physical and mental health outcomes: A systematic review of reviews. Scand J Work Environ Health 45: 546-559.
- Gellert GA, Montgomery S, Gillett J, Gellert TE, Hole J, et al. (2021) The hidden public health problem of inadequate sleep: deploying digital mobile technology to improve employee sleep hygiene in asia. J Community Med Public Health Care 8: 1-4.
- Gellert GA, Montgomery S, Gillett J, Gellert TE, Hole J, et al. (2021) High impact employee stress reduction and wellness promotion delivered via digital mobile technology in the construction and aviation industries. J Community Med Public Health Care 8: 1-8.
- Auf H, Dagman J, Renström S, Chaplin J (2021) Gamification and nudging techniques for improving engagement in mental health and well-being apps. International Conference on Engineering Design 426.
Citation: Gellert GA, Montgomery S, Gillett J, Gellert TE, Chua P (2022) Increasing Employee Understanding of Disease Risks Associated With Excess Sugar Consumption by Engaging Digital Mobile Technology. J Community Med Public Health Care 9: 113.
Copyright: © 2022 George A Gellert, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

