
Evidence-Based Practice Guideline for Post-Spinal Hypotension Prevention in Cesarean Section in, Review of Article, 2023
*Corresponding Author(s):
Minda Abebe SeifeDepartment Of Anesthesia, Collage Of Medicine And Health Sciences, Hawassa University, Hawassa, Ethiopia
Email:mindaabebe21@gmail.com
Abstract
- Background
The most common complication we see in obstetric surgery after spinal anaesthesia is hypotension. Postspinal hypotension prevention is critical during caesarean section for a successful maternal and foetal outcome. National guidelines prioritise treatment of post-spinal hypotension over prevention. Current guidelines emphasise non-pharmacological and pharmacological approaches to preventing post-spinal hypotension in caesarean sections for improved maternal and foetal outcomes.
- Objective
To develop guideline on post spinal hypotension prevention in caesarean section to improve the practical protocols.
- Methodology
The Cochrane review, PubMed, and Google Scholar databases were used to conduct a systematic and manual search of the literature. The key words for PubMed, Cochrane, and Google Scholar were used in the search. [Hypotension AND C-section OR C-section, hypotension AND Preload OR co-loading, spinal anesthesia AND colloid OR crystalloid, hypotension AND prophylaxis OR prevention, sub-anesthetic dose AND post-spinal hypotension, spinal anesthesia AND atropine AND co-load AND leg-elevation AND spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension OR hypotension AND Cesarean section AND sequential compression device, 22 interventional studies, 3 meta-analyses
- Conclusion
When it comes to post-spinal hypotension in obstetrics, they strongly recommend crystalloid co-loading over preloading. Colloid preloading outperforms crystalloid co-loading. Non-pharmacological approaches, as well as a sub anesthetic dose of 0.5 mg/kg ketamine and a 0.5 mg atropine IV bolus, were effective agents in preventing post-spinal hypotension.
Keywords
Cesarean section; Co loading; Hypotension crystalloid; Post spinal hypotension preloading; Positioning; Prevention.
Abbreviations and Acronyms
C/S: Cesarean Section
CB: Elastic Crepe Bandage
CD: Cesarean Delivery
GOR: Grade of Recommendation
HR: Heart Rate
LOE: Level of Evidence
MABP: Mean Arterial Blood Pressure
NPI: Non-Pharmacologic Intervention
PCD: Pneumatic Compression Device
PSH: Post Spinal Hypotension
PSHP: Post Spinal Hypotension Prevention
RCT: Randomized Clinical Trial
SA: Spinal anesthesia
SCD: Sequential Compression Device
Introduction
Cesarean section is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in women, and subarachnoid anesthesia is used more frequently than epidural and combined spinal-epidural techniques [1]. The most common problem of SA is nausea or vomiting, and it can expose the mother and baby to unconsciousness, pulmonary aspiration and hypoxia, acidosis, and neurological injury during caesarean section [2].
The most significant pathophysiological mechanism is the rapid onset of sympatholytic due to increased sensitivity of nerve fibers to local anesthetics during pregnancy, as well as at the preganglionic level and the sympathetic block, which is one to two segments higher than the somatic level [3,4].
Post-SA hypotension after Caesarean section is associated with maternal morbidity and mortality, with reported incidences ranging from 7% to 74%. The incidence varies depending on how hypotension is defined [5]. Post-spinal hypotension is more common in pregnant women due to physiological changes that cause the enlarged uterus to compress the inferior vena cava and increase collateral venous plexus circulation in the epidural space. This change causes an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the lumbosacral area, which causes local anesthetics to be absorbed [6].
Generally, hypotension caused by spinal anesthesia during a cesarean section is associated with tachycardia, with bradycardia being a less common response. According to minimally invasive cardiac output monitoring, this represents a partially compensatory increase in cardiac output in response to a decrease in SVR [7].
The sensory level, anesthetic dose, and fetal birth weight greater than 3900 g were the most important risk factors that increased the incidence of hypotension in cesarean sections performed under spinal anesthesia [8]. Non-pharmacologic intervention (NPI) (such as leg wrapping, leg elevation, left side tilting, and inflatable splints or boots or thromboembolic deterrent stockings) or pharmacological methods such as vasopressors (Ephedrine, phenylephrine, and norepinephrine) and intravenous fluids can prevent post-spinal hypotension (PSH) [9].
Justification
It is common for a pregnant woman to be indicated for a cesarean section under spinal anesthesia, so proper and adequate prevention is essential. According to studies, up to 75% of all pregnant women experience spinal block-induced sympatholytics, resulting in vasodilation and, as a result, maternal hypotension, which may compromise uterine blood flow and foetal circulation, resulting in fetal hypoxia, bradycardia, and acidosis [10]. The standard obstetric prevention has frequently failed to meet the maternal and fetal needs, and dealing with PSH is a daily challenge for anesthetists of varying levels of experience. This demonstrates that anesthetists and post-spinal anesthesia prevention strategies do not work well together during procedure. There are a lot of scientific literatures, that support non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions as necessary components to complete the gap of PSH in obstetrics as needed so, performing review and developing guideline on Post spinal hypotension prevention (PSHP) is very beneficial both for health professionals and giving care for obstetric patients and fetus. The goal of this review is to create PSHP guidelines that include both pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic interventions, thereby improving clinicians' practice in the prevention of PSH-related maternal and fetal outcomes.
One national published guideline specifically focused on PSH management in obstetric undergoing for cesarean section as far as my search. However, currently update evidence, which have the different idea specially the current evidence on the crystalloid co-loading vs preloading, colloid preloading vs crystalloid co-loading and additional the effect of ketamine and atropine in prevention of PSHP than the previous guidelines.
Previous guidelines on the prevention and management of post-spinal hypotension in obstetrics recommend that co-loading be as important as pre-loading to avoid unnecessary time waste. Non-pharmacological approaches should be prioritized over pharmacological methods. Furthermore, rapid crystalloid co-loading has comparable efficacy to colloids and should be preferred due to a lower risk profile [11]. However, current evidence concludes and recommends that co-loading outperform preloading. Colloid preloading outperforms crystalloid co-loading, and a non-pharmacological approach was added to the previous guideline. Furthermore, a 0.5 mg/kg sub anesthetic dose of ketamine and a 0.5 mg IV bolus of atropine are effective agents for preventing post-spinal hypotension.
Objectives
To develop guideline on post spinal hypotension prevention in caesarean section to improve the practical protocols.
- scope of the guideline
Target audience of this guideline involves groups of health professionals working in every operating room or obstetrics patient undergoing cesarean section, including anesthetists, Nurses, doctors and other health care professionals contributing to a multidisciplinary approach for post spinal hypotension prevention.
Parturient undergoing spinal anesthesia for cesarean section was the target populations of this guideline. This guideline will address PSHP for obstetrics patients undergoing cesarean section through both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions supported by current best evidences.
Methods And Materials
The review reported according to Reporting Items for practice Guidelines in Health care (RIGHT) protocol. A systematic and hand search of literature was done from Cochrane review, PubMed, and Google Scholar. The search performed using key words for PubMed, [Hypotension AND Cesarean section OR C-section, hypotension AND Preload OR co-loading, spinal anesthesia AND colloid OR crystalloid, hypotension AND prophylaxis OR prevention, sub-anesthetic dose AND post-spinal hypotension, spinal anesthesia AND atropine OR co-load, leg-elevation AND spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension, Cesarean section OR hypotension, maternal care bundle OR sequential compression device).
This review included interventional studies, meta-analysis and systematic review studies, cohort studies, and cross-sectional studies, as well as full articles published between 2017 and 2022 and written in English. The search engine results were filtered by interventions, outcomes, population data, and methodological quality. Full-term pregnant women (ASA II) were the inclusion criteria for studies on parturients undergoing cesarean sections under spinal anesthesia in obstetric populations, and they were published in English. This is the goal of this policy.
Exclusion criteria studies on parturient with obesity, diabetes, cardiac disease, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, CKD, per partum bleeding, age less than 18 years (Figures 1 & 2), those converted to GA for failed SA, and coagulation disorder are included in this guideline. Following extraction and filtering with a patient population and exclusion criteria, 22 RCTs, 3 SRs and meta-analyses, 4 cohort studies, and 1 cross-sectional study were evaluated for quality and a conclusion was reached based on their level of evidence and recommendation grades adapted from the Oxford Center for Evidence-Based Medicine (Tables 1 & 2). 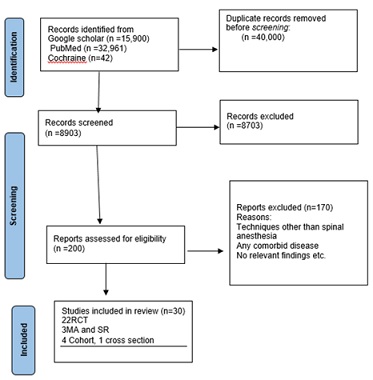
Figure 1: PRISMA flow diagram.
|
Level of evidence |
Grading criteria |
Grade of recommendation |
|
1a |
Systematic reviews of RCTs including meta-analysis |
A |
|
1b |
Individual RCT with narrow confidence interval |
A |
|
1c |
All or none randomized controlled trials |
B |
|
2a 2b
|
Systematic review of cohort study Individual cohort including low quality RCT |
B |
|
2c |
Outcome research study |
C |
|
3a |
Systematic review of case control studies |
C |
|
3b |
Individual case control study |
C |
|
4 |
Case series, poor quality cohort and case control studies |
C |
|
5 |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or “first principles” |
D |
Table 1: Levels of Evidences and Grades of Recommendations.
Note:*Adapted from Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
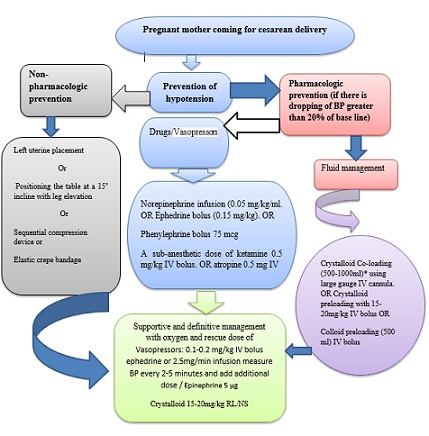 Figure: 2 Prevention and Management Algorithm Flow Chart
Figure: 2 Prevention and Management Algorithm Flow Chart
|
S/No |
Author/year |
Population |
Sample size/design |
Finding of the evidence |
LOE |
GOR |
|
1 |
Meron Abrar et al,2021 |
Obstetrics |
96, Cohort study |
Crystalloid fluid co-loading to the operating mothers during the cesarean section was a better option for the prevention of spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension. |
2b |
B |
|
2 |
Dr Ankita Chandel et al, 2020 |
Obstetrics |
50, RCT |
Co-loading provides a better alternative than preloading for prevention of maternal hypotension secondary to spinal anesthesia given for caesarean section. |
1b |
A |
|
3 |
Diriba Teshome et al,2022 |
Obstetrics |
96, Prospective cohort |
Hypotension occurred 77.1% of the time in the preload group and 35.4 percent of the time in the co-load group, according to this study. As a result, crystalloid co-loading was superior to preloading in preventing spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension in mothers who had a cesarean section. |
2b |
B |
|
4 |
Budi Yulianto Sarim et al,2022 |
Obstetrics |
51, RCT |
Crystalloid fluid co-loading was significantly better in reducing hypotension incidence, after spinal anesthesia in cesarean section compared with the Preloading and control groups. |
1b |
A |
|
5 |
Neha Bhardwaj et al,2020 |
Obstetrics |
50, RCT |
Co-loading of crystalloid fluid is a better method than preloading of crystalloids for prevention of maternal hypotension after SAB given for LSCS. So, we should not waste extra time for preloading of fluid before surgery, which can delay the surgery, for prevention of hypotension after spinal anesthesia. |
1b |
A |
|
6 |
MIAH MAK et al,2020 |
Obstetrics |
90,RCT |
Severity of hypotension and increased ephedrine requirement were evident in patients who received crystalloid pre-loading (group II), which means crystalloid co-loading (group I) was more capable to prevent spinal anesthesia induced hypotension. |
1b |
A |
|
7 |
Riley et al 2019; 47(1): 35-40 |
Obstetrics |
160, Retrospective cohort |
Vasopressor use was lower in colloid preloading than in crystalloid co-loading. However, differences in all outcome measures were minimal and likely clinically insignificant, suggesting that both fluid-loading techniques areappropriate to use for the prevention of spinal hypotension in women undergoing CD |
2b |
B |
|
8 |
Raad Ghazi Reshan,2018 |
Obstetrics |
60, RCT |
There is significant difference between the effect of preloading and co-loading on blood pressure after spinal Anesthesia. It had been found that those patients who were administered preloading dose more likely to develop hypotension than those administered co-loading one. |
1b |
B |
|
9 |
Hai-Fang Ni et al ,2017 |
Obstetrics |
824, A Meta-Analysis |
For parturients receiving crystalloid loading in spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery, coload strategy is superior to preload for the prevention of maternal hypotension. |
1a |
A |
|
10 |
Ahmed Hasanin et al,2017 |
Obstetrics |
150,RCT |
LE performed immediately after spinal block reduced the incidence of PSH in parturient undergoing CS |
1b |
A |
|
11 |
Ebrahim Elgzar et al.2019 |
Obstetrics |
120.RCT |
Lower leg compression technique can effectively reduce PSH and neonatal acidosis |
1c |
B |
|
12 |
Sumita Swain et al.2019 |
Obstetrics |
60, RCT |
Elevation of lower limb just after spinal anesthesia is an effective method to prevent hypotension during spinal anesthesia, for elective caesarean section without any unwanted side effect like hypotension, tachycardia, or any other maternal side effects. |
1b |
A |
|
13 |
Sofia Assen et al.2020 |
Obstetrics |
52, RCT |
This study shows that performing leg elevation after spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean section significantly reduces the incidence of post spinal hypotension and severity of hypotension. |
1b |
A |
|
14 |
Prajith et al.2020 |
Obstetrics |
90,RCT |
Leg-wrapping with Elastic crepe bandage (CB) is cost-effective, non-invasive, non-pharmacological, and effective tool to reduce the incidence of hypotension after spinal anesthesia in a parturient. |
1b |
A |
|
15 |
Feyza Bolcal Çalisir et al.2019 |
Obstetrics |
200, RCT |
The methods of positioning the operating table at a 15º incline and leg elevation, applied on their own or together, to pregnant women receiving spinal anesthesia, insignificantly reduced the frequency and depth of SA-induced maternal hypotension. It could provide maternofetal benefits with respect to less use of vasopressors. |
1b |
A |
|
16 |
Abdelrhman Alshawadfy et al.2021 |
Obstetrics |
100, RCT |
The application of left uterine placement is an important and effective parameter in a maternal care bundle for decreasing the incidence of post spinal anesthesia hypotension in parturients undergoing elective cesarean section. |
1b |
A |
|
17 |
Mostafa Alghozat et al.2020 |
Obstetrics |
76, RCT |
SCD could reduce extensive changes in diastolic blood pressure as an important hemodynamic parameter and the incidence of nausea and vomiting. Thus, SCD can be used in spinal anesthesia care practices for elective C/S. |
1b |
A |
|
18 |
Agarwal et al,2022 |
Obstetrics |
80, RCT |
The sequential compression device is useful for prevention of hypotension in pregnant females undergoing elective caesarean section under spinal anesthesia. |
1b |
A |
|
19 |
Dina Salah et al,2019 |
Obstetrics |
80, RCT |
It is concluded that ketamine in a sub-anesthetic dose is an effective agent that can be used in preventing post spinal hypotension in parturients undergoing CS delivery. |
1b |
A |
|
20 |
Salman Maqbool et al,2022 |
Obstetrics |
144, RCT |
Prophylactic bolus of atropine against to blunt unopposed vagal activity provided stable hemodynamic (pulse and systolic blood pressure) values in caesarean section at time of spinal block. |
1b |
A |
|
21 |
Shang et al. Medicine (2021) 100:7 |
Obstetrics |
587, 33RCT, for Meta-analysis |
Colloid preloading is superior to crystalloid preloading in reducing the incidence of hypotension induced by spinal anesthesia and vasopressor requirement in the healthy parturients undergoing elective cesarean delivery. |
1a |
A |
|
22 |
Susu Zhang et al,2019 |
Obstetrics |
97, RCT |
Infusion of 4mg/minute norepinephrine presented fewer cases of tachycardia, less fluctuation and a lower HR compared to baseline values, as well as a less stressed fetal status compared to ephedrine infusion at 4mg/minute. In addition, norepinephrine infusion presented a lower standardized SBP compared to ephedrine. |
1b |
A |
|
23 |
Jaitawat et al ,2019 |
Obstetrics |
120, RCT |
Prophylactic bolus dose of phenylephrine 75 mcg was found to be effective for the management of spinal-induced hypotension and should be preferred over 100 mcg which causes significant bradycardia and reactive hypertension. |
1b |
A |
|
24 |
Cui-cui Jiao et al ,2020 |
Obstetrics |
80, RCT |
Prophylactic methoxamine infusion for preventing spinal-induced hypotension in obstetric patients were 2.178 (95% CI 1.564 to 2.680) μg/kg/min and 4.821 (95% CI 3.951 to 7.017) μg/kg/min, respectively. Moreover, it is seemed that the higher dose of methoxamine administered as fixed rate, the more maternal hemodynamic stability and the better neonatal out-comes might be got. |
1b |
A |
|
25 |
Preet M. Singh et al ,2020 |
Obstetrics |
4126. 52RCT,Metaanalysis |
The analysis suggests the possibility that norepinephrine and metaraminol are less likely than phenylephrine to be associated with adverse fetal acid-base status during Caesarean delivery. |
1b |
A |
|
26 |
Man-Ping Yang et al ,2021 |
Obstetrics |
190,RCT |
In patients undergoing elective cesarean section with spinal anesthesia, norepinephrine infusion compared to ephedrine, bolus resulted in less hypotension and tachycardia, and exhibited potential neonatal benefit. |
1b |
A |
|
27 |
Shuqin Ma et al ,2021 |
Obstetrics |
99,RCT |
Prophylactic norepinephrine infusion effectively lowers the incidence of post-spinal anesthesia hypotension and results in overall stability of SBP control, with measurements remaining closer to baseline levels. |
1b |
A |
|
28 |
Weijia Du et al ,2022 |
Obstetrics |
62, RCT |
When administered as a prophylactic fixed-rate infusion, phenylephrine and norepinephrine are both capable of maintaining maternal blood pressure following spinal anaesthesia in twin pregnancies. There were no differences in the maternal hemodynamics or foetal outcomes between women receiving norepinephrine and phenylephrine. |
1b |
A |
|
29 |
S.M. Pouryaghobi et al ,2022 |
Obstetrics |
131,Cross-sectional |
5% of lidocaine with ephedrine can reduce the incidence of hypotension among patients undergoing cesarean section. |
3b |
C |
|
30 |
Osmani SG, et al ,2022 |
Obstetrics |
120, observational study |
Both study drugs – phenylephrine and noradrenaline, when used as prophylactic bolus in patients undergoing cesarean deliveries under spinal anesthesia, are effective in reducing the incidence of bradycardia, hypotensive episodes, and nausea, vomiting. |
2b |
B |
Table 2: The studies included in the review for the guideline.
Discussion
- Prevalence of post spinal hypotension
In the developed world, spinal anesthesia is the most commonly used technique for elective cesarean section, accounting for approximately 78% of procedures; in Ethiopia, without prophylactic measures, the incidence is very high (80%-100%) [12].
Prevention
- Non Pharmacologic
Non-pharmacologic methods could be used to prevent post-spinal hypotension. There are various studies that go into detail about non-pharmacological approaches and their vasopressor requirements. Among these, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted on full-term pregnant women in different years with different authors scheduled for CS, to which the participant was randomly assigned. After a fluid preload of 10 mL per kg of crystalloid, spinal blocks were performed in the sitting position. After administering an intrathecal local anesthetic and positioning the patient supine, leg elevation was performed and maintained until the skin incision was begun. Intraoperative hemodynamic parameters (arterial blood pressure and heart rate), intra-operative ephedrine consumption, PSH incidence, and nausea and vomiting incidence were all recorded. Finally, they conclude that performing leg elevation following spinal anesthesia for a cesarean section significantly reduces the risk of complications [13-15].
The study included 120 parturient (60 lower leg compression technique and 60 control), 76 women (36 sequential compression device and control), and 90 term obstetrics divided into G1 (control), Elastic Crepe Bandage (CB)-G2, and Pneumatic Compression Device (PCD)-G3. Furthermore, 80 patients (40 with a sequential compression device and 40 as controls) were studied in different areas with different sociodemographic data and reproductive histories, as well as electronic monitoring of maternal hemodynamic parameters and neonatal hemodynamic assessment sheets and authors. The groups were compared in terms of maternal hemodynamic changes after spinal anesthesia, nausea, vomiting, and neonatal Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes. Almost all of the Conclusions were related: CB leg wrapping is inexpensive and noninvasive, and a sequential compression device was developed [16-19].
A randomized clinical trial was carried out on 200 pregnant women who had caesarean sections. Pregnant women were divided into two groups: Group 1 (15-degree left lateral incline) and Group 2 (15-degree left lateral incline and leg elevation) (Group 2). Another RCT was conducted with a sample size of 100 pregnant women divided into two equal groups. After SA, the MAP, HR, neonatal APGAR scores, and umbilical cord blood gas analysis, the need for total vasopressor and atropine was recorded until the infant was delivered, every five minutes after delivery until the 30th postpartum minute, and at the end of the surgery. During caesarean sections, positioning the table at a 15-degree incline and maintaining leg elevation may provide maternofetal benefits. By lowering the frequency of post-spinal hypotension in pregnant women and reducing the risk of foetal death. The application of left uterine placement is an important and effective parameter in a maternal care bundle for decreasing [20,21].
- Pharmacologic
Fluid Management
Two comparative cohort study designs were used, with a sample size of 96 mothers (48 of whom were preloaded with 20 ml/kg of fluid 20 minutes before spinal block and 48 of whom were co-loaded with 1000 ml of ringer lactate) participating in the study over two years. According to this study within the respective years, hypotension occurred 77.1% of the time in the preload group and 35.4 percent of the time in the co-load group [22,23 ].
The study was conducted in various areas, with various authors and sample sizes. Full-term parturient were randomized in each study, with the preloading group receiving 15-20 ml/kg of ringer lactate 15-20 minutes before spinal anesthesia administration, and the co-loading group receiving 1000 ml of ringer lactate. Blood pressure and heart rate were measured at 1-minute intervals beginning 1 minute after intrathecal injection and continuing until the first 10 minutes, every 5-minute interval until the next 20 minutes and every 10-minute interval thereafter until the surgery was completed. Co-loading of crystalloid fluids is more effective than preloading of crystalloid fluids in reducing the incidence of hypotension after spinal anesthesia in cesarean patients, according to all studies with similar results. It is also more effective at reducing the need for vasopressors and the occurrence of nausea and vomiting after spinal anesthesia [23-28].
A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing crystalloid co-loading with preload and colloid preloading with crystalloid preloading in women undergoing spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery was performed. Co-loading is superior to preloading for the prevention of maternal hypotension in parturient receiving crystalloid loading in spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery, and colloid preloading is superior to crystalloid preloading for reducing the incidence of hypotension induced by spinal anesthesia and the vasopressor requirement in healthy parturient undergoing elective cesarean delivery, respectively [29,30].
Drug / Vasopressors
Parturient were randomly assigned to either a norepinephrine infusion (0.05 mg/kg/min) just before spinal anesthesia lasting 30 minutes or an ephedrine bolus (0.15 mg/kg) just before spinal anesthesia lasting 30 minutes in a double-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial. A rescue bolus of 5 mg of norepinephrine for the norepinephrine group and 5 mg of ephedrine for the ephedrine group was administered when hypotension happened. In another study, norepinephrine (4 mg/minute) or ephedrine (4 mg/minute) were given immediately after spinal anesthesia with an on-off titration to keep systolic blood pressure (SBP) between 80% and 120% of baseline. In both, study the incidence of hypotension within 30 min of spinal anesthesia administration, the outcomes of both maternal and neonatal outcomes 30 min after spinal block, and neonatal cerebral oxygenation 10 min after birth. Norepinephrine infusion, compared to ephedrine, resulted in less hypotension and tachycardia and exhibited potential neonatal benefits. [31,32].
A prophylactic dose of 0.05 or 0.075 g/kg/min norepinephrine was used in the dose-finding trial. And the effect of 75-mcg vs. 100-mcg phenylephrine doses on the incidence of spinal-induced hypotension prevention by different authors in different years, as well as the adverse effect of drugs with different doses during cesarean section by different authors in different years. A bolus dose of phenylephrine 75 mcg and a dose of 0.05 or 0.075 g/kg/min were found to be effective for the prevention and management of spinal-induced hypotension, respectively [33,34].
In another study, researchers compared the levels of phenyl-epinephrine and norepinephrine in healthy twin term pregnancies undergoing CD under spinal anesthesia. Following spinal anesthesia, either norepinephrine (6 g/mL) or phenylephrine (75 g/mL) was infused at a rate of 60 mL/h to maintain systolic blood pressure (SBP) near baseline until delivery. Anesthesia monitors were used to collect HR, SBP, systemic vascular resistance (SVR), and CO. Also compared were umbilical cord blood gases and adverse events. Both phenylephrine and norepinephrine are capable of maintaining maternal blood pressure following spinal anesthesia in twin pregnancies when administered as a prophylactic fixed-rate infusion [35].
The study focuses on prophylactic methoxamine infusion rates of 1 g/kg/min, 2 g/kg/min, 3 g/kg/min, or 4 g/kg/min. No hypotension exists (maternal SBP is 80% of baseline, or 90 mmHg). To prevent spinal-induced hypotension, obstetric patients were given a prophylactic methoxamine infusion at a fixed rate based on body weight, and it was concluded that the higher the dose of methoxamine administered at a fixed rate, the more maternal hemodynamic stability and better neonatal outcomes could be obtained [36].
Patients who received a prophylactic bolus dose of phenylephrine (100 g) and noradrenaline (8 g) immediately after SA, followed by the same bolus dose to maintain SBP at 90% of baseline, were studied for hemodynamic changes and foetal outcomes; This study looked at maternal hemodynamic variables, the Apgar score, and maternal complications. As a result, while providing greater hemodynamic stability, noradrenaline is as effective as prophylactic phenylephrine in preventing spinal hypotension [37].
An ephedrine infusion was compared to lidocaine 75 mg/5% for spinal anaesthesia; after lidocaine administration, the average blood pressure was measured every 1 minute. When the mean arterial blood pressure dropped by at least 20% of the mean baseline blood pressure 0.1 mg/kg ephedrine was injected intravenously. MAP depletion was common following lidocaine spinal anaesthesia. At a dose of 20 mg, ephedrine is effective in reducing the incidence of perioperative hypotension [38]. GOR-C, LOE-3b A vasopressor drug meta-analysis was performed to assess umbilical arterial base excess, foetal umbilical arterial pH, PCO2, and the occurrence of maternal outcomes. According to the findings, norepinephrine and metaraminol are less likely than phenylephrine to be associated with poor foetal acid-base status during pregnancy [38,39].
The researchers looked at how a sub-anesthetic ketamine dose (0.5 mg/kg IV bolus) affected post-spinal hypotension. HR and MAP were measured at baseline prior to the intrathecal injection, then every 5, 10, 15, and 20 minutes after the injection, and then every 15 minutes until the procedure was completed. Every 5 minutes until the surgery was completed, the total dose of ephedrine required and the Ramsay sedation score were recorded. Subanesthetic ketamine has been shown to be effective in preventing post-spinal hypotension in CS delivery parturients [40].
Finally, HR and blood pressure were measured in the first 15 minutes after the block was placed in the study on the efficacy of atropine to blunt unopposed vagal activity in the prevention of hypotension. A prophylactic bolus of atropine against unopposed vagal activity provided stable hemodynamic values during caesarean spinal delivery [41].
Conclusion
Avoiding hypotension during a spinal anesthesia cesarean section is critical for a successful maternal and fetal outcome. To prevent post-spinal hypotension, pharmacological methods, or drug prophylaxis, are commonly used. It is recommended to use a non-pharmacological approach that includes a sequential compression device (SCD) and left uterine placement.
Recommendations
- Use non-pharmacological approaches as needed: Strong recommendation.
- Make use of crystalloid co-loading 1000ml R/L or N/S, no need of delaying the surgery and spinal anesthesia for fluid preloading: Strong recommendation.
- Use colloid preloading 500ml, because it is superior in decrease the incidence of hypotension, vasopressor requirement, and nausea/vomiting and adverse neonatal outcomes compared with crystalloid preloading: Strong recommendation.
- Utilize a sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine 0.5mg/kg IV bolus, since it has effective agent in preventing post-spinal hypotension: Strong recommendation
- Apply prophylactic bolus atropine 0.5mg IV bolus, because it provided stable hemodynamic values in cesarean spinal delivery: Strong recommendation.
References
- Tawfik MM, Tolba MA (2019) Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia. Anesth Analg 129: e170.
- Chooi C, Jj C, Rs L, Middleton P, Chemali M, et al. (2017) For caesarean section (Review).
- Kestin IG (1991) Spinal anaesthesia in obstetrics. Br J Anaesth 66: 596-607.
- Assessment of sympathetic blockade during spinal analgesia - Google Scholar [Internet].
- KlÖhr S, Roth R, Hofmann T, Rossaint R, Heesen M (2010) Definitions of hypotension after spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section: Literature search and application to parturients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 54: 909-921.
- Higuchi H, Hirata JI, Adachi Y, Kazama T (2004) Influence of Lumbosacral Cerebrospinal Fluid Density, Velocity, and Volume on Extent and Duration of Plain Bupivacaine Spinal Anesthesia [Internet]. Anesthesiology 100: 106-114.
- Langesæter E, Dyer RA (2011) Maternal haemodynamic changes during spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 24: 242-248.
- Hernández MGL, Flórez HJM, Robles SÁ, de Lugan A, Arteaga J (2018) Risk factors for hypotension in regional spinal anesthesia for cesarean section. Role of the waist-to-hip ratio and body mass index. Colombian Journal of Anesthesiology 46: 42-48.
- Mercier FJ, Augè M, Hoffmann C, Fischer C, le Gouez A (2013) Maternal hypotension during spinal anesthesia for caesarean delivery. Minerva Anestesiol 79: 62-73.
- Kirkwood I (1987) Spinal anaesthesia for Caesarean section. Anaesthesia 42: 899-900.
- Yilkal D (2019) Review Article on Prevention and Management of Hypotension in Obstetrics after Spinal Anesthesia Developing country. Journal of Anesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine 8: 8-11.
- Traynor AJ, Aragon M, Ghosh D, Choi RS, Dingmann C, et al. (2016) Obstetric anesthesia workforce survey: A 30-year update. Anesth Analg 122: 1939-1946.
- Marye A, Mesfin E, Endris B (2018) Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery At Two Teaching Hospitals Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery At Two Teaching. Ethiop Med J [Internet] 56:133-140.
- Hasanin A, Aiyad A, Elsakka A, Kamel A, Fouad R, et al. (2017) Leg elevation decreases the incidence of post-spinal hypotension in cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol 17: 1-6.
- Mohapatra S, Swain S, Jena P (2019) Aspiration 07: 779-86.
- Assen S, Jemal B, Tesfaye A (2020) Effectiveness of Leg Elevation to Prevent Spinal Anesthesia-Induced Hypotension during Cesarean Delivery in the Resource-Limited Area: Open Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiol Res Pract 2020.
- Ebrahim Elgzar WT, Ebrahim Said H, Ebrahim HA (2019) Effect of lower leg compression during cesarean section on post-spinal hypotension and neonatal hemodynamic parameters: nonrandomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Nurs Sci 6: 252-258.
- Javaherforooshzadeh F, Pipelzadeh MR, Akhondzadeh R, Adarvishi S, Alghozat M (2020) Effect of sequential compression device on hemodynamic changes after spinal anesthesia for caesarean section: A randomized controlled trial. Anesth Pain Med 10: 1-6.
- Upadhya RK, Shenoy L, Venkateswaran R (2018) Effect of intravenous dexmedetomidine administered as bolus or as bolus-plus-infusion on subarachnoid anesthesia with hyperbaric bupivacaine. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 34: 46-50.
- Singh VK, Agarwal A, Singh V, Singh GP (2022) Use of sequential compression device for prevention of hypotension associated with spinal anesthesia in elective caesarean section. Indian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research 9: 48-53.
- Bolcal Çalisir F, Urfalioglu A, Yücel N, Öksüz H, Öksüz G, et al. (2019) Impact of leg elevation added to a 15° left lateral incline on maternal hypotension and neonatal outcomes in cesarean section: A randomized clinical study. Journal of Surgery and Medicine 3: 689-693.
- Mohammed AAEF, Salem E, Alshawadfy A (2021) Role of left uterine placement in maternal care bundle for the prevention of spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension in cesarean section. Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal 19: 287.
- Hunie M, Wubishet T, Fenta E, Teshome D, Kibret S, et al. (2022) The Effect of Preloading and Co-Loading in the Prevention of Hypotension among Mothers Who Underwent Cesarean Delivery under Spinal Anesthesia: A Prospective Cohort Study 13: 213-218.
- Reshan R (2018) Preloading versus Coloading of Crystalloid Fluid To Control Hypotension Due To Spinal Anesthesia. Int J Adv Res 6: 585-588.
- Chandel DA (2020) Comparison of preloading versus coloading with crystalloid for elective caesarean section done under low dose spinal anaesthesia – A double blind randomised trial. Journal of Medical Science And clinical Research 08: 780-784.
- Made Artawan I, Sarim BY, Sagita S, Dedi MAE (2020) Comparison the effect of preloading and coloading with crystalloid fluid on the incidence of hypotension after spinal anesthesia in cesarean section. Bali J of Anesthesiol 4: 3-7.
- Bhardwaj N, Thakur A, Sharma A, Kaushal S, Kumar V (2020) Comparative Study between Crystalloid Preloading and Coloading for Prevention of Hypotension in Elective Cesarean Section Under Spinal Anesthesia in a Secondary Care Hospital. Inter J of Res and Rev 7: 500.
- Mohammad T, Mozaffor M, Akter S, Miah MAK, Rahman MS, et al. (2021) A Comparison of Using Crystalloid Preloading and Co-Loading in Caesarean Section Operation Under Spinal Anaesthesia and Its Association with Spinal Anaesthesia Induced Hypotension and Heart Rate Variability. J of Dhaka Medical College 29: 12-27.
- Ni HF, Liu HY, Zhang J, Peng K, Ji FH (2017) Crystalloid Coload Reduced the Incidence of Hypotension in Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery, When Compared to Crystalloid Preload: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int 3462529.
- Shang Y, Li H, Ma J, Tan L, Li S, et al. (2021) Colloid preloading versus crystalloid preloading to prevent hypotension after spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Medicine 100: e24607.
- Fan QQ, Wang YH, Fu JW, Dong HL, Yang MP, et al. (2021) Comparison of two vasopressor protocols for preventing hypotension post-spinal anesthesia during cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial. Chin Med J (Engl) 134: 792-799.
- Xu S, Mao M, Zhang S, Qian R, Shen X, et al. (2019) A CONSORT-compliant article. 51(October).
- Chen Y, Zou L, Li Z, Guo L, Xue W, et al. (2021) Prophylactic norepinephrine infusion for postspinal anesthesia hypotension in patients undergoing cesarean section: A randomized, controlled, dose-finding trial. Pharmacotherapy 41: 370-388.
- Jaitawat S, Partani S, Sharma V, Johri K, Gupta S (2020) Prophylactic administration of two different bolus doses of phenylephrine for prevention of spinal-induced hypotension during cesarean section: A prospective double-blinded clinical study. J of Obstetric Anaesthesia and Critical Care 9: 81.
- Du W, Song Y, Li J, Zhou X, Xu Z, et al. (2022) Comparison of Prophylactic Norepinephrine and Phenylephrine Infusions During Spinal Anaesthesia for Primary Caesarean Delivery in Twin Pregnancies: A Randomized Double-Blinded Clinical Study. Drug Des Devel Ther 16: 789-798.
- Fu F, Tang YW, Chen H, Jiao CC, Ma N, et al. (2020) A randomised dose-response study of prophylactic Methoxamine infusion for preventing spinal-induced hypotension during Cesarean delivery. BMC Anesthesiol. 20: 1-10.
- Osmani SG, Acharya M, Kamath SS, Suresh YV, Prabhu K (2022) Comparison of prophylactic phenylephrine versus noradrenaline boluses for hemodynamic stability during elective cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia-an observational study. Anaesthesia, Pain and Intensive Care 26: 168-174.
- Pouryaghobi SM, Mashak B, Kabir K, Hajimaghsoudi L, Ahmadinejad M (2021) Comparison of an ephedrine infusion with lidocaine %5 for prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia in cesarean section. Annals of Medicine and Surgery 73: 103136.
- Singh PM, Singh NP, Reschke M, Ngan Kee WD, Palanisamy A, et al. (2020) Vasopressor drugs for the prevention and treatment of hypotension during neuraxial anaesthesia for Caesarean delivery: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of fetal and maternal outcomes. Br J Anaesth 124: e95-107.
- Salah D, Alansary AM (2020) Impact of sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine on post spinal hypotension in cesarean delivery. Open Anesthesia Journal 13: 86-92.
- Maqbool MS, Ashfaq S (2022) Efficacy of Atropine to Blunt Unopposed Vagal Activity in Prevention of Hypotension in Parturients Undergoing Spinal Caesarean Section. J of Bahria University Medical and Dental College 12: 118-23.
Citation: Seife MA, Geleta BA, Ayano GT, Husen F (2023) Evidence-Based Practice Guideline for Post-Spinal Hypotension Prevention in Cesarean Section in, Review of Article, 2023. J Anesth Clin Care: 10: 079.
Copyright: © 2023 Minda Abebe Seife, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

