
Autologous Adult Bone Marrow Total Nucleated Cells for Chronic Heart Failure - 2 Cases Report: 1 Year Follow Up
*Corresponding Author(s):
Fernández Viña MatíasSan Nicolas Clinic, Cardiology And Hemodynamic Service, Argentina
Tel:+54 93364 516062,
Fax:+54 03364 4431000
Email:matiasfernandezvina@hotmail.com
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
The therapeutic options for patients who develop advanced Heart Failure (HF) are limited to heart transplantation or the use of ventricular assist devices [5]. This results in a large HF patient population with progressive symptoms and limited treatment options [6]. Biologically based cell and gene therapies for advanced HF have shown promise [7-10]. Cell therapy is a 21st century approach to treat cardiovascular disease and is being applied worldwide. HF therapy entails syndrome relief, prevention of hospital admission and mortality reduction [8].
Percutaneous Retrograde Coronary Sinus Perfusion (PRCSP) is a well-established technique for delivery of cardioplegia solution in cardiovascular surgery and for protection against myocardial ischemia, heart failure in patients undergoing high risk Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) [10,11].
The technique has the potential advantages of safety delivering a larger number of cells with more homogeneous delivery across the myocardium in patients with heart failure, AMI, refractory angina despite the presence of severe underlying coronary artery disease, valvular disease or previous myocardial infarction which may complicate delivery by either intracoronary or intramyocardial approach [11,12].
In 2002, the publications of Dr. Bodo Strauerr in Germany inspired our group to begin the investigation about the feasibility of practicing autologous stem cells implants by intra arterial coronary injection with the objective of producing angiogenesis and myogenesis according to the pathology to be treated.
In this study, we describe a report of 2 cases with chronic heart failure functional class IV, those were implanted with Bone Marrow Total Nucleated Stem Cells (BM-TNCs) by the retrograde technique.
CASE REPORT
Goals
Materials and methods
 Figure 2: Bone Marrow Total Nucleated Cells (Bm- TNCs) were isolated and enriched by density gradient with the use of Ficoll- Paque Premium.
Figure 2: Bone Marrow Total Nucleated Cells (Bm- TNCs) were isolated and enriched by density gradient with the use of Ficoll- Paque Premium.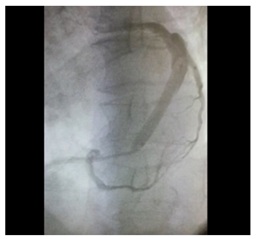 Figure 3: Transplantation of BM-TNCs into coronary veins.
Figure 3: Transplantation of BM-TNCs into coronary veins.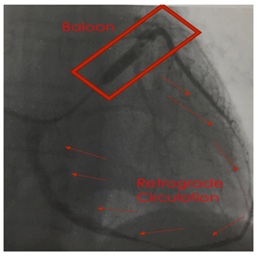 Figure 4: Retrograde venous technique.
Figure 4: Retrograde venous technique.RESULTS
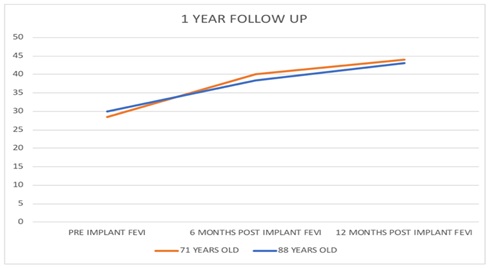
|
Year OLD |
Doppler Echocardiography |
Pre-Implant |
6 Months Post Implant |
12 Months Post Implant |
|
88 |
FEVI |
30% |
38.30% |
43% |
|
|
Left Ventricle Mass |
411 gms |
334 gms |
340 gms |
|
71 |
FEVI |
28.40% |
40% |
44% |
|
|
Left Ventricle Mass |
229 gms |
101 gms |
100 gms |
In addition, it was observed that there was no recurrence in hospital readmissions every 15 days, due to HF, and that there was a marked improvement in the quality of life quickly after implantation of stem cells due to dyspnea modification Functional Class (FC) IV to III-II (NYH Classification) staying for at least one year. The post-implant ergometry test, at 180 days, proved to be encouraging, since both patients tolerated the stress test greater than 6 minutes. No arrhythmias were observed in the Holter ECG of each patient at 6 and 12 months.
There was no modification of the pharmacological medication during the follow-up of this descriptive and observational study.
The implant of autologous adult Bone Marrow Mononuclear and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-TNCs) generated a favorable decrease in the number of hospital re-admissions of the patients and demonstrated an improvement in the quality of life after modification of the FC of dyspnea from IV to III/II, staying for at least one year. It was corroborated that there is a significant increase of the FEVI from 12% to 17%, concomitantly with a decrease in heart mass. There were no presences of arrhythmias. It could be affirmed after a follow-up of 365 days of each patient.
DISCUSSION
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that total occlusion of the coronary sinus for up to 60 minutes is safe owing to the presence of the Thebesian veins, which also drain cardiac venous blood. Zakharova et al., also recently demonstrated the preclinical feasibility of retrograde cell delivery with distribution throughout the left ventricle [13].Retrograde coronary vein way to injection seems to be an excellent method of implanting stem cells in order to carry these cells to improper areas, badly perfunded by coronary arterial system, since this system is, because of its inadequacy, unable to irrigate certain areas where it is necessary to implant cells.
This group of patients of the study with refractory cardiac failure, in spite of having in most cases secondary scars to chronic myocardial infarction, had viable areas that could not be revascularized. The cellular implantation had demonstrated true improvement of the perfusion, surely through angiogenesis, which was without any doubt responsible for the improvement of contractility of viable sectors. However there is a difficulty to show an evidence of existing new angiogenesis to corroborate our hypothesis.
Human bone marrow is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix that contains cytokines and growth factors. The cellular component of bone marrow is composed of differentiated cells, such as monocytes, lymphocytes, fibroblasts, adipocytes, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts, as well as a fractionally small but very diverse group of undifferentiated cells. The undifferentiated stem cell population is composed of hematopoietic stem Cells (hsC), which include hemangioblasts and endothelial Progenitor Cells (ePC), and nonhematopoietic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells (MPCs) that give rise to stromal cells referred to as Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). The undifferentiated stem cell population can be isolated from differentiated cells by density gradient centrifugation. The end product of this centrifugation process is referred to as bone marrow total nucleated cells and contains the undifferentiated hsC and MSC as well as a few committed cells in various stages of maturation. The overall structure of BM-TNCs is primarily that of early committed cells, with only 2% to 4% comprised of hsC/ePC and approximately 0.01% of MSC [13].
Cells-based therapies have been considered overall safe procedures. A recent systematic review of 36 prospective clinical trials for several clinical conditions, including myocardial infarction and chronic cardiomyopathy, did not detect an association between intravascular infusions of mesenechymals or total nucleated cells and the risk of acute infusion toxicity, organ system complications, infection, death, or malignancy in treated patients. Systematic reviews in heart failure population actually describe an association between stem cell therapy and a reduction of mortality and major cardiovascular events albeit most of the analyzed studies used intramyocardial injection or percutaneous intracoronary infusion of bone marrow mononuclear cells [14]. In this investigation, there were no side effects during and after the stem cell implantation procedures for at least 365 days.
Garzon FB et al., published that left ventricular function shows favorable changes after regenerative treatment of infarction and dilated cardiomiopathy. However, no correlation was found between changes in micro vascular and myocardial function after regenerative therapy [15].
Strauerret BE al., confirmed that the use of unselected BM-derived Mononuclear Cells (BMCs) is clearly the most examined cardiac cell-based therapy in clinical studies with a clinical follow-up experience up to 5 years [16]. In 2005, our group of investigators from San Nicolas City, Argentina, showed safety and feasibility of mononuclear stem cells-based therapy in cardiac diseases [17].
CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- World Health Organization (2007) Report of the global survey on the progress in national chronic diseases prevention and control. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, et al. (2013). Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 127: 143-152.
- Taylor DA, Robertson MJ (2009) The basics of cell therapy to treat cardiovascular disease: One cell does not fit all.. Rev Esp Cardiol 62: 1032-1044.
- Terzic A, Waldman S (2011) Chronic diseases: the emerging pandemic. Clin Transl Sci 4: 225-226.
- Shimokawa H, Miura M, Nochioka K, Sakata Y (2015) Heart failure as a general pandemic in Asia. Eur J Heart Fail 17: 884-892.
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, et al. (2013) 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation 128: 1810-1852.
- Sanganalmath SK, Bolli R (2013) Cell therapy for heart failure: a comprehensive overview of experimental and clinical studies, current challenges, and future directions. Circ Res 113: 810-834.
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, et al. (2012) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 14: 803-869.
- Jeevanantham V, Butler M, Saad A, Abdel-Latif A, Zuba-Surma EK, et al. (2012) Adult bone marrow cell therapy improves survival and induces long-term improvement in cardiac parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 126: 551-568.
- Bockeria L, Bogin V, Bockeria O, Le T, Alekyan B, et al. (2013) Endometrial regenerative cells for treatment of heart failure: a new stem cell enters the clinic. J Transl Med 11: 56.
- Tuma J, Fernández-Viña R, Carrasco A, Castillo J, Cruz C, et al. (2011) Safety and feasibility of percutaneous retrograde coronary sinus delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with chronic refractory angina. J Transl Med 9: 183.
- Dib N, Menasche P, Bartunek JJ, Zeiher AM, Terzic A, et al. (2010) Recommendations for successful training on methods of delivery of biologics for cardiac regeneration: a report of the International Society for Cardiovascular Translational Research. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 3: 265-275.
- Zakharova L, Nural-Guvener H, Feehery L, Popovic S, Nimlos J, et al. (2014) Retrograde coronary vein infusion of cardiac explant-derived c-Kit+ cells improves function in ischemic heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant 33: 644-653.
- Asahara T, Bauters C, Zheng LP, Takeshita S, Bunting S, et al. (1995). Synergistic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on angiogenesis in vivo. Circulation 92: 365-371.
- Kandala J, Upadhyay GA, Pokushalov E, Wu S, Drachman DE, et al. (2012) Meta-Analysis of Stem Cell Therapy in Chronic Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 112: 217-225.
- Garzon FB, Álvarez-Ossorio MP, Moreno MAR, Palanco VM, Arroyo CH et al. (2018) Coronary Flow Reserve and Ventricular Function Following Regenerative Treatment in Patients With Revascularized acute Anterior Myocardial Infarction. Rev Esp Cardiol 71: 344-350
- Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, Kostering M, Hernandez A, et al. (2002) Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation 106: 1913- 1918.
Citation: Matías FV, Roberto FV, Federico FV, Jorge S, Federico MSJ, et al. (2018) Autologous Adult Bone Marrow Total Nucleated Cells for Chronic Heart Failure - 2 Cases Report: 1 Year Follow Up. J Stem Cell Res Dev Ther 4: 010.
Copyright: © 2018 Fernández Viña Matías, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

