
Nutrient Compositions and Antioxidant Capacity of E’jiao Gao
*Corresponding Author(s):
Dongliang WangCollege Of Biosystems Engineering And Food Science, National Engineering Technology Research Center Of Glue Of Traditional Medicine, Shandong Dong-E-E-Jiao Co., Ltd., Dong?e, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Shandong, China
Email:wangdl@dongeejiao.com
Jiajin Zhu
College Of Biosystems Engineering And Food Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Tel:+86 57188982732,
Email:jjzhu@zju.edu.cn
Abstract
Background
Aging is a major public health issue and is considered to be associated with oxidative stress. Additionally, foods are basic for nutrients, survival and growth of organisms, and are a good source for antioxidants. E’jiao Gao (EJG, made up of E’jiao, walnut, semen sesame nigrum and rice wine) is a well-known traditional food in China, however, little nutritional and bioactive information is available. Therefore, in the present study, nutritional compositions of EJG, including protein, amino acid, vitamins, fatty acid and mineral contents, were investigated. Furthermore, 55 female aging ICR mice were used to evaluate the anti-aging activity of EJG in vivo, and their antioxidant enzyme activities, including SOD, GPx and CAT, and MDA contents were determined.
Results
EJG is abundant in protein, amino acids, vitamin E, essential fatty acids (linoleic acid and linolenic acid), mineral elements (calcium, potassium, magnesium,) and other biological nutrients (selenium, zinc and iron). After administrated with EJG, the activities of SOD, GPx and CAT were remarkably improved (P<0.05) and the content of MDA remarkably decreased (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Overall, EJG is a functional food for supplementation of protein, vitamin E, amino acid or calcium, and is a potential food for promoting the activities of endogenous antioxidant enzyme to fight against aging. Therefore, these data are essential theoretical basis for the development of the traditional food of EJG and useful for encouraging people to pay attention to the nutritional composition and bioactivities of food they consume.
Keywords
INTRODUCTION
Aging is a major public health issue, and the elderly population will be expected to grow from 17.4% to nearly 30% worldwide by 2060 [1]. In the process of aging, the risk of many chronic diseases, such as cancer, Parkinson’s and cardiovascular diseases increase [2]. Numerous studies indicate that nutrients, food components and whole diets can influence cognitive and ageing [1]. Nutrients are basic for survival and growth of organisms. However, people usually consume foods that are available or palatable. In addition, with the development of food processing technology, nutritional composition of food can be largely affected by the processing. Therefore, it is urgent to produce foods that are palatable, nutritional and capable to fight against aging process.
Colla corii asini (E’jiao), a solid glue prepared from donkey (Equus asinus) skin, has been considered as a health-care food and used as a traditional Chinese medicine in life-nourishing and clinical antianemic therapy for more than 2000 years [3]. E’jiao is mainly composed of amino acids, low molecular weight hydrolyzates of collagen proteins, polysaccharides, volatile substances and inorganic substances [4]. It has attracted great attention due to its biological activities in hematopoiesis, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, anti-ageing, improving immunity, etc [5-8].
E’jiao Gao (EJG), one of the popular edible forms of E’jiao, is made up of E’jiao, walnut, semen sesame nigrum and rice wine. The walnut is a high nutritional food containing high contents of protein, essential fatty acids, polyphenols and to copherols, which has been reported to reduce risk of cancer, coronary heart disease and to improve antioxidant as well as antiproliferative activity [9,10]. Semen sesame nigrum not only benefits in nourishing the liver and anti-ageing, but also in anti-wrinkling, keeping the balance of nerves and beautifying [11]. Rice wine is popular in China and is not only for drinking but also for medical use in traditional Chinese medicine all over the country. Rice wine has been claimed to have physiological functions in preventing aging, cancer and cardio cardiovascular diseases [12].
Free radicals are one of the reasons that associated with aging. In organisms, there are two antioxidant defense systems, antioxidant enzymes and non-enzymatic antioxidant compounds, preventing organisms from damages of free radicals [2]. However, oxidative stress occurs when antioxidant defense systems is too weak to scavenge the excessive free radicals, which is harmful for organisms. It has been reported to suppress the aging process through enhancing antioxidant activity, scavenging free radicals, and modulating expression of aging-related gene [5].
Therefore, the aim of the present study is to investigate the nutritional composition of EJG and evaluate the effects of EJG on antioxidant enzymes in aged mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials and chemicals
Determination of main nutrients
Analysis of fatty acids analysis
Analysis of amino acids
Analysis of elements
Analysis of vitamins
Analysis of antioxidant activity
Animals and treatments
High-dose EJG group (HE): administered EJG (4.29gkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Medium-dose group (ME): administered EJG (1.43gkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Low-dose EJG group (LE): administered EJG (0.71gkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Vitamin E control group (VE): administered VE (72mgkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Model control group (MC): administered normal saline (20mlkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Young control group (YC): administered normal saline (20mlkg-1b.w., i,g) for 60 days
Enzymatic endogenous antioxidant system
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Chemical composition
|
Constituents |
Per 100g |
RDI |
%CS |
|
Moisture (g) |
9.47 |
|
|
|
Lipids (g) |
29.00 |
78a |
3.72 |
|
Protein (g) |
20.90 |
50a |
4.18 |
|
Ash (g) |
3.40 |
|
|
|
Total dietary fiber (g) |
2.96 |
28a |
1.06 |
|
Lnoleic acid (g) |
10.42 |
|
|
|
Linolenic acid (g) |
1.35 |
|
|
|
Amino acids (mg) |
Per 100g |
RDI |
%CS |
|
Essential |
|
|
|
|
Isolecucine |
387 |
1400b |
2.76 |
|
Lysine |
484 |
2100b |
2.30 |
|
Methionine |
196 |
700b |
2.80 |
|
Leucine |
778 |
2730b |
2.85 |
|
Phenylalanine |
789 |
1750b |
4.51 |
|
Tryptophan |
71 |
280b |
2.54 |
|
Threonine |
464 |
1050b |
4.42 |
|
Valine |
546 |
1820b |
3.00 |
|
Non-essential |
|
|
|
|
Arginine |
1330 |
|
|
|
Aspartic acid |
1109 |
|
|
|
Alanine |
1.157 |
|
|
|
Cysteine |
146 |
280b |
5.21 |
|
Glycine |
2307 |
|
|
|
Glutamic acid |
2287 |
|
|
|
Histidine |
274 |
700b |
3.91 |
|
Proline |
1474 |
|
|
|
Serine |
676 |
|
|
|
Tyrosine |
394 |
|
|
|
Vitamins (mg) |
Per 100g |
RDI |
%CS |
|
Vitamin E |
6.525 |
15a |
4.35 |
|
Vitamin C |
1.100 |
90a |
0.12 |
|
Minerals (mg) |
Per 100g |
RDI |
%CS |
|
Ca |
454.09 |
1300a |
3.49 |
|
P |
295.00 |
1250a |
2.36 |
|
K |
283.00 |
|
|
|
Mg |
157.95 |
420a |
3.76 |
|
Mn |
1.59 |
2.3a |
6.91 |
|
Zn |
2.05 |
11a |
1.86 |
|
Fe |
3.24 |
18a |
1.80 |
|
Se |
0.013 |
0.055a |
2.36 |
|
I |
0.004 |
0.150a |
0.27 |
b WHO/FAO/UNU Report (2007). Considering a body weight of 70Kg [20].
The content of protein in EJG was 20.90%, and was mainly composed of 20 amino acids, including 8 essential amino acids, 10 non-essential amino acids and 2 conditionally essential amino acids. 10g EJG contributes to more than 4% of the RDI. The ratio of essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids was 0.44, a little bit lower than the reference value of 0.6 recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [21]. Lysine is the first limiting amino acid in EJG when compared to the RDI. However, EJG is a relatively good source of cysteine, which has the potent antioxidant activity against linoleate oxidation and superoxide due to its higher reactivity of the thiol toward the radical species [22]. In addition, EJG is abundant in glutamic, glycine and arginine, contenting 2287mg/100g, 2307mg/100g and 1.33mg/100g, respectively.
Vitamin E content of the EJG was 6.525mg/100g, and Vitamin C was 1.100mg/100g. Per 10g of the EJG represents 4.35% of RDI in vitamin E. Vitamin E is a lipophilic antioxidant that can increase the proliferation and survival of fibroblasts and elevate the production of collagen, which finally can protect skin from UVB-Irradiation [23].
Linolenic acid and linoleic acid are two essential fatty acids for human beings. In our study, the contents of linolenic acid and linoleic acid were 1.35g/100g and 10.42g/100g, respectively. Lack of essential fatty acids would cause slow growth as well as dermatitis, and supplementing linoleic acid and linolenic acid can prevent these symptoms [24]. What’s more, linoleic acid and linolenic acid have certain effects on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, hypertension and rheumatoid arthritis, asthma and allergy [25].
It implicated that supplementation of EJG could be good for promoting health. Nine kinds of minerals of in EJG were analyzed in the present study. The results showed that calcium was the most abundant (454.09mg/100g) among these minerals. In terms of RDI per 10g, the EJG presents 34.93%. Ca, K and Mg are essential for the energy metabolism, bone development and protein synthesis in humans [26]. She was also found in EJG (0.013mg/100g), which was an essential nutrient element in humans due to its possible roles in oxidative damage, chronic diseases and inflammatory [27].
Weight gain and organ index
|
Groups |
n |
0 days |
30 days |
60 days |
|
HE |
11 |
42.8±3.17 |
41.3±2.75 |
43.1±4.17 |
|
ME |
11 |
42.6±1.90 |
41.6±3.06 |
42.2±3.68 |
|
LE |
11 |
42.6±1.80 |
41.5±2.48 |
41.7±3.38 |
|
VE |
11 |
41.7±3.35 |
44.2±4.02 |
43.9±4.66 |
|
MC |
11 |
41.1±4.07*** |
43.0±4.77*** |
43.3±4.87*** |
|
YC |
10 |
25.8±0.66 |
27.2±1.28 |
29.7±0.88 |
Table 2: Effects of E’jiao Gao (EJG) on the weight gain of experimental mice.
Note: ***compare to group YC, P<0.001. Each value was expressed as mean±SD. HE: 4.29gkg-1b.w., E’jiao Gao; ME: 1.43gkg-1b.w., E’jiao Gao; LE: 0.71gkg-1b.w., E’jiao Gao; VE: 0.72mgkg-1b.w., Vitamin E; MC: 20mLkg-1b.w., normal saline; YC: 20mLkg-1b.w., normal saline.
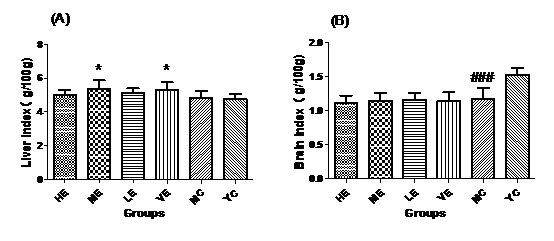 Figure 1: Liver index (A) and Brain index (B) of all groups.
Figure 1: Liver index (A) and Brain index (B) of all groups.Effect of EJG on the MDA content in aged mice
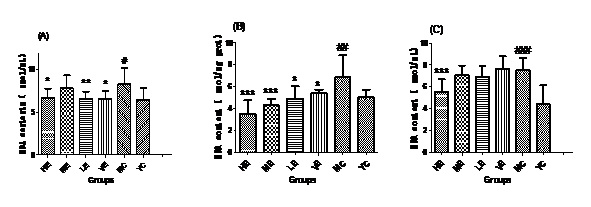 Figure 2: MDA contents of all groups in Serum (A), Liver (B) and Brain (C).
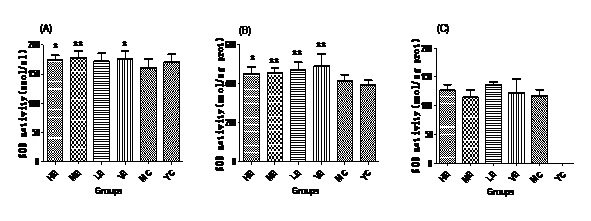
Figure 2: MDA contents of all groups in Serum (A), Liver (B) and Brain (C).Effect of EJG on SOD activity in aged mice
Effect of EJG on GPx in aged mice
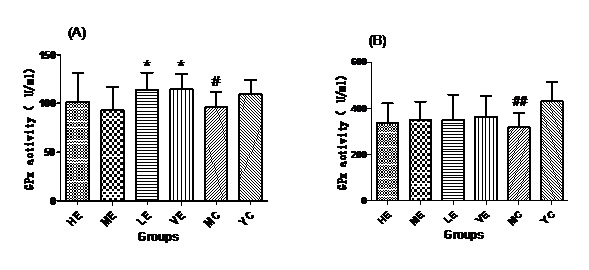 Figure 4: GPx activities of all groups in Serum (A) and Liver (B).
Figure 4: GPx activities of all groups in Serum (A) and Liver (B).Effect of EJG on CAT activity in aged mice
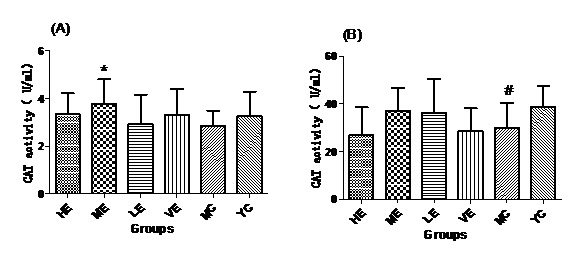 Figure 5: CAT activities of all groups in Serum (A) and Liver (B).
Figure 5: CAT activities of all groups in Serum (A) and Liver (B).DISCUSSIONS
Nutrients are basic for survival and growth of organisms. There are two kinds of nutrients: macro-nutrients and micro-nutrients. Macro-nutrients, including carbohydrates, fiber, fats, protein and water [28], is an energy provider for metabolism of an organism, while micro-nutrients, including at least iron, vitamins, cobalt, copper, manganese, chromium, iodine, selenium, zinc, and molybdenum take part in building and repairing of tissue and regulating body processes. Organisms obtain nutrients from environments and their growth and health conditions are largely influenced by what they eat. A poor diet, especially a Western pattern diet, is associated with many diseases, such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and even deficiency disease of blindness [29-32].
Food intake is greatly influenced by availability, the processing and palatability of food. However, with the development of food processing technology, the nutritional components in food can be largely affected by the processing. Nowadays, nutritional value becomes an important factor in people’s choice of food. EJG is a snack that is mixed with walnut, semen sesame nigrum and rice wine, which is delicious and nutritional and is popular with women in China.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals [33], which can be found in many fibrous tissues, and is believed to be the main active component in E’jiao. It is widely used to nourish the blood. A previous study isolated two collagen-derived peptides from E’jiao and confirmed exhibition of strong hematopoietic activity by elevated CFU-E (colony-forming units-erythroid) and CFU-GM (colony-forming units granulocyte-monocyte) of mouse bone marrow cells [6]. Collagen is important for women, which is not only because of its ability to treat gynecologic diseases but also its importance in delaying natural ageing process by tightening and smoothing the skin internally [34]. Nowadays, many people use the cosmetic products of collagen, such as creams and lotions, to keep skin health. However, these products can only treat some lines and smaller wrinkles on the surface, and to do some substantial effect was considered to take oral applications [35]. From nutrients analysis, protein was a dominated component in EJG and it was mainly from E’jiao. It is known that E’jiao contains about 80% collagen; therefore EJG can be a good supplementation of collagen to fight against aging.
EJG contains many essential or non-essential amino acids that have various biological functions. For example, glycine has been considered an important inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain stem and medulla [36]. Hydroxyproline is an important component of the synthesis of the connective tissue collagen. The deficiency of L-arginine is frequently associated with aging, and L-Arginine supplementation can improve endothelial function and decreased systolic blood pressure by normalizing plasma L-arginine and L-argining/L-ornithine ratio [37].
Recently, many studies suggest that vitamins, minerals and botanicals are natural ingredients to improve antioxidant activities and anti-ageing. In the present study, Vitamin E was extremely abundant in EJG, which suggested that EJG was a potential antioxidant. Vitamin E is considered to be a good peroxyl radical scavenger and has been developed as a commercial antioxidant, protecting tissues from damage of free radicals, protecting lipids and preventing the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids [30]. In addition, many macro-elements and trace elements of mineral that are beneficial for humans have been found in EJG. Among these detected mineral elements, selenium is an essential nutrient for its important antioxidant functions and neuroprotective actions [38]. Human usually obtain natural selenium from dietary, such as meat, eggs and vegetables [39]. EJG contains about 0.013mg/100g selenium, which would be another choice for humans.
Reactive oxygen species or free radicals, including superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide, are unstable and reactive. In general, they play an important role in signal transduction, leukocyte adhesion, gene transcription and many other critical cellular reactions. However, though the excess of free radicals can be detoxified by cell-produced antioxidants, such as catalases, peroxidases and superoxide dismutase, the oxidative stress will happen with aging or other pathological conditions. Oxidative stress can damage many critical molecules, increase DNA mutations and cause cell death [40]. Supplementation with antioxidants can decrease cellular damage from excess reactive oxygen species.
After administrated with EJG, the activities of endogenous antioxidant enzymes in aging mice (SOD, GPx, and CAT) were remarkably improved and the content of MDA was decreased, when compared to the model control group. SOD is the first line of antioxidant-defense systems, the best characterized, to catalyze the dismutation of O2− into non-toxic of H2O2 and O2 [41]. GPx protects the organism from oxidative damage mainly by reducing lipid hydroperoxides [42]. CAT is also a very important enzyme that catalyzes the hydrogen peroxide into less-reactive gaseous oxygen and water molecules [43]. Therefore, it is essential for the organisms to keep the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes. The capability of EJG in improving SOD, GPx and CAT activities in aged mice, may be due to the containment of some potential antioxidant nutrients. For example, zinc and manganese are critical cofactors for superoxide dismutase; vitamin E and other vitamins reduce reactive oxygen species [44].
In conclusion, EJG is a nutritious snack food, which is abundant in protein, essential amino acids, vitamins, essential fatty acids and minerals. In vivo experiments, EJG exhibited a good ability to improve the activities of SOD, GPx and CAT in aged mice. In addition, it decreased the content of MDA in aged mice. It indicated that EJG was a healthy food, containing potential anti-ageing capacity, for consumption.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Authors have no conflict of interests.
REFERENCES
- Vauzour D, Camprubi-Robles M, Miquel-Kergoat S, Andres-Lacueva C, Bánáti D, et al. (2017) Nutrition for the ageing brain: Towards evidence for an optimal diet. Ageing Res Rev 35: 222-240.
- Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev 4: 118-126.
- Tian JS, Zhang X, Liu H, Xiang H, Xing J, et al. (2017) The hematinic effect of Colla corii asini (Ejiao) using 1H-NMR metabolomics coupled with correlation analysis in APH-induced anemic rats. RSC Advances 7: 8952-8962.
- Wang D, Ru W, Xu Y, Zhang J, He X, et al. (2014) Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Colla corii asini. Drug Discov Ther 8: 201-207.
- Wang D, Liu M, Cao J, Cheng Y, Zhuo C, et al. (2012) Effect of Colla corii asini (E'jiao) on D-galactose induced aging mice. Biol Pharm Bull 35: 2128-2132.
- Wu H, Ren C, Yang F, Qin Y, Zhang Y, et al. (2016) Extraction and identification of collagen-derived peptides with hematopoietic activity from Colla Corii Asini. J Ethnopharmacol 182: 129-136.
- Song YM, Mao GN, Kang RR, et al. (2011) Effect of Colla corri asini effervescent granules on immune function in mice. Progress in Veterinary Medicine.
- Fu-dong Z, Jing-cheng D, Yan C, Jin-yu X, Shan-mei W (2006) The effect of Ejiao on airway inflammation and Th1/Th2 cytokines in serum of asthmatic rats. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae.
- Homan M, Fereidoon S (2008) Lipid class compositions, tocopherols and sterols of tree nut oils extracted with different solvents. Journal of Food Lipids 15: 81-96.
- Anjum S, Gani A, Ahmad M, Shah A, Masoodi FA, et al (2016) Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of walnut extract (Juglans regia L.) processed by different methods and identification of compounds using GC/MS and LC/MS technique. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 41: 12756.
- Wang BS (1998) Black sesame and beauty. Chinese cosmetics.
- Que F, Mao L, Pan X (2006) Antioxidant activities of five Chinese rice wines and the involvement of phenolic compounds. Food Research International 39: 581-587
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (1990) Official Methods of Analysis. Changes in Official Methods of Analysis Made at the Annual Meeting. Supplement, Volume 15. Official Methods of Analysis, Rockville, USA
- Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissue. J Biol Chem 226: 497-509
- Metcalfe LD, Schmitz AA, Pelka JR (1996) Rapid preparation of fatty acid esters from lipids for gas chromatographic analysis. Anal Chem 38: 514-515.
- Ishida Y, Fujita T, Asai K (1981) New detection and separation method for amino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 204: 143-148.
- Chatzimichalakis PF, Samanidou VF, Papadoyannis IN (2004) Development of a validated liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of eight fat-soluble vitamins in biological fluids after solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 805: 289-296.
- Ergun R, Lietha R, Hartel RW (2010) Moisture and shelf life in sugar confections. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50: 162-192.
- Leterme P, Buldgen A, Estrada F, Londoño A (2006) Mineral content of tropical fruits and unconventional foods of the Andes and the rain forest of Colombia. Food Chemistry 95: 644-652.
- World Health Organization (2007) Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition: Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Liu Y, Chen D, You Y, Zeng S, Li Y, et al. (2016) Nutritional composition of boletus mushrooms from Southwest China and their antihyperglycemic and antioxidant activities. Food Chem 211: 83-91.
- Miura Y, Honda S, Masuda A, Masuda T (2014) Antioxidant activities of cysteine derivatives against lipid oxidation in anhydrous media. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry 78: 1452-1455.
- Kim WS, Kim I, Kim WK, Choi JY, Kim DY, et al. (2016) Mitochondria-targeted vitamin E protects skin from UVB-irradiation. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 24: 305-311.
- Burr GO, Burr MM (1930) On the nature and rôle of the fatty acids essential in nutrition. J Biol Chem 86: 587-621.
- Weaver B J, Holob B J (1988) Health effects and metabolism of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid. Prog Food Nutr Sci 12: 111-150.
- Lai TN, André C, Rogez H, Mignolet E, Nguyen TB, et al. (2015) Nutritional composition and antioxidant properties of the sim fruit (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa). Food Chem 168: 410-416.
- Yamashita Y, Yabu T, Yamashita M (2010) Discovery of the strong antioxidant selenoneine in tuna and selenium redox metabolism. World J Biol Chem 1: 144-150.
- Fuhrman J (2014) The End of Dieting: How to Live for Life. HarperCollins, New York, USA.
- Esmaillzadeh A, Kimiagar M, Mehrabi Y, Azadbakht L, Hu FB, et al. (2007) Dietary patterns, insulin resistance, and prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in women. Am J Clin Nutr 85: 910-918.
- Whitney EN, Rolfes SR (2005) Understanding Nutrition. Thomson/Wadsworth, California, USA.
- Naja F, Hwalla N, Itani L, Karam S, Sibai AM, et al. (2015) A Western dietary pattern is associated with overweight and obesity in a national sample of Lebanese adolescents (13-19 years): A cross-sectional study. Br J Nutr 114: 1909-1919.
- Medina-Remón A, Kirwan R, Lamuela-Raventós RM, Estruch R (2018) Dietary patterns and the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and mental health problems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58: 262-296.
- Di Lullo GA, Sweeney SM, Korkko J, Ala-Kokko L, San Antonio JD (2002) Mapping the ligand-binding sites and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in the human, type I collagen. J Biol Chem 277: 4223-4231.
- Li Y, He H, Yang L, Li X, Li D, et al. (2016) Therapeutic effect of Colla corii asini on improving anemia and hemoglobin compositions in pregnant women with thalassemia. Int J Hematol 104: 559-565.
- Collagen peptides: Beauty from within.
- Hernandes MS, Troncone LR (2009) Glycine as a neurotransmitter in the forebrain: A short review. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 116: 1551-1560.
- Moretto J, Guglielmetti AS, Tournier-Nappey M, Martin H, Prigent-Tessier A, et al. (2017) Effects of a chronic l-arginine supplementation on the arginase pathway in aged rats. Exp Gerontol 90: 52-60.
- Ellwanger JH, Franke SI, Bordin DL, Prá D, Henriques JA (2016) Biological functions of selenium and its potential influence on Parkinson's disease. An Acad Bras Cienc 88: 1655-1674.
- Lemire M, Fillion M, Barbosa F, Guimarães JR, Mergler D (2010) Elevated levels of selenium in the typical diet of Amazonian riverside populations. Sci Total Environ 408: 4076-4084.
- Buehler BA (2012) The free radical theory of aging and antioxidant supplements: A systematic review. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 17: 218-220.
- den Hartog GJ, Haenen GR, Vegt E, van der Vijgh WJ, Bast A (2003) Superoxide dismutase: The balance between prevention and induction of oxidative damage. Chem Biol Interact 145: 33-39.
- Dulcy CP, Singh HK, Preethi J, Rajan KE (2012) Standardized extract of Bacopa monniera (BESEB CDRI-08) attenuates contextual associative learning deficits in the aging rat's brain induced by D-galactose. J Neurosci Res 90: 2053-2064.
- Gaetani GF, Ferraris AM, Rolfo M, Mangerini R, Arena S, et al. (1996) Predominant role of catalase in the disposal of hydrogen peroxide within human erythrocytes. Blood 87: 1595-1599.
- Fang YZ, Yang S, Wu G (2002) Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition 18: 872-879.
Citation: Cao F, Chen Y, Chang C, Ru W, Chen J, et al. (2019) Nutrient Compositions and Antioxidant Capacity of E’jiao Gao. J Food Sci Nut 5: 043.
Copyright: © 2019 Feiwei Cao, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

