
Training Master’s in Nursing Program of Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City
*Corresponding Author(s):
Hien NPMaster, Ministry Of Education And Training, Vietnam, Japan
Tel:+84 69566100,
Email:nphien@moet.edu.vn
Abstract
Objective: Find out nursing students were willing to be trained in the master’s in specialized nursing program of Nam Dinh University.
Method: a cross-sectional study with self-report on curriculum, need to be trained and some capacities on output standards of the master’s in nursing programs in Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh city during 2017-2018.
Results: The need to be trained in 4 groups of capacities was necessary and very necessary trained (95%). Some students suggested that added some capacities such as soft skills, professional English, IT, statistics, and presenting research data.
Conclusion: Four capacity groups with 30 skills should keep teaching in the master’s in nursing program. However, it is necessary to add more content to the program to help students applying the knowledge on writing the research thesis and improve the professional skills in the future.
Keywords
capacity; nursing; Vietnam
Introduction
In health care, the role of nurses is increasingly confirmed in the ministry's legal documents of The Ministry of Health and the Vietnamese Government on the and especially on missions, especially, the health workforce development [1]. On the large scope, nurses play an important role not only in the human resource of hospitals but also as indispensable manpower in the public health (as an instructor) as well as in training (as a lecturer or as an assistant lecturer) [2]. According to that practice, the roles of nurses will cover many issues relating to patients health and support Doctors in treatment processes.
To determine the functions, tasks of nurses, professional documents of the health sector have come from the point of view that nursing is an independent profession of medical science [3, 4]. From the point of view, in the scope of training, it is very necessary to have a team of specialized lecturers responsible for teaching nursing science, capable and qualified, mastering theory and practice skills profession in nursing. With the purpose of enhancing the training of health human resources, especially to improve nursing capacity, specifically masters of nursing, we conducted this study with the aim: “Explore some capacities in which nursing students were willing to be trained in the master’s in the nursing program of Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City during 2017-2018 and desire to be specialized training.” [3] Stated In-service training of nurses plays an indispensable role in improving the quality of inpatient care. Need to enhance the effectiveness of in-service training of nurses is an inevitable requirement. Then [5-7] mentioned that undertaking pain management aims to prevent negative physiological and psychological outcomes. Inadequate knowledge about pain and its characteristics is a common barrier to effective pain management. Evidence shows that if nurses have adequate knowledge and a positive attitude towards pain, it may lead to more effective pain management.
Research Methods
Research subject
All master's students in nursing of Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City in the academic year 2017-2018.
Research design
Descriptive cross-sectional study.
Research time and location
The study was conducted at Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City from 6/2017 - 6/2018.
Research tools and data collection methods
A self-report measurement was used to survey of curriculum, the need to be trained some capacities which were introduced on output standards of two universities. The questionnaire was designed according to the evaluation of four main skill groups that require master's degree nursing staff to meet the standards developed by the American Association of Colleges of Nursing in 2011 [5]. These standards are being applied by 2 universities to the master's degree program in nursing.
Capacity group of nursing professionals
This include 7 capacities that need training: (1) writing of care records for specific illnesses (including severe, rare cases), (2) Making nursing diagnosis independently in specific disease cases, (3) Care planning for specific illnesses (4) Making appropriate nursing care decisions, (5) Evaluating the results of care, (6) supervising nursing care activities in accordance with the functions and obligations of the unit, (7) supervising other nursing activities of the unit.
Management capacity group
This includes 9 capacities that need training: (1) Organizing activities to care for patients, patient’s families and communities, (2) Organizing and manage nursing activities of the unit, (3) Making plans and organize the implementation of patient care, guide family members and the community on how to care, (4) Organizing the implementation of safe and effective medicine use for patients, evaluate the effectiveness of medicine, (5) Organizing the implementation of care techniques to ensure proper procedures, comply with regulations on infection control and safety rules in the unit, (6) Coordinating with doctors and other health staffs to provide accurate and safe care solutions for patients, (7) Effective management and use of equipment in patient care, (8) Applying management skills to organize, coordinate, and assign care activities in the group, use resources reasonably and effectively, ensure the quality of care, (9) checking and supervising health care activities for patients and communities in accordance with the functions and tasks of the unit.
Training capacity group
This includes 5 capacities that need training: (1) Organizing training to improve qualifications and career development for colleagues, (2) Identifying and analyzing needs and health educational content that need guidance on individuals, their family and communities, (3) Developing and organizing the implementation of health education plans that are suitable to the culture, society and beliefs of individuals, families and communities, (4) Compiling and organizing to compile health education materials suitable to the students' level, (5) Implementing and organizing the implementation of appropriate and effective health education counseling and communication.
Methods of data analysis
Data were analyzed in SPSS 18.0 software.
Research Results
Current situation of some capacity groups being implemented in the training program
The current situation of students attending the master's degree nursing training program in 2017-2018 at Nam Dinh University of Nursing and Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy
|
Characteristics |
Male |
Female |
|
|
Gender |
36 (23,4%) |
118 (76,6%) |
|
|
Age |
31 ± 5,72 Max: 44 - Min: 25 |
28 ± 4,62 Max: 40 - Min: 25 |
|
|
Years of experience |
7,9 ± 2,342 Max: 17 - Min: 2 |
7,6 ± 3,342 Max: 15 - Min: 1 |
|
|
Years of clinical experience |
6,9 ± 2,342 Max: 15 - Min: 2 |
6,7 ± 3,342 Max: 14 - Min: 1 |
|
|
Workplace |
At a university (trains bachelor’s degree and higher) At a college (Nurses are trained 3 years) A vocational school Hospital /health center missing |
9 (25,0%)
12 (33,3%)
2 (5,6%) 3 (8,3%) 10 (27,8%) |
39 (33,0%)
37 (31,3%)
8 (6,8%) 16 (13,6%) 18 (15,3%) |
|
Job types |
Lecturer Officer Nurse – chief nurse A health staff Missing |
21 (58,3%) 0 0 0 15 (41,7%) |
72 (61%) 7 (5,9%) 12 (10,2%) 7 (5,9%) 20 (16,9%) |
Table 1: Characteristics of the trainees of the master's program
Comments: Features vary dependant on male or female age, years of experience and job types, etc. With max and min values vary (Table 1).
The number of females was nearly 3 times higher than that of male students, for the mean age of male students was 31 ± 72 and that of female students was 28 ± 4.62, the difference in mean age was not statistically significant with p> 0.05. The average years working for both sexes were 7 years and the average years of clinical experience were 6 years, there was no statistical difference with p> 0.05. In terms of the workplace, most men and women were working at universities (men 25%, women 33%), colleges (men 33.3%, women 31.3%), vocational schools. (Male 5.6%, female 6.8%), the proportion of people working in the hospital/health center was low (8.3% male, 13.6% female). For working positions, the majority of males had worked for the universities' as lectures (58.3% of men, the remaining one did not provide information about their working positions), the female lecturers accounted for 61%, followed by nurses or chief nurses accounted for 10.2%. Training current situation, level of performance and ability to perform groups of professional capacities, training, management, and organizing of scientific research (Table 2 and Table 3).
|
|
Be trained |
Frequency |
The confident level when implementing |
|||||||
|
Capacity |
Bachelor |
master |
both |
Not trained |
sometimes |
Usually |
Not implem-ented |
confident |
Very confident |
Not confident |
|
Capacity 1 |
51% |
5% |
44% |
1% |
62% |
36% |
1% |
80% |
16% |
4% |
|
capacity 2 |
47% |
5% |
48% |
0% |
57% |
42% |
1% |
76% |
22% |
3% |
|
capacity 3 |
52% |
3% |
45% |
0% |
56% |
44% |
0% |
79% |
19% |
2% |
|
capacity 4 |
40% |
11% |
49% |
0% |
59% |
40% |
1% |
77% |
19% |
3% |
|
capacity 5 |
38% |
8% |
54% |
0% |
56% |
43% |
1% |
73% |
22% |
5% |
|
capacity 6 |
28% |
21% |
37% |
14% |
52% |
25% |
23% |
68% |
18% |
14% |
|
capacity 7 |
23% |
27% |
34% |
16% |
52% |
22% |
26% |
64% |
18% |
18% |
Table 2: The current situation of training capabilities belongs to the professional capacity group
* The level of confidence in performing the capacities: over 95 % of participants felt confident and very confident when performing the capacities (1) to (5), while the figure for the remaining capacities (6) and (7) were 86% and 82%, respectively.
|
Capacity |
Be trained |
Frequency |
The confident level when implementing |
|||||||
|
|
Bachelor |
master |
both |
Not trained |
sometimes |
Usually |
Not implem-ented |
confident |
Very confident |
Not confident |
|
Capacity 1 |
18% |
14% |
64% |
3% |
74% |
20% |
6% |
80% |
9% |
11% |
|
capacity 2 |
18% |
14% |
56% |
13% |
61% |
13% |
26% |
79% |
3% |
18% |
|
capacity 3 |
23% |
12% |
65% |
0% |
77% |
19% |
4% |
79% |
13% |
8% |
|
capacity 4 |
38% |
7% |
53% |
2% |
57% |
36% |
8% |
72% |
18% |
10% |
|
capacity 5 |
43% |
7% |
50% |
1% |
53% |
44% |
3% |
77% |
22% |
1% |
|
capacity 6 |
41% |
9% |
48% |
1% |
56% |
37% |
7% |
78% |
15% |
6% |
|
capacity 7 |
51% |
7% |
37% |
6% |
57% |
34% |
9% |
79% |
13% |
8% |
|
capacity 8 |
26% |
14% |
55% |
5% |
60% |
21% |
19% |
82% |
3% |
15% |
|
capacity 9 |
22% |
15% |
54% |
9% |
66% |
14% |
21% |
80% |
7% |
13% |
Table 3: The current situation of training capacity in management capacity group
- The level of confidence in performing the capacities: among students answering that they performed usually the capacity (5) had the highest percentage of confident and very confident 99%; following by the capacity (6), (7) và (3) with 92-94%; the capacity (4), (1), (9), (8) were 80-85%; the capacity (2) had the lowest proportion with 82% (Figure 1).
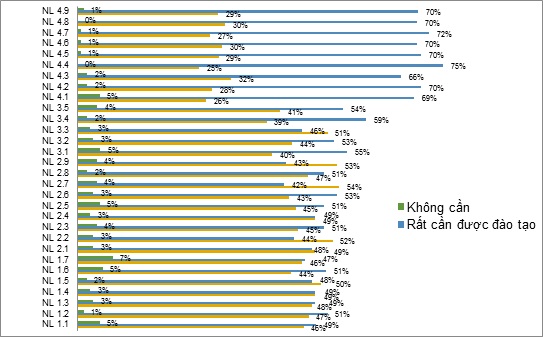 Figure 1: The needs to be trained
Figure 1: The needs to be trained
The need be specialized training for capacity groups
Group 1 professional capacity
The highest percentage were capacity (2) with 99%, then the capacity (5) with 98%, the capacity (4) with 97%, the capacity (1) and (6) were 95% and the lowest one was the capacity (7) with 93%. The needs and extremely needs to be trained, these percentages were approximately equal, mainly 1-2% difference, but the difference between capacity 1.6 was 7%. These differences were not statistically significant with p >0.05
Group 2 management capacity
The proportion of trainees who thought they need and extremely need to be trained was over 95%. Percentage of trainees considered that the capacity group needs to be trained from 43% to 53%, extremely need to be trained from 43% to 54%. The difference in the proportion of trainees between “need” and “extremely need” in this group ranges from 0 to 10%. These differences are not statistically significant with p >0.05.
Group 3 training capacity
The percentage of trainees who evaluated that they need and extremely need to be trained was over 95%. Capacities (1), (2), (4) and (5) had a higher proportion of people answering that they extremely need to be trained 9% to 20% than those who answered that they need to be trained (40% versus 55% *, 44% versus 53%, 39% versus 59% * and 41% versus 54% *). In terms of the capacity (3), the proportion of trainees who considered that it needs to be trained higher than those evaluated that it extremely needs to be trained (51% versus 46%). The difference between “need” and “extremely need” in this group of capacities (1), (4), and (5) was statistically significant with p <0.05.
Group of capacities in organizing and implementing scientific research
95% of trainees evaluated that it is necessary and very necessary to be trained for the capacities of this group. The percentage of people responding “extremely need to be trained” ranged from 66% to 75%, while “need to be trained” was from 25% to 32%. The difference between the group who answered“extremely need” and “need” for all 9 capacities were statistically significant with p <0.05.
Discussion
The characteristic of students enrolled in the master program in nursing
The number of female trainees was nearly 3 times higher than that of male students, for the mean of age of males was 31 ± 5.72 and that of female students was 28 ± 4.62, the difference is the mean age was not statistically significant with p> 0.05; the average number of years working for both sexes was 7 years and the average number of years of clinical work was 6 years, there was no difference with p> 0.05 (Table 1). The majority of students were teacher or lecture at universities, colleges, or secondary schools (male 63.9%, female 71.1%), the number of workers working in hospitals/health centers accounted for a lower percentage (male 8.3%, female 13.6%); most of them were holding the teaching positions of schools: male teachers were the majority of the school's lecturers (58.3% of men), the female lecturers account for 61%. The number of nurses or chief nurses amounted to 10.2%, the number of staff working in the department of the school and hospital were equal to 5.9%. This suited with the goal of training programs of schools when building programs to improve the level for nursing faculty in institutions in Vietnam.
Training capacity group
Training capacity
100% of the participants agreed that the compentency (3) planning and organizing the implementation of patient care, instructing the caring knowledge for the community were trained in undergraduate and/or master programs. 99% of the participants were trained the capacities (5) Organizing the implementation of care techniques to ensure proper procedures, comply with regulations on infection control and safety rules in the unit, (6) Coordinating with doctors and other health staffs to provide accurate and safe care solutions for patients. 90% of the participants were trained the capacities (1) Organizing activities to care for patients, patient’s families and communities, (4) Organizing the implementation of safe and effective medicine use for patients, evaluate the effectiveness of medicine, (8) Applying management skills to organize, coordinate, and assign care activities in the group, use resources reasonably and effectively, ensure the quality of care, (9) checking and supervising health care activities for patients and communities in accordance with the functions and tasks of the unit. 87% of the participants were trained the capacities, (2) Organizing and manage nursing activities of the unit.
Frequency of performance capacities
The capacity (3) and (5) had the highest percentage of students answering that they performed usually (96% and 97%); The capacities (1), (7) and (6) had the proportion of students answering that usually performing were 90-95%. For the capacities (8), (9) and (2), the percentage of students answering that they performed usually were 81%, 79% and 74%, respectively. This capacity is often applied in the group of lectures or teachers at universities, colleges and secondary schools.
The level of confidence in performing the capacities
Among students answering that they performed usually the capacity (5) had the highest percentage of confident and very confident 99%; following by the capacity (6), (7) và (3) with 92-94%; the capacity (4), (1), (9), (8) were 80-85%; the capacity (2) had the lowest proportion with 82%.
The need to be trained
The proportion of trainees who thought they need and extremely need to be trained was over 95%. Percentage of trainees considered that the capacity group needs to be trained from 43% to 53%, extremely need to be trained from 43% to 54%. The difference in the proportion of trainees between “need” and “extremely need” in this group ranges from 0 to 10%. These differences are not statistically significant with p >0.05. This corresponded to the job position of the trainees.
Conclusion
The trainees were considered that all capacities of the 4 capacity groups to be in need and need of training (all over 95%). In addition, some trainees suggested some other capacities that need additional training in the master's program, such as soft skills, Specialized English, IT capacity, research information processing and presentation capacity. Through our analysis and research as above, it is necessary to conduct and implement specialized training program fro nurses in Nam Dinh province. Next, it is necessary to add more content to the program to help students applying the knowledge on writing the research thesis and improve the professional skills in the future. We can organize students into groups then we can deliver programs and increase teamwork training model.
Recommendation
The trainers need to add experience with more contents into the training program and deliver specialized training course for Master of nursing at Nam Dinh hospital.
References
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (2011) The Essentials of Master's Education in Nursing.
- Buchan J (2002) Global nursing shortages: are often a symptom of wider health system or societal ailments. BMJ 324: 751-752.
- Chaghari M, Saffari M, Ebadi A, Ameryoun A (2017) Empowering Education: A New Model for In-service Training of Nursing Staff. J Adv Med Educ Prof 5: 26-32.
- Ministry of Health (2004) Nursing management. Ha Noi, Viet Nam Medical Publshing House.
- Blakey A (2015) Ministry of Health, the National Action Plan to strengthen nursing and midwifery for the period 2002-2010.
- Ministry of Health, Standard basic capacity standards for Vietnamese nurses (2012).
- Ortega MCB, Cecagno D, Lior AMS, Siqueira HCH, Montesinos MJL, et al. (2015) Academic training of nursing professionals and its relevance to the workplace, Rev Lat Am Enfermagem 23: 404-410.
- Salim NA, Joshua R, Abubaker NA, Chehab F, Jose A, et al. (2019) Effect of a Nursing In-Service Education Program on Nurses’ Knowledge and Attitudes towards Pain Management in a Governmental Hospital in the United Arab Emirates: Experimental Random Assignment Study. Dubai Med J 2:146-152.
Citation: Hien NP, Bao LV, Tuan LA (2021) Training Master’s in Nursing Program of Nam Dinh University of Nursing and University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City. J Pract Prof Nurs 5: 026.
Copyright: © 2021 Hien NP, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

