
Knowledge and Perception of Child Abuse among the Adolescent Girls in Some Selected Schools in Dhaka City
*Corresponding Author(s):
Shahria HafizMasters Of Public Health Reproductive And Child Health, National Institute Of Social And Preventive Medicine, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Tel:+880 1726428760,
Email:shahriahafiz@icddrb.org
Abstract
Background
About 40 million children under the age of 18 years are estimated to suffer from abuse and neglect around the world. Child abuse in developing countries, including South Asia, is yet to be recognized as a major social and public health problem with an enormous burden on the economy and society. The present study conducted to find out the level of knowledge and perception of child abuse among the adolescent girls in some selected high schools in Dhaka city.
Method
This cross sectional descriptive study was conducted among 149 adolescent girl students of class VIII, IX and X of three purposively selected high schools in Dhaka city namely Kakoli High School, Rayer Bazar High School, and YWCA Higher Secondary Girls’ School.
Results
Mean±SD of age of the respondents was 14.23±0.90 years with a range of 13 to 16 years. Majority of them (61.7%) were in the age group of 13-14 years. When the respondents were asked from where they got information about child abuse, majority (123), 82% stated that they heard from TV, other common sources were news paper 65 (43%) and parents 36 (24%). In the present study out of 149 respondents said that physical abuse (66.4%) is more prevalent in our country than mental (55.7%) and sexual (29.5%) abuse. In the present study the respondents thought that child was abused by nearest relative, by servant, by teacher, by father, by mother, by brother and sister and by others 47.1%, 27.2%, 20.6%, 18.6%, 17.9%, 9.3% and 24.8% respectively. In the present study opinion of the respondents were sought as to how to prevent child abuse, increase peoples’ awareness, enforcement of law, and increase general level of education of the people and parents awareness about child mentality were the prominent opinions. The responses were scored and graded. Mean±SD of scores of knowledge was 11.7±2.5 with a range of 5-17. Only about 13% had high score while 30% scored poor. Mean±SD of scores of perception was 27.9±4.4 with a range of 14-35. Perception score of ‘poor’ grade was observed in 22% respondents and that of ‘good’ grade in 32% respondents. Relationship between knowledge score and perception score was examined by correlation analysis and a weak positive correlation was observed with correlation coefficient, r=0.186 (p=0.023). The mean±SD of scores of perception among Kakoli High School was 28.78±3.65, among the respondent among Rayer Bazar School was 26.93±5.056) and among the respondents of YWCA was 28.81±2.6. The mean±SD of score of knowledge among Kakoli School was 11.93±2.4, among the respondents of in Rayar Bazar School 11.01±2.34 and among the respondents of YWCA School was 13.52±2.01.
Conclusion
From this study it was revealed that the knowledge and perception about child abuse is considerably significant. But in reality to counter the child abuse is not much practiced in our society. Therefore, the importance of child abuse should be focused and generalized with high priority.
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
The term child is someone who has not reached the age of 18; the age specified by the child protection law of the state in which the child resides. About 40 million children under the age of 18 years are estimated to suffer from abuse and neglect around the world. Child abuse in developing countries, including South Asia, is yet to be recognized as a major social and public health problem with an enormous burden on the economy and society. Therefore, it is imperative not only to recognize child abuse from a clinical perspective but also for society, including professionals, to understand and accept it as a malady as well as to change their attitudes towards it [1].
When parents are unhappy in their parental role or when a frictional relationship exists between them, some babies become neglected or abused. The second year of life is a more common time for abuse than the first, babies are more troublesome to their parents and this triggers the outlet of anger and other unpleasant emotions endangered in the relationship of the parents, results in poor performance in school [2].
Each year, tens of thousands of children are traumatized by physical, sexual, and emotional abusers or by caregivers who neglect them, making child abuse as common as it is shocking. The scars can be deep and long-lasting, affecting not just abused children but society. But the incidence of parents and other caregivers consciously, even willfully, committing acts that harm the very children they’re supposed to be nurturing is a sad fact of human society that cuts across all lines of ethnicity and class. Whether the abuse is rooted in the perpetrator’s mental illness, substance abuse, or inability to cope, the psychological result for each abused child is often the same: Deep emotional scars and a feeling of worthlessness [3].
There is no statistics, to show what family member are most responsible for the child abuse, there is some evidence that it is more common among male than female relatives with father and step father the usual offenders. It is important especially for health educators to the behavior disorders and emotional problems that effect children. The emotional maladjustments of children frequently are characterized by anxiety reactions. In the last half of the 20th century, child abuse and neglect have been seen as a significant factor in childhood disorders [4].
Almost all counties, including Bangladesh, legislation exists concerning the minimum age for admission to employment, services and other activities intended to restrain the economic exploitation of its children and to alleviate its effects. In Bangladesh, the minimum age for employment is 14 years, and the minimum age for hazardous work is 18 years. Many developing countries children are engaged in some gainful employment. Although most of the cases they are low paid due to reasons of being a child. Not only that they are also maltreated in those job situations. Physical torture, not giving food as torture is very common [5].
This study was planned to identify the perception and knowledge on adolescent girl about the meaning, types, symptoms, factors, source, consequences and opinion about preventive measures of child abuse. The spectrum of child abuse is wide. Child abuse and neglect is defined as “at a minimum, any recent act or failure to act on the part of a parent or care taker, which results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation, or an act or failure to act which presents an imminent risk of serious harm [6]”.
Bangladesh is a poor developing country, where majority of the population are farmer and less educated, and majority of the families are comprised of 5-7 members. Children are given least priority in their family. Child abuse and neglect is one of them. This has been poorly recognized as a public health problem in the world, particularly in South-East Asia. This study is taken in consideration to the fact that child abuse is a universal practice and should not be continued. Social awareness which is not up to the mark in each sector should be created to curve this inhuman act of daily life. This study is an attempt to explore the knowledge and perception of child abuse that children continuously experience in their daily sphere of life.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
|
Name of the School |
Class |
Total |
||||||
|
VIII |
IX |
X |
||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Kakoli High School |
23 |
41.8 |
10 |
18.2 |
22 |
40 |
55 |
100 |
|
Rayer bazar High School |
1 |
1.4 |
72 |
98.6 |
0 |
0 |
73 |
100 |
|
YWCA Higher Secondary Girls’ School |
0 |
0 |
21 |
100 |
0 |
0 |
21 |
100 |
|
Total |
24 |
16.1 |
103 |
69.1 |
22 |
14.8 |
149 |
100 |
Mean±SD of age of the respondents was 14.23±0.90 years with a range of 13 to 16 years. Majority of them (61.7%) were in the age group of 13-14 years. In religion majority were Muslim (87%) followed by Hindu (11.4%). Rest of them was Christian (1.3%). In terms of respondents parent’s occupation, majority (48%) of the respondent’s father was service holder, 47% businessman, and rest about 5% were Day labourer, unemployed or other occupation group. Majority (86%) of the respondent’s mother was housewife, 11% service holder and rest were doing business and other activity. Median family income of the parents of the respondents was 12000 BDT with a range of 1500-1,000,000 BDT. Among 149 respondents 53% had 5-6 family members; about 29.5% had 1-4 family and 17.4% above 7 family members. Majority (42.3%) of the respondent were in first position in the family, 31.5% second position, 16.1% third position and least number (1%) were from sixth position by their birth order. Majority (81%) of the respondents had belonged to single family and rest of 18.8% came from joint family (Table 2).
|
Variables |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Age Group (yr) |
||
|
13 -14 |
92 |
61.7 |
|
15- 16 |
57 |
38.3 |
|
Mean±SD |
14.23±0.90 |
|
|
Religion |
||
|
Islam |
130 |
87.3 |
|
Hinduism |
17 |
11.4 |
|
Christianity |
2 |
1.3 |
|
Fathers’ Occupation |
||
|
Service |
72 |
48.3 |
|
Business |
70 |
47 |
|
Day labour |
3 |
2 |
|
Unemployed |
1 |
0.7 |
|
Others |
3 |
2 |
|
Mothers’ Occupation |
||
|
Housewife |
128 |
85.9 |
|
Service |
17 |
11.4 |
|
Business |
3 |
2 |
|
Others |
1 |
0.7 |
|
Family Income (BDT) |
||
|
<10000 |
64 |
43.2 |
|
10000-19999 |
38 |
25.7 |
|
20000-29999 |
18 |
12.2 |
|
30000-39999 |
22 |
14.9 |
|
40000-49999 |
2 |
1.3 |
|
≥50000 |
4 |
2.7 |
|
Family size |
||
|
4-Jan |
44 |
29.5 |
|
6-May |
79 |
53 |
|
7+ |
26 |
17.4 |
|
Mean±SD (Rang) |
5.3±1.9(1-18) |
|
|
Birth Order Position |
||
|
First |
63 |
42.3 |
|
Second |
47 |
31.5 |
|
Third |
24 |
16.1 |
|
Fourth |
8 |
5.4 |
|
Fifth |
6 |
4 |
|
Sixth |
1 |
0.7 |
|
Mean±SD (Median) |
1.99±1.130 (2.00) |
|
|
Family Type |
||
|
Joint family |
28 |
18.8 |
|
Single family |
121 |
81.2 |
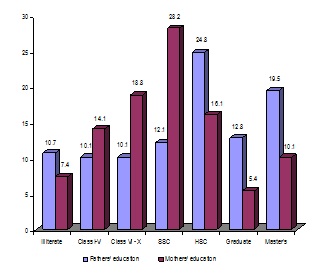
In education about 11% fathers and 7.4% mothers were illiterate. Most of the mothers (61%) had studied up to secondary level including SSC. Sixteen percent (n=24) had HSC level of education while 15.5% (n=23) were graduate or Masters degree holder. The corresponding levels for fathers were 32% (n=48) up to SSC level, 25% (n=37) in HSC level and 32% (n=48) up to Masters Degree level (Figure 1).
In the present study all the respondents known about child abuse. When the respondents were asked from where they got information about child abuse, majority (123), 82% stated that they heard from TV, other common sources were news paper 65 (43%) and parents 36 (24%) (Table 3).
|
Source |
Frequency* |
Percent |
|
Radio |
14 |
9.4 |
|
TV |
123 |
82.1 |
|
Newspaper |
65 |
43.1 |
|
Books |
25 |
16.6 |
|
Friends |
20 |
13.3 |
|
Father and mother |
36 |
23.9 |
|
Others |
6 |
4 |
Regarding type and seriousness of abuse the pinion of the respondents shows that in physical abuse, cigarette burning 91.3% was serious abuse then caning (57%) and (slapping 22%) regarding emotional abuse captivate in room was serious abuse 52% then scolding and compel to study long against desire. Regarding sexual abuse majority state that compel to sexual activity about 86% was serious abuse than compel to view sex picture and forcible de-clothing. Among the respondents 2%, 9%, 4.7% were state that slapping, scolding and forcible de clothing is not any abuse respectively (Table 4).
|
Type of abuse |
Serious |
Moderate |
Mild |
Not abuse |
||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Physical abuse |
||||||||
|
Slapping |
22 |
14.8 |
61 |
40.9 |
61 |
40.9 |
3 |
2 |
|
Caning |
57 |
38.3 |
71 |
47.7 |
18 |
12.1 |
0 |
0 |
|
Cigarette Burning |
136 |
91.3 |
8 |
5.4 |
2 |
1.3 |
1 |
0.7 |
|
Emotional abuse |
||||||||
|
Captivate in room |
79 |
53 |
46 |
30.9 |
14 |
9.4 |
5 |
3.4 |
|
Compel to study long against desire |
11 |
7.4 |
54 |
36.2 |
62 |
41.6 |
10 |
6.7 |
|
Scolding |
35 |
23.5 |
48 |
32.2 |
42 |
28.2 |
14 |
9.4 |
|
Sexual abuse |
||||||||
|
Forcible de clothing |
73 |
49 |
32 |
21.5 |
25 |
16.8 |
7 |
4.7 |
|
Compel to sexual activity |
128 |
85.9 |
3 |
2 |
7 |
4.7 |
0 |
0 |
|
Compel to view sex picture |
122 |
81.9 |
7 |
4.7 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
2.7 |
In the present study out of 149 respondents, 70.5% said that child was abused due to too much mental stress of the parents. When respondents were asked about who were more abused in Bangladesh, most of them stated that girls (86%), and rest of them said didn’t know 14%, not a single respondent had opinion about boy abuse. Most of the respondents (47.1%) thought that child was abused by nearest relative. Regarding effect of child abuse, respondents state that majority of the child may effect to psychiatric disease (94.0%), loss of memory due to head injury (92.6%), drug addict (88.6%), break limbs (87.2%) and may conceive child (61.7%) (Table 5). In the present study out of 149 respondents said that physical abuse (66.4%) is more prevalent in our country than mental (55.7%) and sexual (29.5%) abuse (Figure 2).
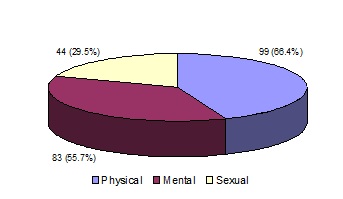
Figure 2: Distribution of respondents by type of abuse.
|
Variables |
Frequency* |
Percent |
|
Causes of abuse |
||
|
Too much mental stress |
105 |
70.5 |
|
Poverty |
59 |
39.6 |
|
Lack of education |
47 |
31.5 |
|
Mentally imbalanced guardian |
30 |
20.1 |
|
Don't know |
12 |
8 |
|
Others |
3 |
2 |
|
Who is more abused |
||
|
Girl |
128 |
86 |
|
Don't know |
21 |
14 |
|
Abusers |
||
|
Father |
28 |
18.6 |
|
Mother |
27 |
17.9 |
|
Brother and sister |
14 |
9.3 |
|
Teacher |
31 |
20.6 |
|
Nearest relative |
71 |
47.1 |
|
Servant |
41 |
27.2 |
|
Others |
37 |
24.8 |
|
Effect of child abuse |
||
|
Break limbs |
130 |
87.2 |
|
Memory loss due to head injury |
138 |
92.6 |
|
Psychiatric disease |
140 |
94 |
|
Drug addict |
132 |
88.6 |
|
Early motherhood |
92 |
61.7 |
|
Others |
11 |
7.4 |
“Forbid to go out” and “stopping food” appear to be the type of abuse practised by parents. Out of 149 girls 78% (n=116) and 76.5% (n=114) respectively mentioned as such (Figure 3).
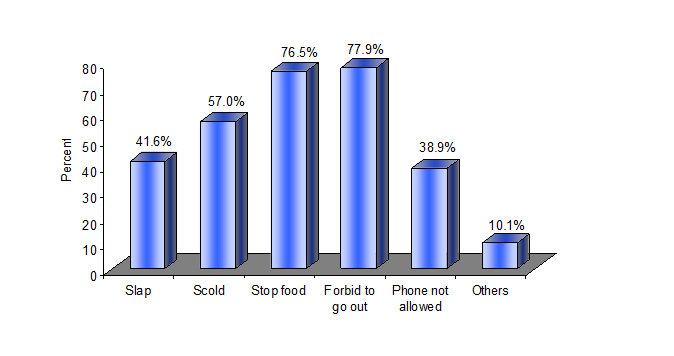
In response to whether respondents themselves had experienced parental abuse, 92 (62%) stated of having had a slap. Experience of scolding was mentioned by about 50% (n=74). When respondent asked whether they became suffer from abuse by parents, they state that about 61.7% respondent received slap from parents. Regarding abuse at school, majority 80% of the respondents stated that caning is a type of abuse in school. When respondents asked whether they became victim at school, they state that about 47.7%, were suffer from school by stand on the bench 39% had caning, 36% had slap, 33% scold and 21% pull by ear (Table 6).
|
Variables |
Frequency* |
Percent |
|
Type of abuse at home |
||
|
Slap |
92 |
61.7 |
|
Scold |
74 |
49.7 |
|
Stop food |
9 |
6 |
|
Forbid to go out |
28 |
18.8 |
|
Phone not allowed |
39 |
26.2 |
|
Others |
4 |
2.7 |
|
Type of abuse at school |
||
|
Slap |
96 |
64.4 |
|
Scold |
102 |
68.5 |
|
Caning |
119 |
79.9 |
|
Pull by ear |
90 |
60.4 |
|
Stand on the bench |
67 |
45 |
|
Others |
10 |
6.7 |
|
Victim of abuse at school |
||
|
Slap |
54 |
36.2 |
|
Scold |
50 |
33.6 |
|
Caning |
58 |
38.9 |
|
Pull by the ear |
31 |
20.8 |
|
Stand on the bench |
71 |
47.7 |
|
Others |
2 |
1.3 |
In the present study opinion of the respondents were sought as to how to prevent child abuse, increase peoples’ awareness, enforcement of law, and increase general level of education of the people and parents awareness about child mentality were the prominent opinions (Table 7).
|
Opinion |
Frequency* |
Percent |
|
Increase the awareness of the people |
90 |
60.4 |
|
Enforcement of law to prevent child abuse |
38 |
25.5 |
|
Increase the education status of the people |
28 |
18.8 |
|
Parents should revised about child mentality |
26 |
17.4 |
|
Tele-communication through mass media |
13 |
8.7 |
|
Govt. Co-operation necessary |
16 |
10.7 |
|
People should be sympathetic to the child |
14 |
9.4 |
|
Good relationship of parents to their child like friend |
4 |
2.7 |
|
Parents should know about all the affairs of the child |
4 |
2.7 |
|
To abolish child labour |
3 |
2 |
|
Prevent poverty rate |
7 |
4.7 |
|
Parents should give enough time to their child |
1 |
0.7 |
*Multiple responses
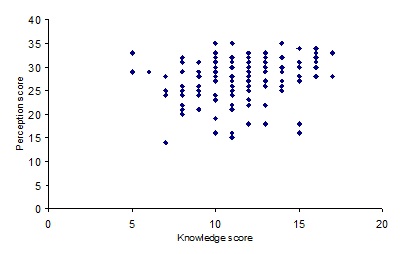
Perception and knowledge were measured by asking related questions. The responses were scored and graded. Mean±SD of scores of knowledge was 11.7±2.5 with a range of 5-17. Only about 13% had high score while 30% scored poor. Mean±SD of scores of perception was 27.9±4.4 with a range of 14-35. Perception score of ‘poor’ grade was observed in 22% respondents and that of ‘good’ grade in 32% respondents (Table 8).
|
Level of knowledge |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
|
Grade |
Score |
||
|
Poor |
Upto 10 |
45 |
30.2 |
|
Average |
11-14 |
85 |
57 |
|
Good |
15 or more |
19 |
12.8 |
|
Mean±SD=11.7±2.5; Median=12; Mode 11; Range=5-17 |
|||
|
Level of perception |
|
|
|
|
Grade |
Score |
||
|
Poor |
Below 25 |
33 |
22.1 |
|
Average |
25 - 30 |
68 |
45.6 |
|
Good |
Above 30 |
48 |
32.2 |
|
Mean±SD=27.9±4.4; Median=29; Mode=32; Range=14-35 |
|||
The mean±SD of scores of perception among Kakoli High School was 28.78±3.65, among the respondent among Rayer Bazar School was 26.93±5.056) and among the respondents of YWCA was 28.81±2.6. The mean±SD of score of knowledge among Kakoli School was 11.93±2.4, among the respondents of in Rayar Bazar School 11.01±2.34 and among the respondents of YWCA School was 13.52±2.01 (Table 9).
|
N |
Mean |
Std. Deviation |
Std. Error |
|
|
Knowledge Score |
||||
|
Kakoli |
55 |
11.93 |
2.471 |
0.333 |
|
Rayar bazar |
73 |
11.01 |
2.348 |
0.275 |
|
YWCA |
21 |
13.52 |
2.015 |
0.44 |
|
Total |
149 |
11.7 |
2.486 |
0.204 |
|
Perception Score |
||||
|
Kakoli |
55 |
28.78 |
3.65 |
0.492 |
|
Rayar bazar |
73 |
26.93 |
5.056 |
0.592 |
|
YWCA |
21 |
28.81 |
2.6 |
0.567 |
|
Total |
149 |
27.88 |
4.368 |
0.358 |
|
Variables |
Level of perception |
x2, df, P value |
|||||||
|
Poor |
Average |
Good |
Total |
||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
||
|
Age Group (years) |
|||||||||
|
13 - 14 |
21 |
22.8 |
43 |
46.7 |
28 |
30.4 |
92 |
100 |
x2=0.350, df=2, p=0.839 |
|
15-16 |
12 |
21.1 |
25 |
43.9 |
20 |
35.1 |
57 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
33 |
22.1 |
68 |
45.6 |
48 |
32.2 |
149 |
100 |
|
|
Mother’s Education |
|||||||||
|
Illiterate |
5 |
45.5 |
4 |
36.4 |
2 |
18.2 |
11 |
100 |
x2=8.731, df=4, p=0.068 |
|
Up to SSC |
21 |
23.1 |
40 |
44 |
30 |
33 |
91 |
100 |
|
|
HSC and above |
7 |
14.9 |
24 |
51.1 |
16 |
34 |
47 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
33 |
22.1 |
68 |
45.6 |
48 |
32.2 |
149 |
100 |
|
|
Father’s Education |
|||||||||
|
Illiterate |
7 |
43.8 |
4 |
25 |
5 |
31.3 |
16 |
100 |
x2=8.731, df=4, p=0.068 |
|
Up to SSC |
14 |
29.2 |
18 |
37.5 |
16 |
33.3 |
46 |
100 |
|
|
HSC and above |
12 |
14.1 |
46 |
54.1 |
27 |
31.8 |
84 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
33 |
22.1 |
68 |
45.6 |
48 |
32.2 |
149 |
100 |
|
|
Father's Occupation |
|||||||||
|
Service |
14 |
19.4 |
38 |
52.8 |
20 |
27.8 |
72 |
100 |
x2=2.907, df=2, p=0.234 |
|
Business |
17 |
24.3 |
27 |
38.6 |
26 |
37.1 |
70 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
31 |
21.8 |
65 |
45.8 |
46 |
32.4 |
142 |
100 |
|
|
Family Income (BDT) |
|||||||||
|
≤12,000 |
22 |
29.3 |
33 |
44 |
20 |
26.7 |
75 |
100 |
x2=4.989, df=2, p=0.083 |
|
>12,000 |
11 |
15.1 |
34 |
46.6 |
28 |
38.4 |
73 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
33 |
22.3 |
67 |
45.3 |
48 |
32.4 |
148 |
100 |
|
|
Family Size |
|||||||||
|
4-Jan |
11 |
25 |
16 |
36.4 |
17 |
38.6 |
44 |
100 |
x2=2.205, df=2, p=0.332 |
|
5 or more |
22 |
21 |
52 |
49.5 |
31 |
29.5 |
105 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
33 |
22.1 |
68 |
45.6 |
48 |
32.2 |
149 |
100 |
|
|
Variables |
Score of knowledge |
x2, df, P value |
|||||||
|
Poor |
Average |
Good |
Total |
||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
||
|
Age Group (years) |
|||||||||
|
13 - 14 |
24 |
27 |
52 |
58.4 |
13 |
14.6 |
89 |
100 |
x2=0.428, df=2, p=0.807 |
|
15-16 |
18 |
32.1 |
33 |
58.9 |
5 |
8.9 |
56 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
42 |
29 |
85 |
58.6 |
18 |
12.4 |
145 |
100 |
|
|
Mother’s Education |
|||||||||
|
Illiterate |
3 |
27.3 |
8 |
72.7 |
0 |
0 |
11 |
100 |
x2=8.731, df=4, p=0.068 |
|
Up to SSC |
31 |
35.6 |
47 |
54 |
9 |
10.3 |
87 |
100 |
|
|
HSC and above |
8 |
17 |
30 |
63.8 |
9 |
19.1 |
47 |
100 |
|
|
Total |
42 |
29 |
85 |
58.6 |
18 |
12.4 |
145 |
100 |
|
|
Father’s Education |
|||||||||
|
Illiterate |
4 |
26.7 |
10 |
66.7 |
1 |
6.7 |
15 |
100 |
x2=20.011, df=4, p=0.001 |
|
Up to SSC |
23 |
50 |
DiscussionChild abuse also called cruelty to children, the willful and unjustifiable infliction of pain and suffering on children. The term can denote the use of inordinate physical violence; unjustifiable verbal abuse; the failure to furnish proper shelter, nourishment, medical treatment, or emotional support; other cases of sexual molestation or rape; and making of child pornography. Frequently described by the medical profession as the ‘battered child syndrome: Abusive treatment of children is almost universally prescribed by criminal statutes [5]. In the present study total 149 adolescent girls between the ages 13 to 16 years, were interviewed at three purposively selected schools of Dhaka city. In religion majority ware Muslims, most (42.3%) of them were 1st child of their parents and majority (53.0%) belonged to 5-6 member size family. This result accords with our national statistics [7]. Among them majority (62%) were 13-14 years old and living with their parents in a single family. It is evident from the findings that the school going children’s father, (48.3%) were service man. Another group stated that 47% of the father’s occupation was business and majority (43.2%) had monthly income <10,000 BDT. Among the mother’s 128 (85.9%) were mainly housewives and other 17(11.4%) was service women. This result does not correspond to our national statistics; maybe they belong to privileged group of our country who resides in the capital city. In developing countries numerous studies across many countries have shown a strong association between poverty and child maltreatment8. The abuse against children mostly occurs in the poor income group. Numerous studies across many countries have shown a strong association between poverty and child maltreatment [8,9]. Regarding the source of hearing about child abuse, majority (82%) heard from TV, which accords with national findings [3]. About type and seriousness of abuse shows that slapping was found moderate in (41%), caning was found moderate (48%), cigarette burning was regarded as serious abuse by 91%, captivate in room serious by 53%, compel to study long against desire mild (42%), scolding was regarded as moderate (32%) type of abuse. Child strike such as, caning [4] physical torture by not giving food, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation, are regarded as serious harms [5,6]. Forcible de-clothing was regarded as serious abuse by 49%, Compel to sexual activity was regarded as serious by majority of the (86%) respondents and Compel to view sex picture was also regarded as serious abuse by majority (82%) of the respondents. Children and adolescent girls are the primary victims of sexual abuse [10]. Regarding causes of child abuse, 70.5% said due to “Too much mental stress”, finding similar with national finding [3]. About 86% opinion reported that girls are more abused. Findings are similar with the study by Anwar et al. [11]. Distribution by more prevalent type of abuse, 66.4% said physical, distribution by abusers, 47.1% said by nearest relative. What is more horrifying is that the abusers of this gruesome act are people whom the children are familiar with i.e. family members, family friends, neighbors, domestic servants, teachers, even those who teach them religion [12]. Effect of child abuse was regarded as 94.0% psychiatric disease. Abused child often suffers from deep emotional scars and a feeling of worthlessness [3]. Regarding abuse by parents, 77.9% forbid to go out. They can learn anger management and child rearing techniques, and try to suppress their violent tendencies through conscious and diligent effort at all times [4]. Respondents about their types of abuses shows, 62% had slap but in their school, majority (80%) had caning. Respondent’s knowledge about abuse was found poor (32%) and average (59%) in 15-16 years age group, and good knowledge was found more in 13-14 year’s age group. Regarding knowledge about child abuse, average level (67%) was found more in illiterate, and good level (18%) of knowledge was found more in HSC and above group. Similarly, poor level of knowledge was found more (36%) in mother’s educated up to SSC level, average level (73%) was found more in illiterate, and good level (19%) of knowledge was found more in HSC and above group. They are all symptoms of disordered parent- child relationship [2]. Poor level of knowledge was found more (32%) in lower income group (<=Tk.12,000), average level was found more (61%) in lower income group and good knowledge was found more in higher income group (>Tk.12, 000). Poor knowledge was found more (30%) in 5 or more member family, average knowledge was more (59%) in 5 or more member family and good knowledge was found more (16.3%) in 1-4 member family size. Child abuse was found more in low socioeconomic status and large family size [4,10,13]. Trocme and colleagues [14,15] highlighted poor knowledge and poor income are highly associated with child abuse and maltreatment. Perception was found poor (23%) and average (47%) in 13-14 years age group, and good (35%) perception was found in 15-16 years respondents. Father’s Perception was found poor (44%) in illiterate father, average (54%) in HSC and above educated father and good level was found (33%) in up to SSC leveled father’s education. Mother’s perception was poor among illiterate (45.5%), average (51%) and good (34%) perception was found in HSC and above educated mothers. Poor level of perception was found more (29%) in lower income group (up to Tk. 12,000), average and good level was found in higher income group (>Tk.12, 000). Good (38.6%) level of perception was found among 1-4 member family, Average (49.5%) level was found among 5 or more member family. Opinion about child abuse prevention, majority (60%) to increase the awareness of the people, 26% to enforcement of law to prevent child abuse, 19% to increase the education status of the people, 17% said parents should revised about child mentality and only 1% gave opinion about parents should give enough time do their child. Social weariness can protect children from such abuse and its consequences [16]. Reducing the incidence of child abuse is a matter of education and intervention [17]. Traumatized children should be treated with medically or psychologically [18]. CONCLUSIONAll the respondents were aware about child abuse and got the information from different sources. Study reported that girls were mostly abused by their nearest relatives and too much mental stress of the parents were the major causes of child abuse, which causes psychiatric disease of child in future according to respondents opinion. Regarding knowledge about child abuse among the adolescent girls, good level of knowledge was found in 13-14 yrs girls, in educated parents, small family and high income groups. Corresponding respondent’s perception was found good in 15-16 years girls, educated parents more income family and small family size. Further study with large sample size needed to validate the finding of the results.
REFERENCES
Citation: Hafiz S, Nahar S, Rahman A, Begum A (2019) Knowledge and Perception of Child Abuse among the Adolescent Girls in Some Selected Schools in Dhaka City. J Neonatol Clin Pediatr 6: 028. Copyright: © 2019 Shahria Hafiz, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. 
© 2026, Copyrights Herald Scholarly Open Access. All Rights Reserved!
| ||||||
