
Reconstruction of Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis in Patients Older than 70 Years under Local Anaesthesia
*Corresponding Author(s):
Alina FazlicDepartment Of Anesthesiology, Public Institution, Hospital Of Travnik, Bosnia And Herzegovina, Balkans, United Kingdom
Tel:0038761 614 423,
Email:alina.fazlic@gmail.com
Abstract
Patients older than 70 years old with stenosis of the internal carotid artery, followed by the problems in the function of other systems in the body, are becoming more common patients in our clinic. In this work, we have a case report of a patient with Carotid Artery Stenosis (CAS) (Stenosis ACC et ACI, left ACI stenosis over 80%,right ACI stenosis 70%, Atherosclerosis ACC et ACI, Insuff. Verthebrobasilaris) solve Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) under local anesthesia. Diseases present in a patient, aged 81 years, are: Status post ICV per emboliam /lacunaris/ am X; Hypertensio arterialis gr II; Cor atheroscleroticum chronicum compensatum; Arrythmia absoluta cordis; COPB; Status post infiltratio pulmonum lat.dex. am II; DM typ II; Cholecystitis chronica calculosa.
Keywords
High risic patient; Internal carotid arthery; Local anesthesia; Stenosis
INTRODUCION
Surgery of the large blood vessels is a major challenge for anesthesia. The dramatic disruption physiology builds on the existing complex patient conditions. Vascular surgery requires a temporary interruption of the flow of arterial blood resulting in tissue ischemia, possible organ damage and production anaerobic metabolites [1]. A significant health problem, in the world and in our country, represents cerebrovaskularba disease that is on the top of the causes of death [1,2]. Over 85% of strokes are caused by thromboembolic complications in the heart and/or blood vessels. 90% of ischemia related to the current field of carotid artery. All contributing risk factors: arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ages (people older than 55 years are more prone to diseases of blood vessels), cigarette smoking, genetic predisposition, hyperlipidemia/dislipoproteinemia [3]. Indications for treatment of patients with carotid artery stenosis are set on the basis of several factors: neurological symptoms and the degree of carotid stenosis, comorbidity and high riskiness of the patient and local anatomical features stenosis. As the choice of surgical treatment, CEA has proven to be a safe and effective method of reducing the risk of stroke in patients with a high percentage of stenosis [3,4]. Becouse of the bad general condition of patients, who are increasingly appearing in our clinic, more in practice perform CEA under local anesthesia. The results are very good, the patients during surgery and postoperative care, are less exposed to complications.
CASE REPORT
81 year old patient, a man, coming to our clinic with a referral from a health center under suspicion of cholecystitis. After laboratory results and EHO abdomen, shows us that it is a chronic inflammation of the gallbladder with solitary calculi size of about 15 mm. The medical documentation shows that the patient has CVI before three month. Color Doppler vascular neck showed: Both ACC proper width, lumen 5.9 mm, VPS 270cm/s Ved 58cm/s turbulent flow. 1.5 mm with established atheroplaque diffuse stenosis ACC both sides as well as the initial segments of the ACI. ACI Left stenosis of about 80%, right around 70%. Also with diffuse gentle atheroplaque. ACC right VPS 215cm/s Ved 26cm/s, AVD diameter of 3.0mm, VPS 72cm/s Ved 28cm/s, AVS diameter of 2.6 mm, VPS 54c/s Ved 21cm/s. It is the expressed atherosclerotic changes diffused with turbulent flow and mutual stenosis above as well as the initial segments of ACI. On the right art.verthebralis accelerated flow as a result of extravassal compression, the left retrograde flow (steal phenomenon) with stenosis of the left subclavian artery. Neurological examination: Status post ICV per emboliam/lacunaris/am III, dysphasia sensomotoria bene sanata. The patient conscious, oriented, communicative, mobile, eyeball normal conjugated moving, without nystagmus and double vision, face no asymmetry, the extremity without lateralization, MTR moderate symmetrical, GMS preserved, Babinski reflex mutually negative, in the Romberg discreetly slaughtered (Therapy: Aspirin 150mg tablets 1x1, 1x1 Plavix 75mg tablets).
CARDIAC EXAMINATION
ECG sinus rhythm fr = 73/min, the PQ 0.14, HLV, EF = 44-46%, RR on the right hand of 200/80 mmHg and 160/80 mmHg of the left hand with the diagnosis Cor artheroskleroticum compesatum (in the therapy used: Lanibos 0.125 mg tablets 1x1-no weekends, Lopril-H and 5 mg 0 + 0 + 1/2 tablets, Aldactone 25mg tablets 1x1, NTGR and 2.5mg 1 + 1 + 0 caps, and Controloc 40 mg 1/2 + 0 + 0 tbl.). Pulmonary examination has shown: Status post Insuf.pulmonum hypoventilation acuta aa II; status post effusio cavi pleaurae bill I aa; Status post Bronchopneumonia bill. am X; (Therapy: Onbrez inhalation 2x1 breath, Alvesco 160mg inhalation 2x1 breath) increased airway resistance leads to the lake ventilatory insufficiency predominantly obstructive type. FEV1 Prev3:02, Act1 1.87, (%A/P)61.9%. prolonged expiratory with poliforne whistles, X-ray in PA projection: shadow hearts neat size, hilar differentiated, hemidiaphragm duly reduced, the lung parenchyma no pathological acute activitis and inflammation.
After preparation of the patient, it was decided that surgery will done under local anesthesia. Provide the arterial line (punctio right radial artery with 20-gauge arterial chateter), i.v.canila 14G, ECG, SpO2, spontaneously breathing with oxygen support to the mask, Mannitol 20% 250ml, total liquid 0.9% NaCl 750 ml, 5000 IU of Heparin. The initial blood pressure was 200/120 mmHg, fr 80/min, SpO2 100%. During surgery, the patient was, all time, conscious and communicative. Apply on Xilocain to achieve anesthetic action left carotid region. Access to the ACC, ACI and ACE left with facial vein ligation and preservation n. hypoglossus (Figures 1 and 2).
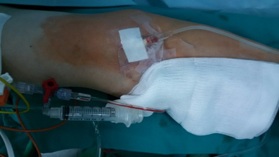 Figure 1: Punctio right radial artery.
Figure 1: Punctio right radial artery.
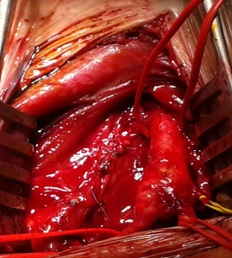 Figure 2: Stenosis of the left internal artery carotidne.
Figure 2: Stenosis of the left internal artery carotidne.
The taxidermist is difficult because of inflammatory changes in the individual layers of the left carotid region. Also recorded anatomical dislocation of nerve and vascular structures that hamper the preparations. During the operation there was no neurological disturbances. At one point, blood pressure rises up to 275/140 mm Hg, the patient was conscious, communicative, without any problems, answer all questions. Clamping mentioned artery endarterectomy everzion bifurcation and ACI and then TL anastomosis ACI on bifurcation ACC thread Prolene 5/0. Clamping time was 10 min. Arterial pressure 170/110 mmHg. At the end of surgery, blood pressure was 130/52 mmHg (Figures 3 and 4).
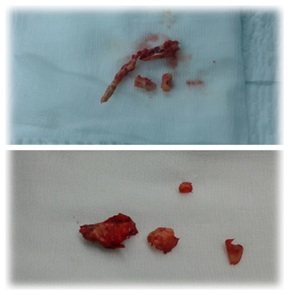 Figure 3: Atherosclerotic plaque.
Figure 3: Atherosclerotic plaque.
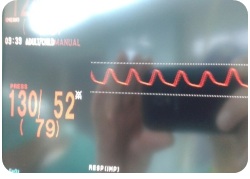
Figure 4: Blood pressure at the end of surgery.
DISCUSSION
Early diagnosis and treatment are of utmost importance for the patients. Sometimes, diagnosis can be challenging in patiazents without neurological symptoms, in particular. Radak et al., showed that 31,9% of cases are asymptomatic at the time diagnosis [5]. The first step in the diagnosis is Doppler ultrasound, which is a simple and noninvasive imaging modality. Also, artheriography is the gold standard for thrombus location and collateral circulation [6]. The primary indication for surgery is the prevention for permanent neurological damege from thromboembolic events [7]. However, a many patientsdo not have any simptoms and that resulted with stroke. Our patient, is recovering from a stroke, but the problem arises when you have the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder without solution of stenosis of the internal carotid artery. Having in mind that this is a surgery in which the required clamping the carotid artery, and that the most patients have advanced coronary disease, anesthesia must be balanced so that: prevent drastic hemodynamic disturbances on the introduction of anesthesia during the operation, as well as during waking and extubation, and the provide patient wakefulness at the end of the operation and the ability to carry out controls during neurological assessment [8]. Seeing the general situation of our patients, we decided to use a local anesthetic that has proven safety for our patient.
REFERENCES
- Jukic M, Husedžinovic I, Kogler VM, Peric M, Žunic J, et al. (2013) Klini?ka anesteziologija. Medicinska Naklada, Serbia, Balkans. Pg no: 1180.
- Europien Registers of Stroke (EROS) Investigators, Heuschmann PU, Di Carlo A, Bejot Y, Rastenyte D, et al. (2009) Incidence of stroke in Europe at the beginning of the 21st century. Stroke 40: 1557-1563.
- Larsen R (2012) Anästhesie und Intensivmedizin in der Herz-,Thorax- und Gefäß 8 Auflage: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, New York, USA.
- Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, Fox AJ, Taylor DW, et al. (2003) Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet 361: 107-116.
- Radak D, Davidovic L, Vukobratov V, Ilijevski N, Kostic D, et al. (2007) Carotid artery aneurysms: Serbian multicentric study. Ann Vasc Surg 21: 23-29.
- Windfuhr JP (2001) Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery following soft tissue penetration injury. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 61: 155-159.
- Szopinski P, Ciostek P, Kielar M, Myrcha P, Pleban E, et al. (2005) A series of 15 patients with extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: surgical and endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 29: 256-261.
- Millers RD, Eriksson LI, Fleisher LA, Wiener-Kronish J, Young W (2009) Miller's Anesthesia (7thedn). Churchill Livingstone, London, United Kingdom.
Citation: Fazlic A, Zuko M, Sokic-Begovic E, Suskic S, Suskic A (2019) Reconstruction of Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis in Patients Older than 70 Years under Local Anaesthesia. J Anesth Clin Care 6: 44.
Copyright: © 2019 Alina Fazlic, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

