
Huaier Inhibits Cancer Progression and Induces Tissue Regeneration by Transcriptional Regulations of Pluripotency of Stem Cells
*Corresponding Author(s):
Manami TanakaBradeion Institute Of Medical Sciences, Co. Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan
Tel:+81 463580952,
Email:tubu0125@gmail.com
Abstract
Significant impact of Huaier treatment is tissue regeneration observed simultaneously with cancer cell death and active elimination of those damaged cell debris. Here we present Huaier effects on prevention of cancer progression in the patients with high risks, and simultaneous tissue regeneration after the dissection of damaged lesions by transcription regulation of pluripotency in induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) /Embryonic Stem (ES) cells. The patients were suspected as hepatocellular carcinoma by image analysis of multiple low-density cysts in liver, also identified in pancreas or kidney which appeared within a short range of time, with symptoms of skin problems, multiple polyps in colon, with symptoms such as severe fatigue and body weight loss. Within 3 months of Huaier treatment, MEGA-DATA analysis of total transcriptomes and non-coding RNAs revealed the rescue of dysfunction in multiple signaling pathways in those patients, including Notch, NFkB and Wnt signaling pathway with regulatory transcription factors in those pathways. These rescued control systems influenced to, the regulation of stem cell transformation which regulates the proliferation and differentiation of newly-borne cells. The induced normal tissue regeneration was the results of transcriptional control of iPS/ES cell production. Among the gene families to control iPS/ES production, especially c-my expression level played a major role among the other genes or gene families. These results provide a clue to clarify the Huaier effects not only for recovery from cancer, but also for the prevention of many related diseases and disorders caused by daily accumulation of environmental stresses and ageing by controlling normal tissue regeneration by stem cell control.
Keywords
Huaier (Trametes robiniophila murr); Tissue regeneration; Transcriptional regulation on pluripotency of iPS/ES cells; c-myc; Wnt; Notch; Hippo signaling pathways
Introduction
We have to cope with various aspects and symptoms when we initiate the treatment of cancer; 1) to promote cancer specific cell death inside the pathogenic lesion; 2) to discard the resulting, damaged cell debris; 3) to repair damaged and/or dissected tissues with normal cells; 4) to prevent the relapse and recurrence together with adjacent and distinct metastasis. It is obvious that surgical dissection of tumor mass is the first choice [1,2], if applicable, however, it is just the beginning to overcome the disease like cancer.
Our genome scope project proved that many “normal” individuals were not normal from a point of view of molecular and biophysiological functions [3-6]. Many normal persons showed drastic genomic and genetic alterations for the rescue of the latent, invisible disruptions of multiple signaling pathways after Huaier administration. Even with no symptoms, there was an enormous daily risk of cancer caused by accumulation of environmental stresses and ageing process. Early diagnostic technology has some limitations for correct and precise evaluation of the risk [7,8] and excessive, frequent medical examinations using endoscopy and radiographic measures in contrast increase risks for carcinogenesis [9].
Huaier was reported to show significant efficacy on the specific cancer cell death, even on the occult metastasis remained after surgical operation [3-6,10-12]. In the present study, we specifically focused on the successful prevention of cancer progression by Huaier in those latent, stress-accumulated individuals. Those patients had Huaier administration beforehand of diagnosis of cancer, and successfully inhibited the cancer progression. In addition, the tissue repair was detected clearly by CT image analysis. The massive loss of tissues (> 2 cm in diameter each) suddenly appeared in multiple organs were regenerated according to the time course of Huaier administration. The swift recovery and tissue repair changes were also observed in the dissected lesions of skin (basal cell carcinoma), and in the area of dissected benign adenoma (polyps) in colon.
Here we report the further analysis of Huaier efficacy on the prevention of cancer progression and on the tissue regeneration with normal differentiated cells. We have already reported the significant impact of Huaier on the transcriptional control mediated by microRNA and small non-coding RNAs, and the potential for tissue regeneration by the rescue of Hippo signaling pathway [13,14]. In the present study, we provide further insights into the none the less essential effects of Huaier for promoting cancer recovery by utilizing stem cell production and normal differentiation.
The patients introduced in the present study were all high-responders to Huaier treatment, with a massive genomic potential [3]. One of the patients showed the changes of expression at most 85% of total transcriptomes. The efficacy of cancer treatment is measured, or dependent on the controlling ability of stem cells to recover the function of damaged tissues. For the repair function, there should be enough cells to regenerate, including the potential of cancer stem cells for normal differentiation. We have already indicated the potential of Huaier to determine the cell fate to normal differentiation by the rescue of Hippo signaling pathway functions [13] and here we present more detailed information related to tissue regeneration in the process of Huaier treatment.
KEGG pathway characterization [15] demonstrated Huaier effects on regulation system of pluripotent cell production with detailed transcription control on related genes. It is the first in vivo data in humans, especially with the successful results to control the diseases and disorders. The Huaier effects on tissue regeneration was observed only at the time of requirement, such as after the dissection of benign adenomas, and remained silent after the recovery of healthy condition. The opportunistic infection drastically increased the quantitative changes, and strong corticosteroid therapy ceased down total molecular changes in every function. There have been reported many genes and gene families related to the process [16-19] and the present study identified that c-myc regulation influenced chiefly for this purpose.
Thus, we identified definitive efficacy of Huaier on the tissue regeneration and its molecular mechanisms. Even before the diagnosis of cancer, Huaier has its potential to minimize the damage causing disruption in many kinds of biological functions, and plays a key role to maintain homeostasis for a long-range of life.
Materials And Methods
Project Design and patients’ characterization
The present study specifically focussed on Huaier effects to the patient with high risk of cancer, but without any cancer lesions defined yet (Table 1). They were suspected to have cancer progression chiefly in liver, and additional lesion in pancreas, kidney, and colon by CT image analysis and positive results in Bradeion blood test [7,8]. Patient No.4 was the control with colorectal adenoma without Huaier treatment [3].
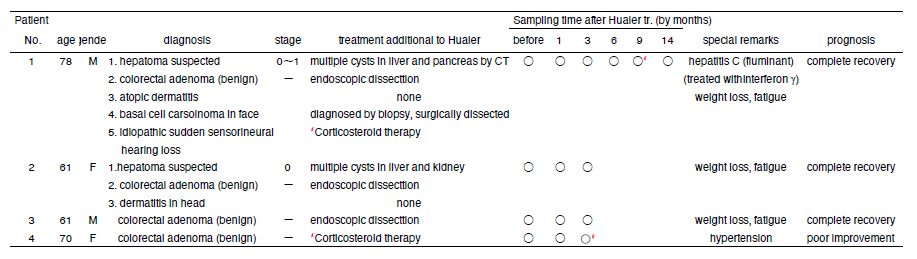
Table 1: Clinical features of the cancer patients appeared in the present study. The asterisk (*) indicates the time just after the surgical dissection of basal cell carcinoma, followed by the cortisone treatment for idiopathic dysacousis.
Huaier compounds were provided by the manufacturer for this purpose with a strict control on transfer to Japan, good condition for maintenance, and provision to the patient volunteers, just as the same as the previous reports [3-6,13].
The present study was strictly conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and the principles of good clinical practice. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients. This clinical research was applied according to the Consolidated Standards of Clinical Research Trials guidelines and was applied to the Japanese Medical Association on 9th February 2018 and approved on 5th March, 2018 (ID: JMA-IIA00335).The project has been strictly conducted with a monthly review by the ethics committee consisted by the experts on Medicine, Nursing, Laws, Pharmaceutics, and Business Community (first committee held on 9th February, 2018).
We used Huaier compounds as complementary therapy, without any chemotherapy and radiotherapy which disrupt the molecular systems. Only surgical operation was allowed if applicable, even in the period of during Huaier therapy. We thus planned and initiated an open-style, before-after controlled study, using peripheral blood as sampling materials to understand the almost all molecular events in each Huaier taking patient. The sampling materials were total blood, the same as reported previously [3-6]. To compare with the other sampling, RNA extraction using nuclear cell components in peripheral blood rapidly reflects the biophysiological changes, and that more sensitive to monitor the course of any treatment than any other samples such as dissected organs.
RNA extraction, miRNA library construction and mRNA Library Construction
RNA extraction, miRNA library construction, and Total RNA- and small non-coding RNA-sequencingon the MGISEQ-2000 and BGISEQ-500 platformwere processed in BGI, Shenzhen, China, as descrived previously [3-6]. The subseuent bioinformatics work was also processed in BGI, Shenzhen, China. The detailed protocols were provided and demonstrated at BGI website: http://www.bgitechsolutions.com/.
The identified DEGs (differentially expressed genes) and DESs (differentially expressed small RNAs) were analyzed between samples and do clustering analysis and functional annotations.
With quantitative analysis of DEGs, we performed Gene Ontology (GO) classification by three categories of molecular biological function, cellular component and biological process, with a consideration of time course of Huaier administration. We also analyzed every signal transduction pathway by KEGG pathway classification [15] (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/). Furthermore, we applied the enrichment analysis of DEG in KEGG database. The obtained novel transcripts and small nuclear non-coding RNA have been deposited to the NCBI GEO (GSE157086).
Results
Clinical features of the patients
As shown in table 1, samples from 4 patients were designated to MEGA-DATA analysis [3-6,20,21] in the present study. Although cliniical features were different among individuals, they shared common symptoms and disorders, such as (aropic) dermatits, liver dysfunction, severe fatigue, and body weight loss [3]. The CT examinations in walk-in clinics revealed multiple cycts suddenly appeared in liver, pancreas, and kidney, not found in within 3 to 6 months. In addition, the results of Bradeion blood tests [7,8] were all positive, which indicated excessive stress accumulation and the production of > 1 million cancer cells in colon.
Just after the evaluation of high-risk of cancer in patients No.1 to 3, they chose to have Huaier, 20g per day, beforehand of diagnosis by further examinations. Especially the Patient No, 1 had a past history of fluminant Hepatitis C by blood transfusion for more than 20 years ago, and recovered by the injection of Interferon gannma. He took frequent health check ince then by blood test, CT and MRI, andno significant disorders and diseases so far until the observation of sudden multiple cysts over 2 cm diameter in the liver and pancreas. He had heaavy duty task dailly, and was unable to reduce the overwork, so chose Huaier treatment at once after seeing his own CT data. The past experience of significant improvement of his mother from hepatocellular carcinoma influenced largely to his decision.
The successful inhibition of carcinogenesis in liver and pancreas were confirmed at 6 months after Huaier administration with no cysts detected by CT image analysis, but opportunistic papilloma virus infection and basal cell carcinoma detected in face (surgically dissected, 9 months after Huaier administraion). After swift recovery from those disorders, be becane idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss, and treated with srong corticosteroid theralpy (12 months after). All these diseases and disorders seemed to be derived from continuous stress accumulation and ageing process, and it lasted at the end of 2019 by the pandemic outbreak of COVID-19.
The patient No. 2 showed the similar observation of multiple cysts in the liver and kidney by CT analysis, and symptoms of dermatitis in the head, heavey fatigue with body weight loss. She also had a heavy duty work on teaching in the two Universities. Similar symptoms were observed in the patient No. 3, but without any cysts detected by CT.
The patient No.4, control patient without Huaier administration, diagnosed as benign adenoma in Colon (multiple)by endoscopic examination, based on the positive results from Bradeion blood test. She did not have any additional treatment to the endoscopic dissection of multiple polyps later. One month after the first blood sampling, she had a stroke with hupertention, hospitalized, and also had strongcorticosteroid therapy similar to the patient No.1 .
MEGA-DATA analysis of molecular characterization of the patients with successful inhibition of cancer progression
Figure 1 (patient NO. 1) and 2 (patient No. 2 to 4) summarized the Genome-scope view of anti-cancer effects of Huaier by expressed genes DEGs), transcription factor-DEG network, miRNA- and piRNA-mediated transcriptional control with similar techniques introduced previously [3-6]. The upper column in figure 1 Panels A and B, the Transcription Factor (TF)-Differentially Expressed Genes (DEG) networkchanges well demonstrated the successful recovery and inhibition of carcinogenesis within 6 months in the patient No. 1. The existence of atypical, or cancer cells were suggested by KEGG ontology analysis [15] on DEGs classified by biological functions shown in the lower column of each panel. The quantitative analysis indicated the possibility of lung cancer and pancreatic cancer in the lower column in figure 1 Panel A (highlighted by red box). After 6 months’ Huaier treatment, all these risks disappeared, and also significant decrease of stress accumulation was detected.
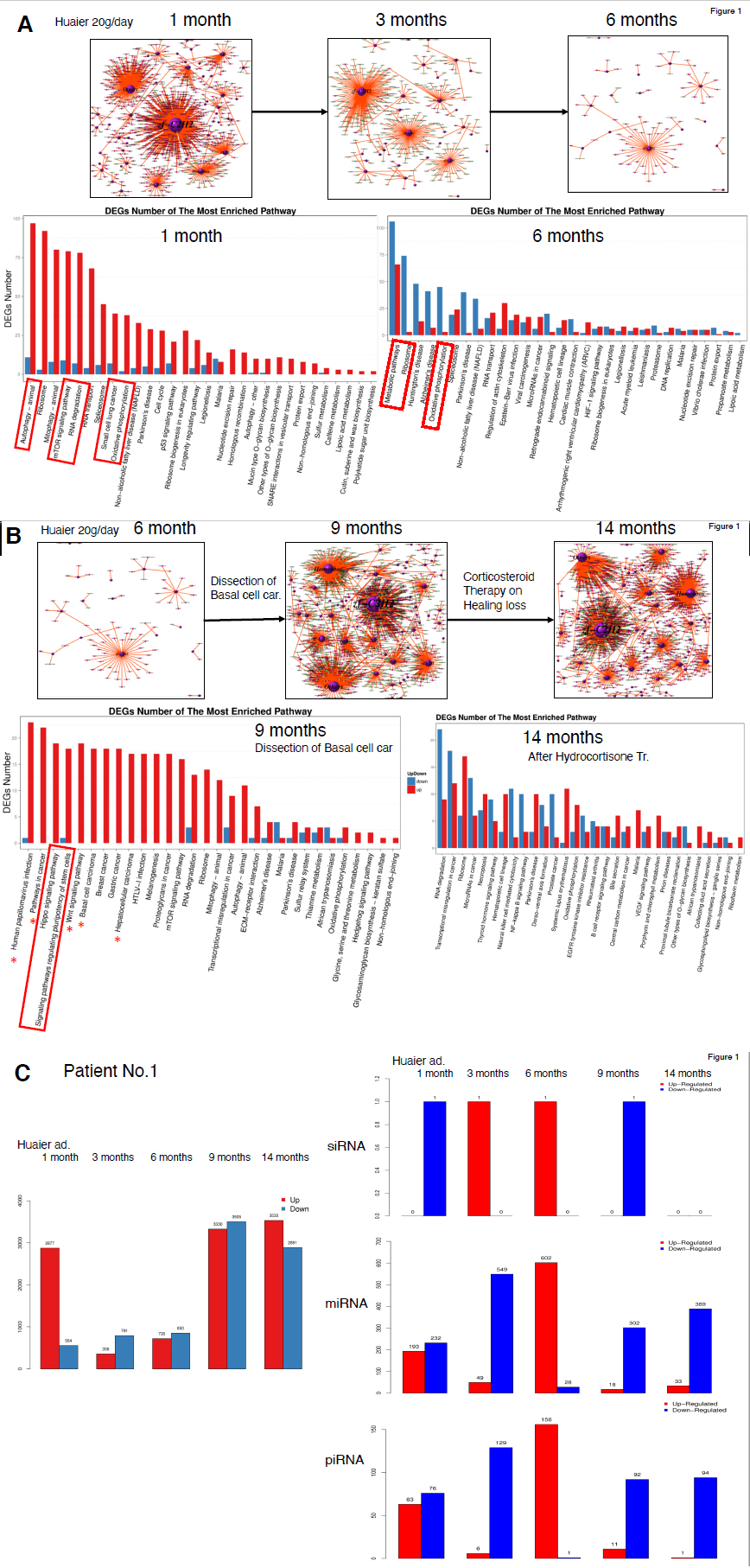
However, 3 months later, the drastic changes observed again, caused by opportunistic papilloma viris infection and basal cell carcinoma in face. The rescue of functions were prominant in Hippo signaling pathway and Wnt signaling pathway [3,13,14] and the basal cell carcinoma was sucessfully dissected surgically.
Continuous stress accumulation in these period then caused idiopathic dysacousis and treated with strong steroid therapy with hydrocorisone injections at 14 months of Huaier trreatment (continued even during the hospitalized period). Massive steroid injections resulted in down-regulation of wide variety of expressed genes irrespectively to their functions, and caused RNA degeneration, disrupted transcription control. In figure 1 Panel C, the changes and alterations of DEGs thgoughout the observation period were shown with the changes of small nuclear RNAs (si RNA, miRNA and piRNAs). The synergical transcriptional control mediated by miRNA and piRNA regulations were totally changed into massive down-regulations of miRNA and piRNAs after 9 months.
The patient No. 1 is a high-responder to Huaier, with a large genomic potential of flexbility and capability, to rescue any phases of the risk to health conditions. The disturbance, risk of the carcinogenesis coontinued until his envioromental stresses, overwork situation ceased by pandemic situation of COVID-19. During those 14 months, it is surprizing that Huaier could inhibit the risk of any active carcinogenesis in the liver, pancreas, and lung (except basal cell carcinoma, well-differenciated type). The multiple polyps (benign adenoma) in colon were dissected by colorectal endoscope.
Considering radical therapy mentioned above, the more attention should be paied to therepair system for rapid recovery. The swift recovery from steroid therapy, surgical dissection of skin, and the endoscopic dissection, requires activation of tissue repair, regeneration system. On the other hand, the regulation of pluripotency of any kind of stem cells are also required to stop the possible process of carvinogenesis.
Figure 2 demonstrated the same genome scope view using TF-DEG network, Kegg ontocology panel (Panels A and B), and up-/down-regualation of transctipromes with comparison to those of small non-coding RNAs (Panel C). As compared with figure 1 (patient No. 1), those three patients were also high-responders to Huaier (Panel C) and the miRNA- and piRNA-mediated tra¥nscriptional control well synchronized with the regulation of DEGs in the patient No.2 and 3. In these patients, Huaier effects on tissue regeneration was more prominennt than the inhibition of carcinogenesis, since apparent cancer risk was not deteced by KEGG ontocology analysis shown in the lower column of figure 2 Panels A and B. The level of uantitative up-regulation changes in miRNA and piRNAs at 3 months after Huaier administration were about the same as detected in the patinet No.1, and the clinical features were also similar, too, but the risk of carcinogenesis was speculated much less in these patients No. 2 and 3.
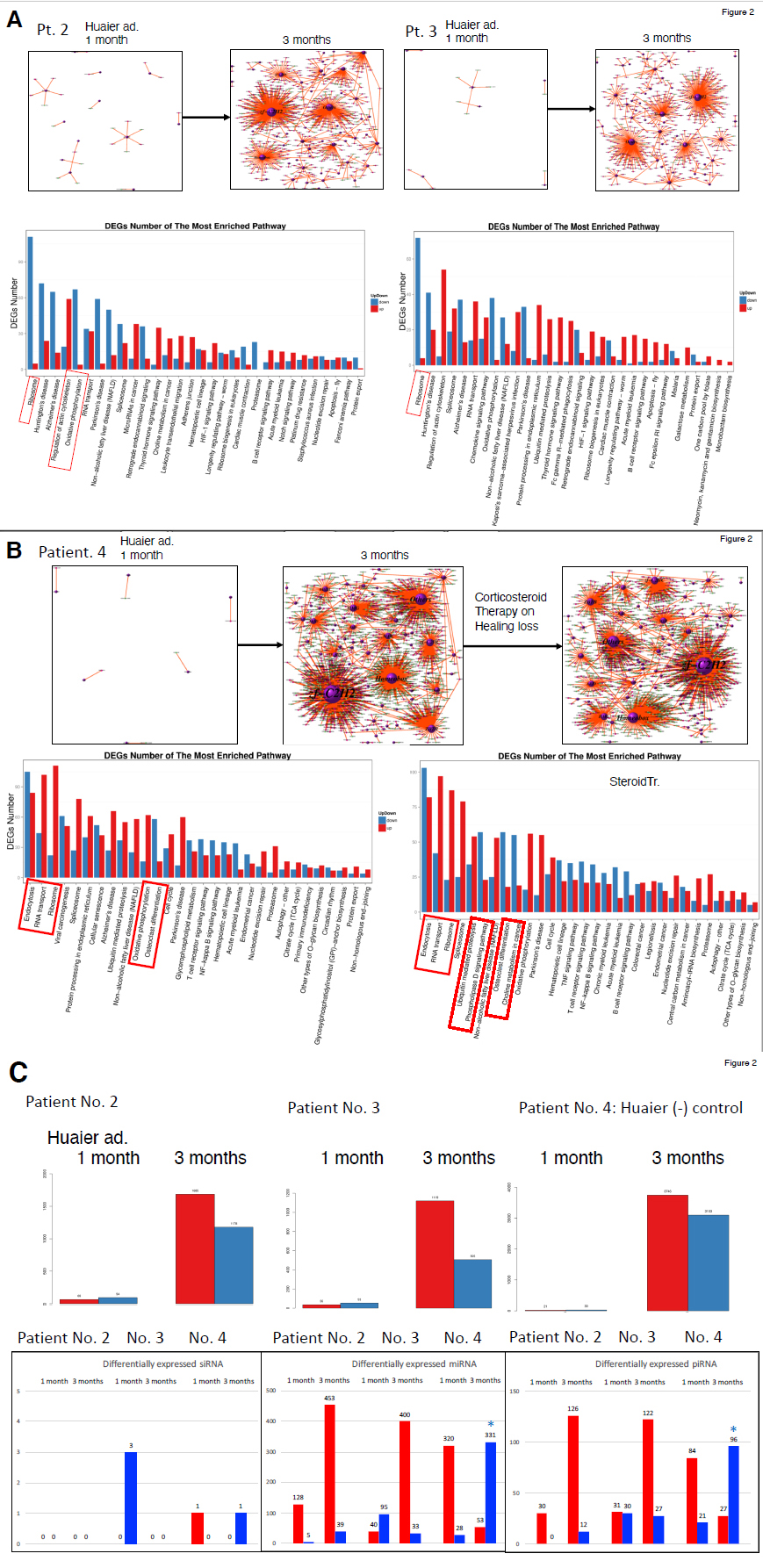
In contrast, the patient No.4, without Huaier administration, showed significant increase in down-regulation of miRNA and piRNAs, after strong corticosteroid therapy (details unknown). These massive down regulation was similarly observed in the patient No.1 after 14 months’ Huaier administration. Evenafter the dissection of multiple polyps (2 cm in diameter at largest), the symptoms continued and more polyps were detected one year later by colorectal endoscopic examination, together with liver dysfunction by blood test.
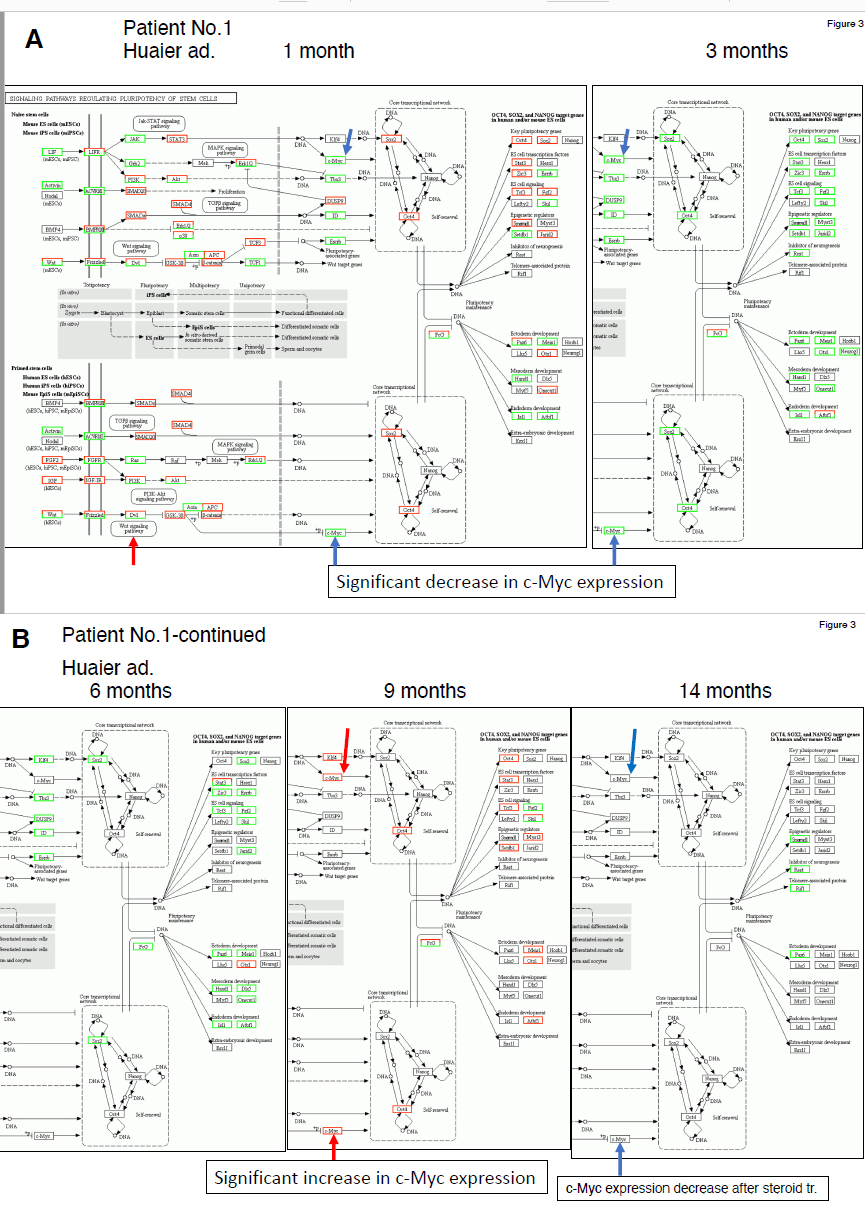
KEGG analysis on signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
Figure 3 (patient No.1) and 4 (patient 2 to 4) demonstrated detailed factors and molecule network on signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cellsaccording to the KEGG pathway map [15] (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/). Table 2 demonstrates detailed quantitative analysis on the expression level of the genes reported as responsible for iPS/ES cell production and functionnal lineages of the related factors. The numbers were caluculated by the comparison to those detected before Huaier administration. The serial changes of KIT, Myc, Oct3/4, Sox2, LIN28A and NANOG expression levels were clearly indicated [3,16-19]. Overall up-/down-regulation was highlighted, too. A significant increase in c-myc expression level was observed after successful Huaier treatment and endoscopic dissection of benign adenoma in the patient No. 1, 2 and 3, but no synchronied changes identified among these genes and gene families related to iPS/ES production. The the results obtained from in vitro experiments were not coinsident with those obtained in in vivo physiological conditions.
|
Patient No. |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
iPS-related gene name |
|
1 month |
3 months |
6 months |
9 months |
14 months |
|
|
1 month |
3 months |
|
|
1 month |
3 months |
|
|
1 month |
3 months |
|
KIT |
|
* |
* |
* |
Up |
Up |
|
|
* |
Up |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
MYC |
|
* |
Down |
* |
Down |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
* |
Up |
|
|
* |
Down |
|
OCT3/4 |
|
* |
* |
* |
Down |
* |
|
|
* |
Up |
|
|
* |
Up |
|
|
* |
Down |
|
SOX2 |
|
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
LIN28A |
|
* |
* |
* |
Down |
Down |
|
|
* |
Down |
|
|
* |
Down |
|
|
* |
* |
|
NANOG |
|
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
* |
* |
|
*no changes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
calculated copy numbers |
before Huaier treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
before Huaier treatment |
|
|
|
before Huaier treatment |
|
|
|
before Huaier treatment |
|
|
|
KIT |
0.26 |
0.38 |
0.26 |
0.43 |
0.58 |
0.65 |
|
0.22 |
0.19 |
0.54 |
|
0.32 |
0.28 |
0.60 |
|
0.38 |
0.44 |
0.64 |
|
MYC |
21.79 |
20.99 |
10.62 |
19.60 |
2.68 |
25.60 |
|
12.52 |
9.78 |
18.37 |
|
7.39 |
8.78 |
17.35 |
|
17.46 |
20.76 |
2.54 |
|
OCT3/4 |
3.71 |
3.65 |
3.14 |
4.99 |
1.45 |
3.40 |
|
2.43 |
3.00 |
6.19 |
|
1.56 |
1.68 |
4.23 |
|
4.95 |
5.77 |
2.31 |
|
SOX2 |
0.02 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.02 |
0.01 |
0.02 |
|
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
- |
- |
|
0.02 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
|
LIN28A |
2.19 |
1.36 |
1.92 |
1.32 |
0.43 |
1.15 |
|
1.31 |
1.46 |
0.60 |
|
1.70 |
1.58 |
0.85 |
|
1.44 |
1.25 |
0.73 |
|
NANOG |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.08 |
0.04 |
0.03 |
|
0.13 |
0.13 |
0.07 |
|
0.11 |
0.03 |
0.02 |
|
0.08 |
0.10 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2: The comparison of DEGs related to the production of iPS cells (KIT, Myc, OCT3/4, SOX2, LIN28A and NANOG).
In order to understand the close links of the related molecules with their expression chanes, the KEGG panel demonstrated representative molecules regulating signaling pathways on regulation of pluripotency of stem cells, including iPS/ES production and maintenance (Figures 3 and 4). It also contains the further inforation on the related multiple signaling pathways such as Kas-STAT, MAPK, TGFb and Wnt signaling pathways [3-6]. As for Hippo signaling pathways [13,14], we described in the previous reports. The results obtained were shown sequencially according to the time course of Huaier administration.
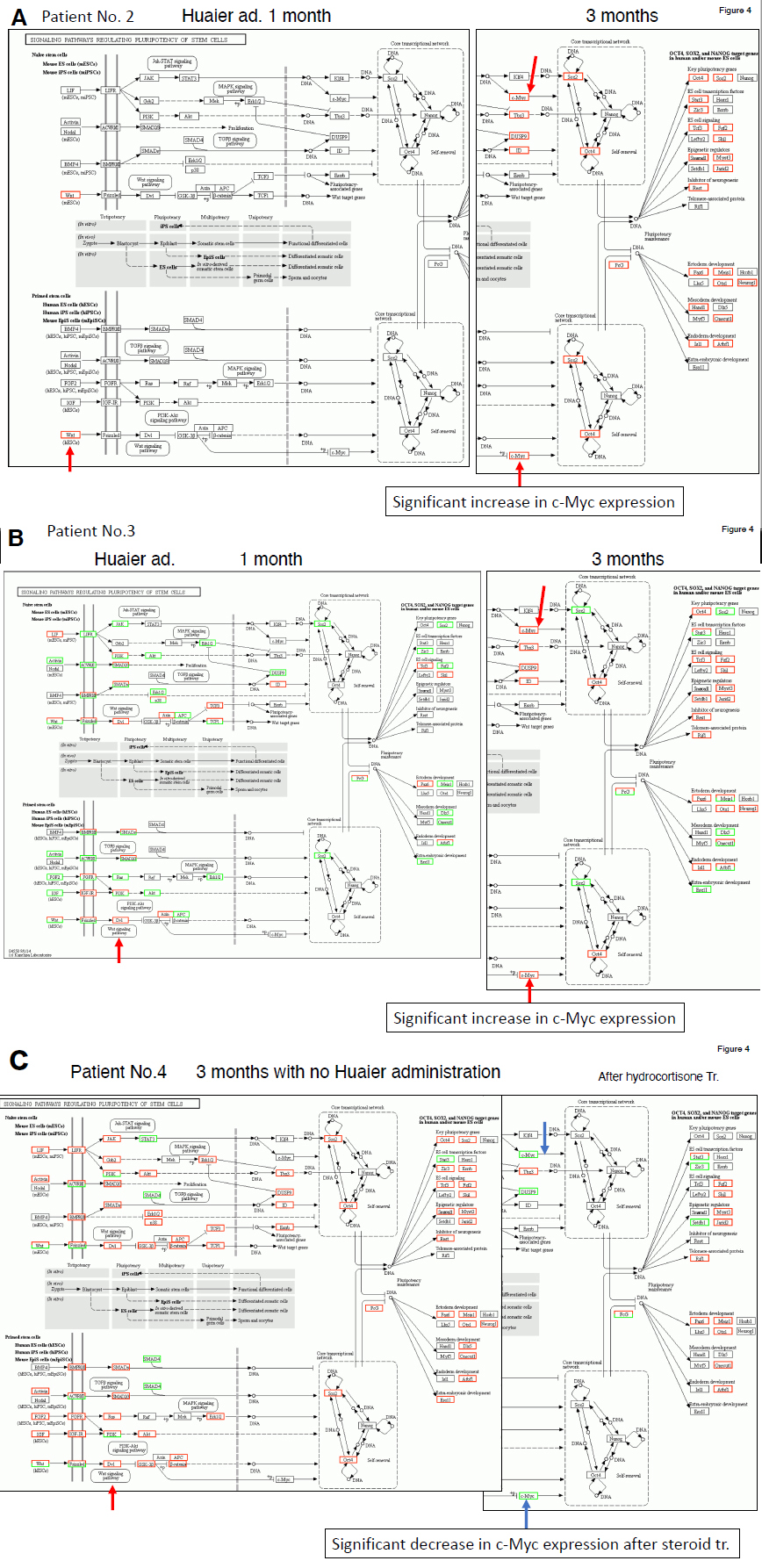
As shown in figure 3 Panels A and B and Figure 4 Panel A, Huaier administration influenced stem cell production or inhibition chiefly by c-myc expression regulation among all the genes and gene families reported. In the patient No.1, the enhancement of iPS production observed one month after Huaier administration was strongly down-regulated at 3 months after Huaier treatment (Figure 3 panel A), until 6 months after treatment. These down-regulations were correlated with the down-regulation of c-myc. The opportunistic infection up-regulated drastically c-myc and Oct4 expression level, but decreased to normal level at 14 months after treatment. Effective down-regulation of iPS/ES cells were typical observation in the patient No.1.
In contrast, typical up-regulation of c-myc and Oct 4 expression levels were detected in the patient No. 2 and 3 (Figure 4 Panels A and B), 2 months after endoscopic dissection of multiple polyps (benign adenoma) in colon. Together with these observations, it is emphasized that Wnt signaling pathways were up-regulated in the patient 1, 2 and 3. The details on the rescue and activation of rescued Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways in those patients were as described previously, and the results were confirmed in the present study.
In the patient No. 4, massive up-regulation was observed after endoscopic examination of colon (not dessected polyps yet). Up-regulation of the molecules were detected in almost all the molecules involved in Jak-STAT, MAPK, TGFb and Wnt signaling pathways, with iPS/ES production, except c-myc (Figure 4 Panel C). After steroid treatment just the same as injected in the patient No.1 after 14 months of Huaier treatment, c-myc down regulation resulted in the end of iPS production, however, ES cell production and maintenance still remained. The steroid therapy was the same in both patients, however, the influence to down-regulation of stem cell production was very much in different forms with (the patient No.1, Figure 3 Panel B) and without (the patient No. 4, Figure 4 Panel C).
Discussion
Regenerative medicine generally means “process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function” [22]. The term “regenerative medicine” was first used in a 1992, with a clear declaration, “A new branch of medicine will develop that attempts to change the course of chronic disease and in many instances will regenerate tired and failing organ systems” [23]. Among numerous attempts, some of the biomedical approaches within the field of regenerative medicine may involve the use of stem cells, and the generation of induced pluripotent cells became most popular strategy since 2006 [16]. However, this method was proved crucially dependent on the transcription factor regulation used for the induction [24], which is highly toxic and unstable even in the experiments using in vitro cultured cells.
The present study demonstrated that Huaier treatment initiated spontaneous c-myc regulation by transcriptional control, which contributed to inhibit cancer progression as well as to regenerate damaged tissues from the disease and also radical medical treatment such as surgical operations. There have been reported that, together with myc family, transcription factors and proto-ontogenesis implicated in cancer, Oct-3/4 and certain products of the SOX gene family(Sox1, Sox2, Sox3, and Sox15) have been identified as crucial transcriptional regulators involved in the induction process whose absence makes induction impossible [17-19]. By the MEGA-DATA analysis performed throughout our genome scope project, those genes and gene families were not detected to play major roles for tissue regeneration in vivo [3-6].
Pluripotent stem cells hold promise in the field of regenerative medicine [16-19,24]. The generation of induced Pluripotent cells is crucially dependent on the transcription factors used for the induction [24].
The results shown in figures 3 and 4 confirmed that the induction was controlled by multiple signaling pathways such as Wnt and TGFb signaling pathways reported previously [3]. The Notch signaling pathway has been reported to play an important role on controlling stem cell proliferation for several cell types including hematopoietic, neural and mammary stem cells [25]. A branch of the Notch signaling pathway that involves the transcription factor. Huaier effects on the rescue and regulation of those signaling pathways contributed largely for iPS/ES production for tissue regeneration. It is emphasized that the first findings of Huaier effects in our project is the rescue of Hippo signaling pathway to determine the cell fate [13,14], with rewinding the time of the cell to stem cell level.
As for normal differentiation and maintenance of pluripotent stem cells, the reprogramming process is as much important. This is particularly challenging because the genome-wide epigenetic must be reformatted to that of the target cell type in order to fully reprogram a cell. In 2008, Ding et al., used the inhibition of Histone Methyl Transferees (HMT) with BIX-01294 in combination with the activation of calcium channels in the plasma membrane in order to increase reprogramming efficiency [18]. We have not yet further analyzed epigenetic effects of Huaier in cancer patients, and these investigations will follow [6].
Measuring variations in microRNA expression in iPS cells can be used to predict their differentiation potential [26,27]. ES cell-specific microRNA molecules (such as miR-291, miR-294 and miR-295) have been reported to enhance the efficiency of induced pluripotency by acting downstream of c-Myc [26], but we could not observe these specific changes in the patients. In contrast, quantitative up-regulation of microRNAs were detected as describer previously [3-6,27], including numerous novel sequences (deposited to The NCBI GEO : GSE157086) irrespectively to any of specified known sequences.
Conclusion
Thus, Huaier treatment provides significant potential for tissue regeneration by c-myc up-regulation together with the rescue and activation of Wnt signaling pathway and also Wnt and Hippo signaling pathway. Anti-cancer effects of Huaier seemed to be observed in order of; first to inhibit cancer progression, and tissue regeneration followed. Although the previous reports described the correlation with specific polymorphisms in SNP and INDELs and microRNAs such as miR-291, miR-294 and miR-295, these alterations were not identified in our MEGA-DATA analysis. In contrast, massive and quantitative alterations were observed in genome-wide sequences and almost all the microRNAs including novel sequences as previously reported. C-myc up-regulation seemed more closely related to iPS/ES production.
Thus, we present here another efficacy of Huaier relating to the tissue regeneration and provide a clue to the reality of stem cell control in vivo.
In addition, the results presented in the present study indicate that, behind “normal healthy condition”, there are many latent and invasive disruptions to be rescued, and MEGA-DATA analysis should be hired as routine health check options more widely. Huaier treatment seemed to have significant effects on the requirement of the rescue of disrupted functions even when the changes are latent, which prevents the cancer progression and the onset of the other severe diseases.
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank cancer patient volunteers and many healthy volunteers kindly collaborated with the present study. The present study was grant-in-aid from QiDong Gaitianli Medicines Co., Ltd. And Japan Kampo New Medicine, Co. Ltd.
Author’s Contribution
TT, MT designed the study from the clinical observation of the cancer patients with Huaier treatment (as a complementally therapy) and managed the sampling and clinical assessment of the patient volunteers, statistically analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. FT, HL, managed total RNA and small nuclear RNA sequencing and conducted systematic analysis of the data. NL, ZL, managed blood sample handling and transfer from Kobe to Shenzhen, and quality control of RNA samples for further analysis. ZL, DW, contributed to the provision of Huaier granules and clinical evaluation of the data, especially focused on Immunological evaluation.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
References
- Mecedo FI, Ryon E, Maithel SK, Lee RM, Kooby DA, et al. (2019) Survival outcomes associated with clinical and pathological response following neoadjuycant FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine/Nac-paclitaxel chemotherapy in resected pancreatic cancer. Annals Sur 270: 400-413.
- Barnes CA, Chavez MI, Tsai S, Aldakkak M, George B, et al. (2019) Survival of patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer who received neoadjucant therapy and surgery. Surgery 166: 277-285.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Teng F, Lin H, Li N, et al. (2020) Huaier Induces Cancer Recovery by Rescuing Impaired Function of Transcription Control Based on the Individual Genomic Potential. Arch Clin Biomed Res 4: 817-855.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Teng F, Lin H, Li N, et al. (2021) Anti-cancer effects of Huaier on prostate cancer; miRNA-mediated transcription control induced both inhibition of active progression and prevention of relapse. J Altern Compl Integr Med 7: 146.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Teng F, Lin H, Li N, et al. (2021) Complete remission ofthe severe advanced stage cancer by miRNA-mediated transcriptional control of Bcl-xL with Huaier therapy compared to the conventional chemotherapy with platinum (II) complex. Arch Clin Biomed Res 5: 230-261.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Teng F, Lin H, Li N, et al. (2021) Huaier inhibits cancer progression correlated with the mutated EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases (c-MET/erbB-2) by down-regulation of multiple signal transduction pathways. Arch Clin Biomed Res 5: 262-284.
- Tanaka T, Kawamura Y, Usui Y, Terachi T, Kimura F, et al. (2010) Bradeion Project: Monitoring and Targeting of Cancer: Molecular Marker Diagnosis of Cancer by Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS). The Open Conf Proc J 1: 129-137.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Kijima H, Itoh J, Matsuda T, et al. (2003) Rapid and quantitative detection of a mammalian septin Bradeion as a practical diagnostic method of colorectal and urologic cancers. Med Sci Monit 9: 61-68.
- Barlow WE, Beaber EF, Geller BM, Kamineni A, Zheng Y, et al. (2020) Evaluating screening participation, follow-up, and outcomes for breast, cervical, and colorectal canceer in the P`ROSPR consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 112: 238-246.
- Song X, Li Y, Zhang H, Yang Q (2015) The anticancer effect of Huaier (Review). Oncol Rep 34: 12-21.
- Wang X, Wang N, Cheung F, Lao L, Li C, et al. (2015) Chinese medicines for prevention and treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma: current progress on pharmacological actions and mechanisms. J Integr Med 13: 142-164.
- Chen Q, Shu C, Laurence AD, Chen Y, Peng BG, et al. (2018) Effect of Huaier granule on recurrence after curative resection of HCC: A multicentre, randomised clinical trial. Gut 67: 2006-2016.
- Tanaka T, Suzuki T, Nakamura J, Kawamura Y, Sadahiro S, et al. (2017) Huaier Regulates Cell Fate by the Rescue of Disrupted Transcription Control in the Hippo Signaling Pathway. Arch Clin Biomed Res 1: 179-199.
- Mo JS, Park JW, Guan KL (2014) The Hippo signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep 25: 642-665.
- Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, et al. (2008) KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 480-484.
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126: 663-676.
- Huangfu D, Maehr R, Guo W, Eijkelenboom A, Snitow M, et al. (2008) Induction of pluripotent stem cells by defined factors is greatly improved by small-molecule compounds. Nature Biotechnol 26: 795-797.
- Shi Y, Desponts C, Do JT, Hahm HS, Schöler HR, et al. (2008) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic fibroblasts by Oct4 and Klf4 with small-molecule compounds. Cell Stem Cell 3: 568-574.
- Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu C, Guan J, et al. (2013) Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds.Science 341: 651-654.
- Peng Z, Cheng Y, Tan BC, Kang L, Tian Z, et al. (2012) Comprehensive analysis of RNA-Seq data reveals extensive RNA editing in a human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol 30: 253-260.
- Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, et al. (2014) Identification of genomic alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature 509: 91-95.
- Mason C, Dunnill P (2008) A brief definition of regeneratice mediine. Regen Med 3: 1-5.
- Kaiser LR (1992) The future of multihospital systems. Topics in Health Care Financing 18: 32-45.
- Riazi A, Kwon SY, Stanford WL (2009) Stem cell sources for regenerative medicine. Methods in Mol Biol 482: 55-90.
- Dontu G, Jackson KW, McNicholas E, Kawamura MJ, Abdallah WM, et al. (2004) Role of Notch signaling in cell-fate determination of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Breast Cancer Res 6: 605-615.
- Bao X, Zhu X, Liao B, Benda C, Zhuang Q, et al. (2013) MicroRNAs in somatic cell reprogramming. Curr Opin in Cell Biol 25: 208-214.
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al. (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433: 769-773.
Citation: Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Teng F, Lin H, Li N, et al. (2021) Huaier Inhibits Cancer Progression and Induces Tissue Regeneration by Transcriptional Regulation of Pluripotency of Stem Cells. J Altern Complement Integr Med 7: 162.
Copyright: © 2021 Manami Tanaka, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

