
Chapter Three: Level of Nurses Knowledge Regarding Adverse Events Post Immunization at the Health Care Centers in the Northwest of Jerusalem District
*Corresponding Author(s):
Hadi Dar BadwanFaculty Of Nursing And Health Sciences, Bethlehem University, Bethlehem, Palestine
Email:hadbad446@gmail.com
Abstract
Background: Childhood immunization against common childhood diseases is the most powerful public health strategy to keep children healthy. It has been the most cost-effective public health intervention, saving an estimated 2–3 million lives around the world each year. However, because no vaccine is 100% safe and effective, so adverse events post-immunization may occur. These adverse events are any untoward medical occurrences that occur following immunization and do not necessarily have a causal relationship with the use of the vaccine. Moreover, if not rapidly and effectively dealt with it, it can undermine confidence in a vaccine and ultimately have dramatic consequences for immunization coverage and disease incidence.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the level of nurse’s knowledge regarding adverse events post immunization at the health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district.
Methodology: Study designs: A descriptive cross-sectional study design was used. Study population: The study population consists of all of community health nurses who are working at health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district. Study sample: The study sample was consisted of community health nurses that working in this area and who did not administer the vaccination. A convenience sampling method was used to collect data, so, the number of nurses who enrolled in our study was 40 nurses. Setting: This study was conduct at health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district from 1st of December to the end of December of 2022. Study tools: The study tool that used in our study was the questionnaire tool. Study strategies for analysis: The collected data was analyzed by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Version (28).
Results: The results of the research show that more than two-thirds of nurses were female and held Bachelor’s Degree, and more than half of nurses aged 21-30 years old and have 1-4 years old experience. Almost two-thirds of nurses 62.5% have good knowledge, while 37.5% of nurses have poor knowledge, also it found that the nurses who work in governmental clinics have more knowledge score than others nurses (p= < 0.001).
Recommendations: This study recommended to establish an educational program in health care centers to improve the nurse's knowledge regarding adverse events post-immunization and also for nursing students in universities and colleges. Furthermore, routinely validate staff's knowledge and competencies regarding vaccine administration and its adverse events were suggested.
Keywords
Adverse events post immunizations; Immunization; knowledge; Community health nurses; Vaccination; AEFI
Introduction
This chapter describes the design, purpose, and setting of the study. Furthermore, it identifies the techniques that help the research team choose the population and the samples that are related to the research. Also, the researchers determined the conceptual framework of community health nurses' knowledge regarding adverse events post immunization and the contributing factors that have an impact on them. Moreover, this chapter will explain the variable, instrument, pilot study, validity, reliability, ethical considerations, and how the data was analyzed.
Study Design
A descriptive cross-sectional study design was used through comprehensive, and examining data from a specific group at one point in time without influencing their behavior in any way. This specific approach was used to determine level of nurses' knowledge regarding adverse events post immunization.
Purpose of This Study
The purpose of this study was to determine the level of nurse’s knowledge regarding adverse events post immunization at the health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district.
Setting
This study was conduct at health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district from 1st of December to the end of December of 2022; furthermore, 20 health care centers were enrolled.
Identification of Population and Sample
The study population consists of all of community health nurses who are working at health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district, and there were some difficulties in determine the specific number of them because there is no specific study about the numbers of community health nurses in this area, so the research team was asked all of health care center in this area about the number of nurses that working in every health care center, so it was approximately 66 nurses.
The study sample was consisted of community health nurses that working in this area and who did not administer the vaccination. A convenience sampling method was used to collect data, so, the number of nurses who enrolled in our study was 40 nurses that given an response rate 60% from all population.
Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria:
- Nurses who currently do not administer the vaccination
- Nurses who are consent to participate in the study voluntarily
- Nurses who have had work experience for at least one year
Exclusion criteria:
- Nurses who currently administer the vaccination
- Nurses who did not consent to participate in the study
- Nurses who did not complete the questionnaire form
- Having work experience less than one year.
Framework
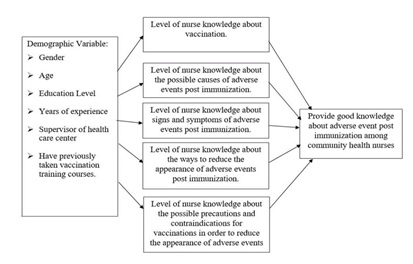
Relationship between the Concepts
There are many variables that affect or increase the knowledge of community health nurses at the health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district regarding adverse events post immunization, such as gender, age, education level, years of experience, supervisor of the health care center, having training courses on the vaccination or not, and also general information about vaccination, causes of adverse events post-immunization, ways to reduce the appearance of adverse events post immunization, and possible precautions and contraindications for vaccinations to reduce adverse events; thus, all of these variables may influence the goal, which is to improve nurses’ knowledge regarding adverse events post-immunization.
Variables
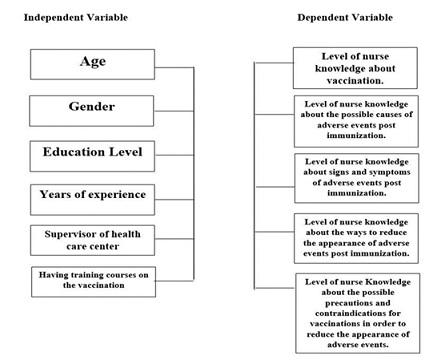
Dependent variables:
- Level of nurse knowledge about vaccination
- Level of nurse knowledge about the possible causes of adverse events post immunization
- Level of nurse knowledge about signs and symptoms of adverse events post immunization
- Level of nurse knowledge about the ways to reduce the appearance of adverse events post immunization
- Level of nurse knowledge about the possible precautions and contraindications for vaccinations in order to reduce the appearance of adverse events
Independent variables:
- Gender
- Age
- Education Level
- Years of experience
- Supervisor of health care center
- Having training courses on the vaccination
Instrument
The study tool or instrument that used in our study was the questionnaire tool. The questionnaire tool was in Arabic, and there is another copy in English. It was used to collect the data by fulling the questionnaire papers by community health nurses that are working at health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district. This happened after obtaining verbal informed consent from the respondents. Moreover, the questionnaire was developed by the researchers’ team by using some of the literature and previous studies in the field of study to determine the appropriate question formulas, and then the questionnaire was presented to the research supervisor as well as some arbitrators to verify its validity. The researchers made the modifications referred to by the arbitrators, so that some study demographic, variables, and items were modified, so, by this modification the questionnaire's final form included (50) items of knowledge and (8) items of demographic data. From using this instrument, the researcher’s team was able to determine the level of nurses' knowledge regarding adverse events post immunization at the health care centers in the northwest of Jerusalem district.
Table 1 illustrates the fields of the questionnaire with the number of their items, which showed that the largest number of items was in the field of knowledge about the possible causes of adverse events post-immunization and in knowledge about signs and symptoms of adverse events post-immunization, and the smallest number of items was in the field of general knowledge about vaccination.
|
Fields of the Questionnaire: |
Number of items: |
|
General knowledge about vaccination. |
5 items |
|
Knowledge about the possible causes of adverse events post |
13 items |
|
immunization: |
|
|
Knowledge about signs and symptoms of adverse eventspost immunization. |
13 items |
|
Knowledge about the ways to reduce the appearance ofadverse events post immunization. |
8 items |
|
Knowledgeaboutthepossibleprecautionsandcontraindications for vaccinations in order to reduce theappearance of adverse events. |
11 items |
|
|
|
|
Total |
50 tems |
Table 1: Filed of the of the Questionnaire
Pilot Testing
A pilot study was conducted on 10 community health nurses as test prior to thebegin the actual data collection in order to:
- Provide feedback on the questionnaire
- Test the clarity of the instrument
- To assess the time required to complete the questionnaire
- To know areas of weakness to modified the study instrument
- To evaluate the stability coefficient (Cronbach alpha)
The nurses in the pilot study were excluded from the total original sample.
Validity
The validity of the questionnaire was presented to the academic supervisor and to a group of arbitrators and specialists in the field of study (7 members), they reported the validity and validity of the scale for the purposes of this study.
Reliability
The stability of the tool was confirmed by extracting the stability coefficient (Cronbach alpha) on the entire study sample, where the stability coefficient of the tool was (0.75), which is an acceptable stability coefficient in educational and scientific research (Table 2).
|
|
Variables |
N |
Cronbach's Alpha |
|
|
All Knowledge items |
50 |
0.75 |
Table 2: Reliability coefficient.
Table 2 shows the reliability coefficient. The Cronbach’s Alpha of the knowledge was 0.75.
Data Analysis
The collected data was analyzed by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Version (28). Data entry was performed and double-checked for outliers or errors. Data was tested for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test which shown that the total sum scores were normally distributed (p= >0.05).
Data analysis of descriptive and inferential statistics was conducted. Regarding descriptive statistics: frequency, percentages, the mean score, and the Standard Deviation (SD) were used to describe the study variables. Regarding inferential statistics: parametric tests such as the independent t test and One Way ANOVA were used to assess the differences between variables. Regarding the instrument scoring system, the correct answer was given 1 point, and the incorrect answer and "I don’t know" were given 0 points. The maximum score is 50, and the minimum score is 0. The median is considered as a cut-off point, which was set at 30 (<30 = poor knowledge and ≥ 30 = good knowledge).
Ethical Consideration
Ethical approval was obtained from the Bethlehem University to conduct the study.A consent form from the subjects was obtained before started the questionnaire. The confidentiality and anonymity of the received data were completely secured by providing code numbers for each subject. Also, it done by:
- Participants was asked to participate before giving them cover letter/consent/ questionnaire
- Participants names or any private information were not asked during filling the questionnaire
- Participants were ensured that their identities or data will be strictly use for research purpose in order to maintain confidentially
- Participants was given a space to fill the questionnaire
Summary
This chapter addresses issues related to methodology, Study design, Identification of population and sample, sample size, study setting, purpose of the study, clarify framework map, variables, instruments, validity, reliability, pilot testing, and method of data analysis.
Acknowledgement
We appreciate the Almighty ALLAH for the courage, competence and protection to carry out this research project successfully.
We thank our families for supporting us and their efforts in order to reach this success.
We are grateful to our supervisor Mrs. Inas Zahran for her tireless efforts and enthusiasm that have always encouraged us to carry on with this study.
We do not forget to extend our thanks to teaching staff at Faculty of Nursing in Bethlehem University, especially Sister. Mary and Mr. Usama Zahran. Without their tireless efforts with us, we would not have reached here.
Thank you to the friends who shared the good and bad four years with us, thank them for their support, even in a simple word.
Finally, grateful thanks to the community health nurses who trust us and participate in this work.
Citation: Badwan HD, Jamhour S, Faqeeh A, Hoshia R, Taha L (2023) Chapter Three: Level of Nurses Knowledge Regarding Adverse Events Post Immunization at the Health Care Centers in the Northwest of Jerusalem District. J Pract Prof Nurs 7: 037.
Copyright: © 2023 Hadi Dar Badwan, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

