
Post COVID-19 Reactive Arthritis: An Emerging Existence in the Spectrum of Musculoskeletal Complications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
*Corresponding Author(s):
Muhammad Shariq MukarramDepartment Of Medicine, Jinnah Medical College Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan
Email:shariq.msm@gmail.com
Abstract
Reactive arthritis is commonly preceded by a gastrointestinal or a sexually transmitted infection. However, its association with different viral infections has also been reported. Herein, we report a case of a 34 year old male who developed Reactive arthritis few days after the severe acute respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus 2 infection (SARS-CoV-2). The patient was positive for COVID-19 infection from nasopharyngeal swab specimen. He was advised self-isolation/quarantine, considering his mild form of disease, along with medication. Ten days later he developed severe pain and tenderness in his right knee joint. His MRI of the affected joint revealed mild effusion (secondary to inflammation) in the patella-femoral compartment. Patient was diagnosed with Reactive arthritis and was prescribed Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). Intra articular glucocorticoid was injected, to which he responded dramatically. His symptoms completely resolved in next ten days.
Keywords
COVID-19, Reactive arthritis, Viral infections
INTRODUCTION
Reactive arthritis belongs to a group of diseases called Spondyloarthropathies typically causing monoarthritis or oligoarthritis that usually involves the lower limbs (ankles and knees) as seen in our patient [1]. It usually takes 1-4 weeks for ReA (Reactive arthritis) to occur after an infection [2]. ReA is triggered by an extra-articular infection not present in the synovial fluid of the joint [1]. It occurs classically secondary to sexually transmitted or gastro intestinal infections. Common causative agents are Chlamydia Trichomatis, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia and Compylobacter species [3]. However, other viral infections may also cause ReA. A case of clinical ReA occurring after HIV infection was reported by Kishimoto, et al. in 2006 [4]. A syndrome consistent with ReA has also been reported with Dengue, Chickungunya and Parvo virus B19 [5].
CASE PRESENTATION
A 34 year old male patient with no prior known co-morbid or significant past medical history presented to the outpatient department with complaints of low grade fever, dry cough, and severe fatigue/lethargy, loss of appetite and taste sensation for last 6 days. Although there was no travelling history, he recently had a direct contact with a COVID-19 patient. At presentation his temperature was 100F, heart rate was 95bpm, blood pressure 100/60mmhg, and respiratory rate of 20bpm. His oxygen saturation at room air was 96%. Physical examination including chest examination was unremarkable.
Laboratory investigations showed a TLC count of 4.2x109/L, lymphocytes 12x109/L, platelets 205x109/L. His C-reactive protein, D-dimer and serum Ferritin levels were 20mg/l, 0.5mcg/ml and 750ng/ml respectively. Nasopharyngeal swab for COVID-19 PCR turned out to be positive. Three days later antibody (IgM) for COVID-19 was also tested which turned out to be positive. Patient was discharged on Azithromycin (for 5 days), zinc and multivitamins. Patient was advised self-quarantine/isolation for 14 days.
Ten days later, patient returned with swelling, severe pain and tenderness in his right knee which was more marked in the morning (Figure 1). There was no history of urinary complaints, visual disturbances or loose stool. At the same time he had elevated levels of C-reactive protein and serum Ferritin. Plain radiograph (X-Ray) of the joint was unremarkable (Figure 2). However, the MRI of the affected joint revealed mild effusion especially in patella-femoral compartment which extended to the supra-patellar region (Figure 3). There was also associated pre-patellar soft tissue swelling with subcutaneous edema and blurring of myofascial planes. Because of typical findings and clinical presentation patient was diagnosed with Reactive arthritis secondary to COVID-19 infection. Patient was treated with Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and intra articular steroid was injected. His symptoms of arthritis resolved completely within next 10 days.
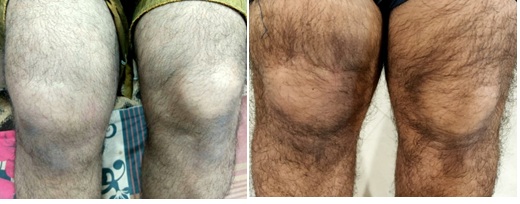 Figure 1: A) Images of arthritis in the right knee; B) Images of affected joint after NSAID treatment and Glucocorticoid infiltration.
Figure 1: A) Images of arthritis in the right knee; B) Images of affected joint after NSAID treatment and Glucocorticoid infiltration.
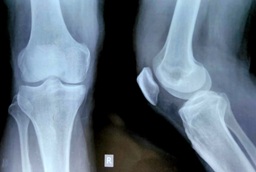 Figure 2: Plain radiograph (X-Ray) of the affected joint which is unremarkable.
Figure 2: Plain radiograph (X-Ray) of the affected joint which is unremarkable.
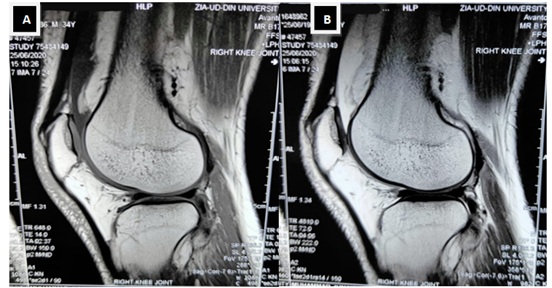 Figure 3: MRI of the affected joint showing mild effusion in the patella-femoral compartment extending to the supra-patellar region. A) MRI T1 weighted image; B) MRI T2 weighted image.
Figure 3: MRI of the affected joint showing mild effusion in the patella-femoral compartment extending to the supra-patellar region. A) MRI T1 weighted image; B) MRI T2 weighted image.
DISCUSSION
ReA commonly occurs in men aged between 20 to 50 years, as also evident in our case. A 30-50% patients have associated HLA-B27 [6-7]. The disease is five times more prevalent than general population in patients who are HLA-B27 positive [8-9]. However, it can also occur in patients who are negative for HLA-B27.
COVID-19 infection is now known to cause a host of complications that are extra pulmonary. This includes cardiovascular, neurologic and skin manifestations [10]. The gastrointestinal tract may serve as a secondary site for COVID-19 infection in relation to the expression of the Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 in the gastrointestinal tract [11]. Nearly 12% of COVID-19 patients reported gastrointestinal symptoms [12].
Very recently two cases of ReA occurring secondary to COVID-19 infection were reported. The first case was a 73 year old man with multiple co morbid conditions who was test (PCR) positive for COVID-19. Eight days after completing the treatment he developed ReA in his left first metatarsophalyngeal, proximal and distal interphalyngeal joints. The second case was also an old male in his 50’s who was admitted for COVID pneumonia. Three weeks later he developed acute bilateral arthritis in his ankles along with mild enthesitis in Right Achilles tendon [5,13].
Management of acute Reactive arthritis involves the use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) as first line therapy. It has proven efficacy in treatment of peripheral arthritis occurring due to ReA [14-16]. Treatment with glucocorticoids is considered in patients who have inadequate response to NSAIDs or persistent active disease for more than 4 weeks. In case of mono or oligoarthritis, steroid infiltration has a remarkable symptomatic response as seen in our case [17-19].
CONCLUSION
COVID-19 infection is now presumed to target the musculoskeletal system in its post infectious stage, especially the joints, causing acute Reactive arthritis. Therefore the treating physician or rheumatologist should have a high index of suspicion while treating any post infectious COVID-19 patient who presents with joint pain or arthralgia.
REFERENCES
- Selmi C, Gershwin ME (2014) Diagnosis and classification of reactive arthritis. Autoimmune Rev 2014; 13: 546-549.
- Toivanen A, Toivanen P (2014) Reactive arthritis. Best pract Res Clin Rheumatol 18: 689-703.
- Leirisalo M, Skylv G, Kousa M, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Suoranta H, et al. (1982) Followup study on patients with Reiter's disease and reactive arthritis, with special reference to HLA-B27 Arthritis Rheum 25: 249-259.
- Kishimoto M, Mur A, Abeles AM, Solomon G, Pillinger MH, et al. (2006) Syphilis mimicking Reiter’s syndrome in an HIV positive patient. AmJ Med Sci 332: 90-92.
- Ono K, Kishimoto M, Shinasaki T, et al (2020) Reactive arthritis, after COVID -19 infection. RMD Open 6: 001350.
- Hannu T (2011) Reactive arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 25: 347-357.
- Carter JD, Hudson AP (2009) Reactive arthritis: Clinical aspects and medical management. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 35: 21-44.
- Colmegna I, Cuchacovich R, Espinoza LR (2004) HLA-B27-associated reactive arthritis: pathogenetic and clinical considerations. Clin Microbial Rev 17: 348-369.
- Feltkamp TE (1995) Factors involved in pathogenesis of HLA B27 associated arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 101: 213-217.
- Wang L, Wang Y, Ye D, Liu Q, et al. (2020) Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55: 105948.
- Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, et al. (2020) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin angiotensin system. Circ Res 126: 1457-1475.
- Parasa S, Desai M, Thoguluva C, Patel HK, Kennedy KF, et al. (2020) Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal viral shedding in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. JAMA Network Open 3: 2011335.
- Saricaoglu EM, Hasanoglu I, Guner R (2020) The first reactive arthritis case associated with COVID-19. J Med Viral Pg no: 1-2.
- Douados M, Baeten D (2011) Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 37: 2127-2137.
- Koehler L, Kuipers JG, Zeidler H (2000) Managing seronegative spondarthritides. Rheumatology 39: 360-368.
- Reveille JD, Arnett C (2005) Spondyloarthritis: Update on pathogenesis and management. Am J Med 118: 592-603.
- Toivanen A (2000) Managing reactive arthritis. Rheumatology 39: 117-119.
- Lassus A (1976) A comparative pilot study of azapropazone and indomethacin in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and Reiter’s disease. Curr Med Res Opin 4: 65-69.
- Palazzi C, Oliveri I, D’amico E, Penese E, Petricca A (2004) Management of reactive arthritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5: 61-70.
Citation: Mukarram IG, Mukarram MS, Ishaq K, Riaz SU (2020) Post COVID-19 Reactive Arthritis: An Emerging Existence in the Spectrum of Musculoskeletal Complications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J Clin Stud Med Case Rep 7: 0101.
Copyright: © 2020 Muhammad Ishaq Ghauri, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

