
Development and Clinical Application of Percutaneous Compressive Locking Intramedullary Nail for Humerus
*Corresponding Author(s):
Zhang ZuojunLuoyang Orthopedic Hospital And Institute, No 82 South Qiming Road, Luoyang, Henan, China
Tel:+86 13838838000, +86 37963546746,
Fax:+86 37963552102
Email:zzjlip@163.com
Abstract
Objective: To simplify the usage of locking intramedullary nail; to increase the therapeutic effect and decrease the medical costs for patients.
Methods: According to the proximal constitution of the humerus and the anatomic features of the medullary cavity, percutaneous compressive locking intramedullary nail was developed. Mechanical tests and clinical observation were performed. All the data were compared and analyzed, such as firmness of fixation, result of reduction, fracture union, joint function recovery, the simplicity of application and medical costs, etc.
Results: Through mechanical tests, it is proved that all the indices of percutaneous compressive locking intramedullary nail can meet the requirements of biomechanical fixation of humeral fractures. In addition, clinical observation of 1078 cases further proved that percutaneous compressive locking intramedullary nailing for humeral fractures has the advantages of easy application, firm fixation, fast fracture union, early function recovery and so on.
Conclusion: Percutaneous compressive locking intramedullary nailing is a simple and reliable method for humeral fracture. It can be spread and widely used.
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
Introduction of instruments
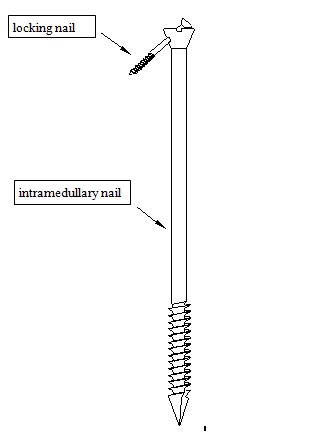
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of intramedullary nails.
MECHANICAL TEST
Mechanical test of percutaneous compressive locking intramedullary nail (bare nail test)
Compression test: Screw the threaded intramedullary nail into the special loading base to have the compression test. The compressive modulus was 5213mN/mm2 with strength greater than 339N/mm. The compressive modulus was 5213mN/mm2 with strength greater than 339N/mm.
Bending test: Place the intramedullary nail horizontally in the testing machine so as that spacing between two bending points is 80mm. Force was loaded in the middle of the nail. The bending strength was 1631N/mm2; and the modulus of elasticity was 119287N/mm2.
Bending test of locking nail: spacing between two bending points was 20mm. Bending strength of the nail body was 1203N/mm2; and flexible modulus was 61886N/mm2.
Damage test of locked structure: Intramedullary nail was locked with locking nail. Force was 83.6N pre-load, then continued to 495N until the pressure load begun to decrease and the body of locking nail begun to bend. The body of locking nail broke when 2627N was loaded. Proximal locking notch of intramedullary nail showed no significant change when nail body was broken. All mechanical tests showed that mechanical properties of various components of SPCLIN can meet the need of fixation.
Comparing the installation time between SPCLIN and traditional intramedullary nail
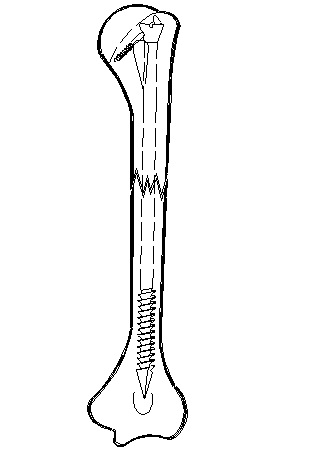
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of fixation.
Method two of internal fixation: A 5mm diameter hole is made same as above. Humerus marrow cavity is then expanded to 7.5mm with depth meeting the need of intramedullary nail installation. Put the 7mm G-K intramedullary nail on the remote target locator. Then put the nail into the expanded bone marrow cavity to reduce the fracture sites. With the help of remote target locator, drill the distal nail hole and nail the locking nail. Install the proximal nail target locator. With the help of proximal target locator, drill the proximal locking hole. Reduce accurately the fracture; and screw firmly the proximal locking nail. Remove the target locator.
The results showed that installation time for SPCLIN is about 3 minutes and installation time for traditional nails is about 7 minutes. About 43% of installation time is saved by using SPCLIN (Table 1).
| Group | Installation time of internal fixation | Total | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Experimental group (SPCLIN) | 3’24” | 2’09” | 2’43” | 2’48” | 3’31” | 2’56 ” | 2’55 ” ± 0’30” * |
| Control group (traditional intramedullary nail) | 6’41” | 6’51” | 10’40” | 7’49” | 7’02” | 6’48” | 7’39 ” ± 1’32” |
| Time difference | 3’17” | 4’42” | 7’57” | 5’01” | 3’31” | 3’52” | 4’33 ” ± 1’43” * |
Comparison of mechanical properties of fixation between SPCLIN and traditional intramedullary nail
Compression test: Loading speed was 5mm/min. Test results are shown in figure 1. The results showed that: (1) when compressive displacement is between 0.5 and 3.5mm, SPCLIN-fixed group has higher compressive load than control group; (2) when compressive displacement is between 4 and 4.5mm, control group has higher compressive load than SPCLIN-fixed group; and (3) only when compressive displacement is at 0.5 and 1mm, difference of compressive load is significant (P<0.05).
Bending test: Three points bending test was conducted. Span was 180mm. Loading speed was 5mm/min. Data is shown in figure 2. The results show that the average bending moment of SPCLIN-fixed group is not less than control group for each displacement. However, the difference between two groups for each displacement is not significant. This indicates that anti-bending property between two groups has no significant difference.
Torsional test: After the intramedullary nail is fixed, same square blocks were cast at the ends of humerus specimens with denture powder. Testing machine then clasped at the square blocks. Clockwise torsion was loaded with speed of 5°/min (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Different types of intramedullary nails.
Test results showed that: (1) between 0.25° and 1.50° twist angle, SPCLIN has greater torque than control group; (2) between 2.0° and 5.00° twist angle, control group has greater torque than SPCLIN group. The difference is significant only at 0.25° and 0.50° (P<0.05).
From above data, we can easily see that SPCLIN and traditional nails have no significant difference in fixation results and performance, and can both meet the need of fracture fixation.
CLINICAL OBSERVATION
General information
Treatment procedure
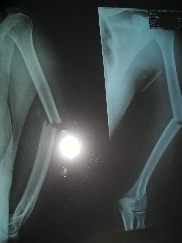
Figure 4: Humeral fractures.
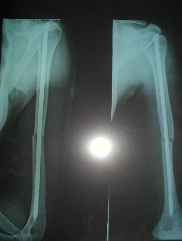
Figure 5: Fixed humeral fractures.
Results of treatment
DISCUSSION
Selection of intramedullary nail
Principles of fixation: SPCLIN has four principles
Intensity of fixation
Fracture healing
Advantages of SPCLIN
Cautions
REFERENCES
- Williams GR, Ramsey ML, Wiesel SW (2010) Operative Techniques in Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA.
- Brumback RJ, Bosse MJ, Poka A, Burgess AR (1986) Intramedullary stabilization of humeral shaft fractures in patients with multiple trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68: 960-970.
- Müller ME, Allgöwer M, Schneider R, Willenegger H (1979) Manual of Internal Fixation, Springer verlag, New York, USA.
- Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, Friedman RJ, Gartsman GM, et al. (1994) A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 3: 347-352.
- Dehong P, Zheng ancestral roots (2000) Anatomical measurement of the humerus bone marrow cavity and the correlation between the humeral interlocking intramedullary nail design. The Orthopedic Journal of China 7: 862-865.
- Wang Qihua, Sun Bo (1996) Clinical anatomy books. People’s Health Publishing House, Beijing, China.
- Wang Jin, Wang Jielin (1988) Orthopedic biomechanics, 1st edition, People’s Health Publishing House, Beijing, China 163.
- Chen Cai-Ping, Feng Ectocarpus, Yang Dexing (2002) Clinical Efficacy of humeral shaft fracture fixation methods three. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 17: 296-297.
- Gu Long Hall, Jia-wen, Wu Lianghao (2002) Intramedullary nail and plate fixation of long bone fracture analysis. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 17: 283-285.
- Luo is, QIU Gui-xing (1997) Intramedullary nail fixation. People’s Health Publishing House, Beijing, China.
Citation: Zuojun Z (2015) Development and Clinical Application of Percutaneous Compressive Locking Intramedullary Nail for Humerus. J Orthop Res Physiother 1: 009.
Copyright: © 2015 Zhang Zuojun, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

