
Single-Shot Sub-Dissociative Dose Ketofol versus Ketamine Alone for Emergency Department Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in Adult
*Corresponding Author(s):
Shihab AL SheikhEmergency Department, Rashid Hospital Trauma Center, Dubai Health Authority, United Arab Emirates
Tel:+971 4 219 1000,
Email:shamahdi@dha.gov.ae
Abstract
Study Objective: To compare the recovery time, effectiveness, adverse events and patient satisfaction between I/V mixed 0.5:1 Ketofol (Ketamine and Propofol) and Ketamine alone for adult Procedural sedation and Analgesia (PSA) in Emergency Department.
Methods: Prospective randomized data were collected in 100 patients above 14 years of age over six months, the patients presented with various types of injuries which needed PSA. Half of them (50%) were given Ketofol and other half Ketamine. Head injury patients, pregnant women, hemodynamically unstable patients and history of allergy to the drugs used were excluded from the study. All the procedures were carried out in ED with all facilities of resuscitation. Informed consent was taken from each patient. We mixed 10ml Propofol (10mg/ml) plus 1ml Ketamine (50mg/ml) plus 9ml of normal saline in 20 ml syringe so for each ml of this mixture contains 2.5mg Propofol plus 5mg Ketamine. Ketofol was given in a dose of 1ml per 5Kg of patient body weight and Ketamine given in a dose of 1mg per Kg. The total calculated dose of Ketofol or Ketamine must be given with a one minute. All the required parameters were recorded in the prescribed forms, and results were tabulated and compared.
Results: 50% of patients received Ketofol, and 50% received Ketamine. The most commonly performed procedures were orthopaedic, comprising 95% of both groups and mostly shoulder dislocation 49% secondly elbow dislocation 22 % and thirdly Colles` fracture. Seven patients (14%) of Ketamine and three patients (6%) Ketofol required additional doses to complete the procedure.80% of Ketofol group patients and 66% of the ketamine group patients did not exhibit hypoxia signs. In Ketofol group, 92% of patients had no complications while in the Ketamine group, 48% did not show any complications. Recovery time was less than 30 minutes in 92% of Ketofol group and 62% in the Ketamine group. 82% of the Ketofol group and 72% in the Ketamine group with zero visual analog scales. Patient satisfaction was 10/10 in 90% of the patient from Ketofol group while 56% in the Ketamine group.
Conclusion: When compared with Ketamine alone for PSA in ED settings, the Ketofol with rapid onset of action, faster recovery time, cardio respiratory stability, less adverse events, and high patient satisfaction level make it a better option.
Keywords
Ketamine; Ketofol; Procedural sedation and Analgesia; Sub-dissociative dose
Introduction
Background
Procedural sedation and analgesia is a crucial component in the emergency department for a painful procedure. Many studies recently proved that the combination of Ketamine and Propofol is safe and effective for procedural sedation and analgesia (PSA) [1-4].
Propofol has a rapid onset of sedation and short duration of action. This nonbarbiturate, non opioid, sedative-hypnotic agent has amnestic but no analgesic properties [5]. Propofol is associated with a dose-depended risk of respiratory depression, and this risk appears to be heightened with concomitant opioid use [6]. Ketamine is a unique sedative agent that causes dissociation between the thalamic and limbic systems of the brain. At doses commonly used for procedural sedation (1 to 1.5 mg/kg), Ketamine produces a trance-like cataleptic state [7], whereas at sub dissociative doses (0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg; most commonly 0.3 mg/kg) it maintains potent analgesic and amnestic effects that are accompanied by preservation of protective airway reflexes, spontaneous respiration, and cardiopulmonary stability [8-10].
Many studies reveal that mixing Ketamine and Propofol will synergy the effect and balanced the side effect of each other [11-13]. Propofol can be associated with dose-dependent hypotension and respiratory depression [14]. Ketamine is known to preserve respiratory drive, and its sympathomimetic properties increase blood pressure [15]. Ketamine is emetogenic, and Propofol has intrinsic antiemetic properties [16]. Post procedural agitation is a common complication of ketamine sedation, where Propofol is known to be an anxiolytic [17]. Furthermore, the addition of Ketamine provides an analgesic effect that is lacking in a propofol-only procedural sedation and analgesia regimen [18].
The Mixture of Ketamine and Propofol at 50:50 and 30:70 ratios were physically compatible and chemically stable for up to 3 hours when stored in capped polypropylene syringes at room temperature with exposure to light [19].
Importance
If the combination of Ketamine/Propofol is safer or more effective than Ketamine alone, it would be preferred for procedural sedation and analgesia in ED.
Goals of this study
We want to compare the total sedation and full physiological recovery time (SRT) of Ketofol and Ketamine alone in ED for procedural sedation and analgesia according to the Quebec guideline (end of induction phase to end of physiologic recovery phase), (Figure 1) [20].
The secondary outcomes were the time of onset, hypoxia incidence, cardiovascular changes, adverse events, Visual analog pain scale, and patients' satisfaction scores.
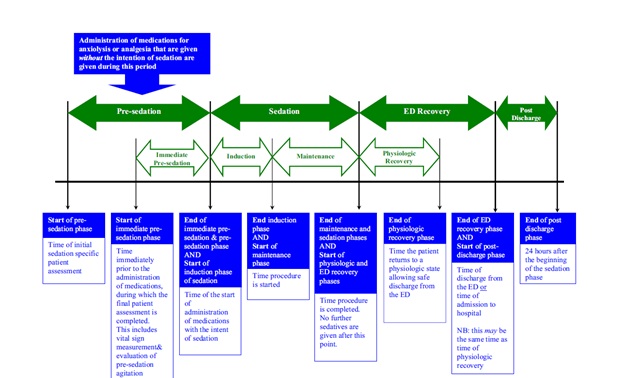 Figure 1: Sedation Time Interval.
Figure 1: Sedation Time Interval.
Materials and Methods
Study design
This is a prospective randomized controlled trial of adults receiving procedural sedation and analgesia from April 2019 until September 2019 in the ED of a 700beds trauma center Rashid hospital with an annual census of 160,000 patient visits. The study was approved by the medical research committee of Dubai health authority, and informed consent was obtained from all participants or first-degree relative.
Selection of participants
Eligible patients were identified by the treating emergency physicians according to inclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria include patients aged 14 years old or older, and the American Society of Anaesthesiology class 1 to 2 status and patients of any country of origin. Exclusion criteria consisted of hemodynamic instability; pregnancy; head injury; intoxication; an allergy to egg, soy and study medicine; and other traditional ketamine contraindication.
Intervention
A hundred patients were randomized to either Ketamine/Propofol or Ketamine alone using a fixed 1:1 allocation ratio determined by a computer-based random number generator. Small, random block sizes of 4 were used to ensure equal allocation to each treatment arm. All procedural sedation and analgesia events required the attendance of one certified emergency physician (treating doctor), two registered nurses and whenever possible, a second certified emergency physician (sedating doctor) assigned to the administration of the PSA medication was also present. Ketofol was prepared as a 0.5:1 mixture of 1ml of 50mg/ml Ketamine plus 10ml of 10mg/ml propofol plus 9ml normal saline into a single 20ml polypropylene syringe. Thus, each one milliliter of Ketofol solution contained 2.5mg ketamine and 5mg Propofol and the dosage given to the patients was 1ml of Ketofol solution per 5kg of patient body weight.
Ketamine prepared as a mixture of 2ml of 50mg/ml Ketamine plus 18ml intra-lipid solution in 20 ml polypropylene syringe. Thus, each milliliter of ketamine solution contained 5mg Ketamine also the dosage given to the patients was 1ml of Ketamine solution per 5kg of patient body weight. The total calculated dose of Ketofol or Ketamine must be given with a one minute. All procedures were performed in the ED in an area equipped with continuous Oxygen saturation, cardiac monitoring and complete airway and resuscitation cart.
Preprocedural analgesia was administered by the emergency doctor according to the clinical judgment to control the patient's pain when arrival to the ED but a minimum 30-minute washout period between administering any opioid analgesic and the commencement of the procedural sedation and analgesia procedure was mandated. Patients were given supplemental oxygen if pulse oximetry value less than 90% and do not improve by vigorous tactile stimulation and airway repositioning.
Data collection and processing
The standardized procedural and analgesia datasheet was used for all procedures conducted and was completed by the registered nurse and supervised and signed by attended emergency physician. The information collected included three stages.
The first stage: include presedation documentation like ID number, chief complaint, fasting time for liquid and food, vital signs cardio respiratory examination.
Second stage: include sedation documentation type of procedure performed, any pre procedural medication, weight, the total dose of procedural medication, time of onset, vital sign( pulse rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, systolic, diastolic and mean blood pressure) recorded by the cardio respiratory monitor (NIHON KOHDEN TEC -8300 series), modified Ramsay sedation scale (Table 1), available online at http://www.annemergmed.com) and visual analogue scale every 5 minutes and any adjunctive medication was given.
Third stage: post sedation documentation or recovery time (recovery time was define as the time when the procedure is completed till a cumulative score of 9, with minimum scores of 2 for the respiratory and oxygen saturation parameters according to the modified Aldrete Recovery Scale (Table 2), available online at http://www.annemergmed.com), patient satisfaction, recall of procedure and agreement about the sedation, lastly the fate of the patient.
All adverse events are reported according to the Quebec guidelines 14 and documented by the attending physician on standardized datasheet with specific events checkboxes and free-text area for any other events could be recorded.
|
Score |
Patient Response |
|
1 |
Anxious or restless or both |
|
2 |
Cooperative, orientated and tranquil |
|
3 |
Asleep - responds quickly to normal voice commands |
|
4 |
Asleep - no response to normal voice - brisk response to loud voice, or light forehead tap |
|
5 |
Asleep-no response to above - shows sluggish response to loud voice or light forehead tap |
|
6 |
Asleep - no response to loud voice or forehead tap - sluggish purposeful response to pain only |
|
7 |
Reflex withdrawal (not purposeful) to pain only |
|
8 |
No response, even to pain |
Table 1: Ramsay Sedation Scale.
|
Parameter |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Level of consciousness/sedation |
Nonresponsive, or responsive only to painful stimuli |
Responds to verbal stimuli but falls asleep readily |
Awake and orientated (child oriented to parent), or equivalent to preoperative status |
|
|
Circulation |
Systolic BP <100 mm Hg |
Systolic BP >100 mm Hg |
Systolic BP within normal limits for patient |
|
|
Respiration |
Apneic: requires airway support |
Shallow, irregular breathing |
Able to breathe deeply and cough on command or equivalent to preoperative status |
|
|
Oxygen saturation |
SpO2 ≤92% on oxygen |
SpO2>92% on oxygen |
SpO2≥94% on room air or equivalent to preoperative status |
|
|
Activity level |
Unable to lift head or move extremities voluntarily or on command |
Lifts head or moves extremities on command |
Lifts head and moves all extremities spontaneously. Is able to ambulate consistent with surgical procedure or equivalent to preoperative status. |
|
|
SP02, Oxygen saturation; BP, blood pressure. *Recovery criteria: minimum score of 8, with a minimum of 2 in respiratory and oxygen saturation. |
||||
Table 2: Modified Aldrete Recovery Scale*.
Primary data analysis
Data are reported using descriptive statistics (IBM SPSS STATISTICS19). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD. Differences in the average (SRT) in minutes between the two groups of patients were tested using t-test. The results were considered to be significant if p < .05 and are presented with 95% CIs.
Since the results of the F test (Levene’s test) for evaluating the equality of variance has a p-value of 0.002, which indicates that the variances are significantly different, The independent samples t-test assuming unequal variances was performed to test the hypothesis that the average SRT time in minutes of the two groups of patients given Ketamine and Ketofol was equal.”
Results
Characteristics of the study subjects
This study was conducted during six months, in which 100 patients were enrolled for procedural sedation and analgesia with Ketofol and Ketamine for a painful procedure in the ED. The two groups were similar in demographics and baseline characteristics (Table 3).
|
Characteristics |
Ketofol ( n = 50 ) |
Ketamine ( n = 50 ) |
Total ( n = 100 ) |
|
Age, years ( mean ± SD ) |
31.1 ± 8.4 |
30.4 ± 11.9 |
30.7 ± 10.2 |
|
Gender ( % ) · Female · Male |
6 ( 12 ) 44 ( 88 ) |
2 ( 4 ) 48 ( 96 ) |
8 ( 8 ) 92 ( 92 ) |
|
Weight, Kg ( mean ± SD ) |
76.8 ± 15.2 |
67.7 ± 17.3 |
72.2 ± 16.8 |
|
Baseline vital signs ( mean ± SD ) · Pulse rate (Br/min) · Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) · Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) · Mean arterial pressure (mm Hg) · Respiratory rate (Br/min) · A pulse oximeter (% of oxygen saturation) |
87.2 ± 17.1 136.9 ± 22.1 84.5 ± 15.8 98.8 ± 15.7 19.3 ± 3.2 99.3 ± 1.3 |
89.5 ± 16.4 134.0 ± 16.5 82.6 ± 11.9 97.8 ± 12.3 18.7 ± 3.0 99.2 ± 1.5 |
88.4 ± 16.7 135.5 ± 19.5 83.5 ± 13.9 98.3 ± 14.1 19.0 ± 3.1 99.2 ± 1.4 |
|
Time since last meal, hours ( mean ± SD ) |
5.9 ± 3.0 |
5.4 ± 2.5 |
5.7 ± 2.7 |
|
Time since last drink, hours ( mean ± SD ) |
3.8 ± 2.6 |
3.3 ± 2.6 |
3.5 ± 2.6 |
|
The preprocedural dose of Morphine ( mean ± SD ) |
2.5± 3.9 |
2.0± 3.2 |
2.2± 3.5 |
|
Ketamine dosage, mg ( mean ± SD ) |
37.3 ± 7.5 |
68.3 ± 17.5 |
52.8 ± 20.5 |
|
Propofol dosage, mg ( mean ± SD ) |
75.7±14.9 |
0000 |
75.7±14.9 |
|
Total sedation and Recovery time, min ( mean ± SD ) |
19.7 ± 5.0 |
27.4 ± 9.1 |
23.6 ± 8.3 |
Table 3: Baseline characteristics of study subjects.
The most commonly performed procedures were orthopedic, comprising 95% of both groups and mostly shoulder dislocation 49% secondly elbow dislocation 22 % and thirdly Colles` fracture, (Table 4). 57% of the study patients were from South Asia country, and 13% were from UAE (Table 5).
|
Diagnosis (group) |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Shoulder dislocation |
49 |
49 |
|
Elbow dislocation |
22 |
22 |
|
Colles fracture |
11 |
11 |
|
Hip dislocation |
3 |
3 |
|
Patella dislocation |
3 |
3 |
|
Lock jaw |
2 |
2 |
|
Bilateral fracture of femur shafts |
2 |
2 |
|
Ankle dislocation |
2 |
2 |
|
Knee joint dislocation |
1 |
1 |
|
Suturing & removing FB |
1 |
1 |
|
Lacerated wound in the scalp |
1 |
1 |
|
Right pneumothorax |
1 |
1 |
|
Left gluteal abscess |
1 |
1 |
|
Burn on the lower limb |
1 |
1 |
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
Table 4: Diagnosis.
|
Nationality (grouped) |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
South Asia |
57 |
57 |
|
UAE |
13 |
13 |
|
Arab countries |
12 |
12 |
|
Rest of Asia |
6 |
6 |
|
West |
5 |
5 |
|
Unclassified |
4 |
4 |
|
Others |
3 |
3 |
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
Table 5: Nationality.
Three patients with epilepsy, two with diabetic mellitus, two asthmatic and 88% without any prior medical history, and (Table 6). 32% of the patients are given narcotics, and 19% were given Voltaren as preprocedural pain management. 8% of the patients were given Maxolon as post procedural treatment. Only three patients required an additional dosage of Ketofol to complete the intended procedure, and seven patients required an additional dosage of Ketamine only.
|
Present illness |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Nil |
88 |
88 |
|
Epilepsy |
3 |
3 |
|
Asthmatic |
2 |
2 |
|
Diabetes mellitus |
2 |
2 |
|
Hypertension |
1 |
1 |
|
Depression |
1 |
1 |
|
Thyroid disease |
1 |
1 |
|
Myasthenia gravis |
1 |
1 |
|
Duodenal ulcer |
1 |
1 |
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
Table 6: Present illness.
For our primary outcome, “The average SRT ( minutes ) of the group of patients given Ketamine ( M = 27.4 min , SD = 9.1, N = 50 ) is significantly different from the group of patients given Ketofol ( M = 19.7 min, SD = 5.0, N = 50 ), t ( 76 ) = 5.24, p < 0.0001, 95% confidence Interval is ( 4.78, 10.63 ), (Figure 2). The number of patients discharged over time is more in the Ketofol group than the ketamine group, and patients are discharged sooner in the Ketofol group (20 min) compared to the Ketofol group (30min), (Figure 3).
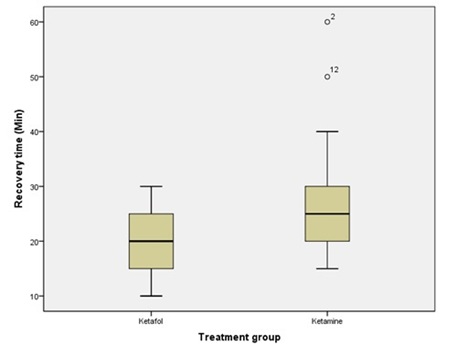 Figure 2: RST time (mins) by treatment group for 100 procedural sedations. Circles indicate outliers.
Figure 2: RST time (mins) by treatment group for 100 procedural sedations. Circles indicate outliers.
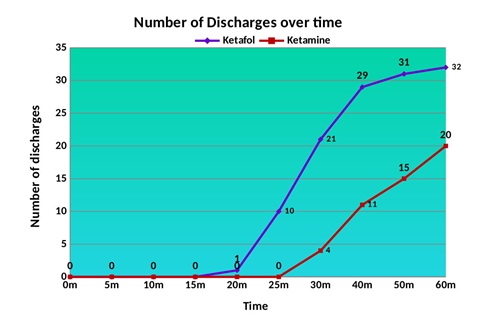 Figure 3: Number of discharges over time.
Figure 3: Number of discharges over time.
For our secondary outcome, The average time of onset (sec) of the group of patients given Ketamine ( M = 47.8 sec, SD = 23.4, N = 50 ) is significantly different from the group given Ketofol ( M = 35.5 sec, SD = 13.6, N = 50 ), t ( 98 ) = 3.202, p = 0.002, 95% confidence Interval is ( 4.6, 19.9 ), (Figure 4).
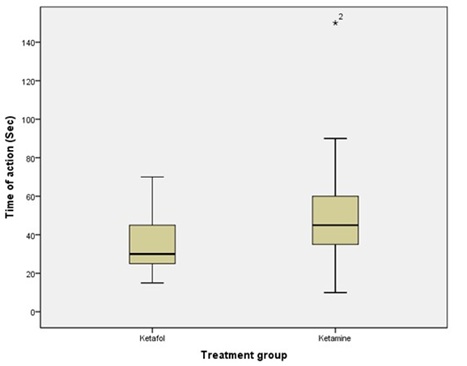 Figure 4: Time of onset (sec) by treatment group for 100 procedural sedations. Asterisks indicate extreme cases.
Figure 4: Time of onset (sec) by treatment group for 100 procedural sedations. Asterisks indicate extreme cases.
The hypoxia incidence was 21.6% in Ketofol group compared to 34% in the Ketamine group but patient in either group not required bag-valve ventilation, tracheal intubation, or any airway intervention other than airway repositioning or increased oxygen supplement. The average percentage of oxygen saturation of the patients' given Ketamine is lower than the average for the Ketofol patients, except at 5 minutes (Figure 5). However, the patients' average respiratory rate given Ketamine is more or less the same as the Ketofol patients' a (Figure 6).
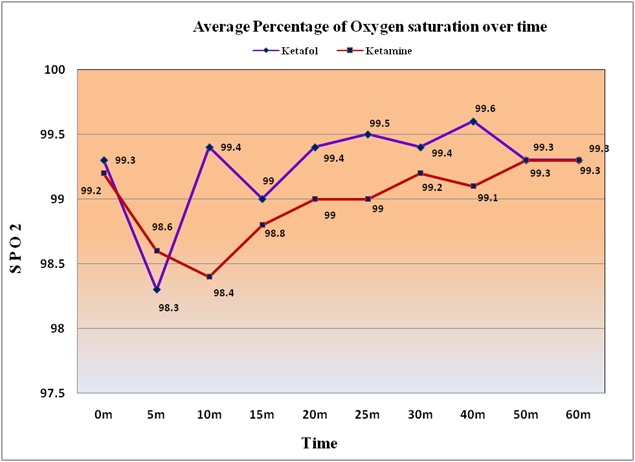 Figure 5: The average percentage of oxygen saturation of the patients given Ketamine is lower than the average for the Ketafol patients, except at 5 minutes.
Figure 5: The average percentage of oxygen saturation of the patients given Ketamine is lower than the average for the Ketafol patients, except at 5 minutes.
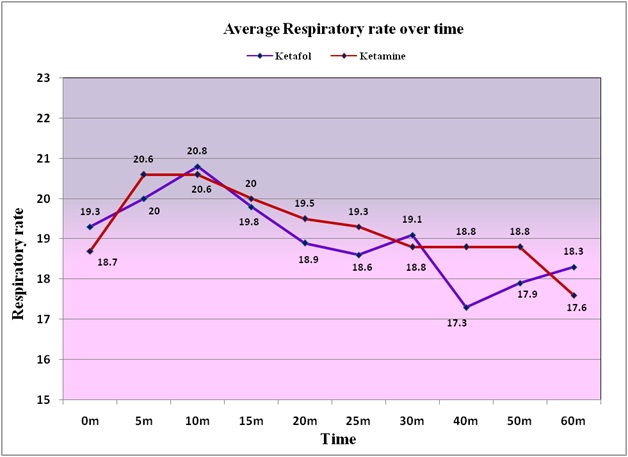 Figure 6: The average Respiratory rate of the patients given Ketamine is more or less the same as the average for the Ketafol patients.
Figure 6: The average Respiratory rate of the patients given Ketamine is more or less the same as the average for the Ketafol patients.
Cardiovascular changes are compared between two groups during procedural sedation and analgesia and summarized as the average pulse rate of the patients given Ketamine is consistently more than the average for the Ketofol patients, except at 30 minutes after treatment (Figure 7).
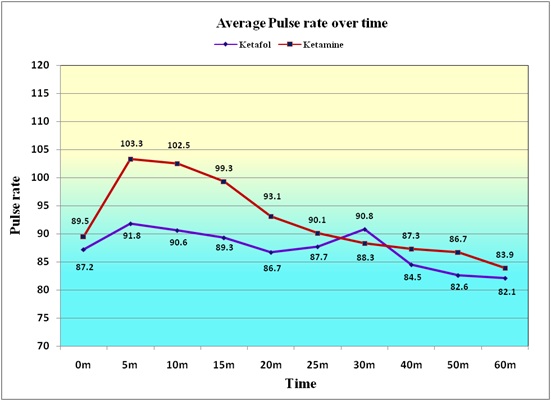 Figure 7: The average pulse rate of the patient given Ketamine is consistently more than the average for the Ketafol patients, except at 30 minutes after treatment.
Figure 7: The average pulse rate of the patient given Ketamine is consistently more than the average for the Ketafol patients, except at 30 minutes after treatment.
The average SBP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketofol patients up to 25 minutes, and the average is lower than the Ketofol group after 25 minutes after treatment (Figure 8).The average diastolic BP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketofol patients up to 30 minutes, and the average is lower than the Ketofol group from 40 minutes after treatment (Figure 9). The average MAP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketofol patients up to 30 minutes, and the average is lower than the Ketofol group from 40 minutes after treatment (Figure 10).
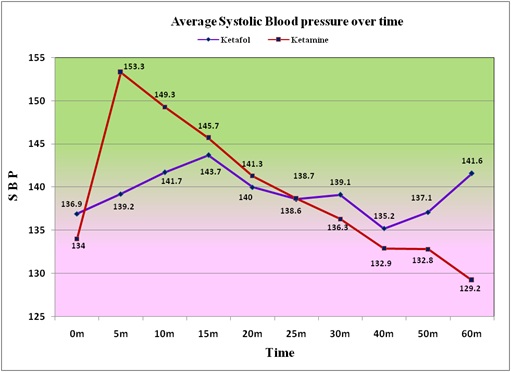 Figure 8: The average SBP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patient’s up to 25 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group after 25 minutes after treatment.
Figure 8: The average SBP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patient’s up to 25 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group after 25 minutes after treatment.
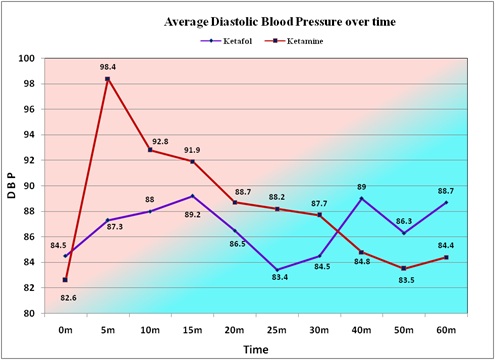 Figure 9: The average Diastolic BP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patient’s up to 30 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group from 40 minutes after treatment.
Figure 9: The average Diastolic BP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patient’s up to 30 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group from 40 minutes after treatment.
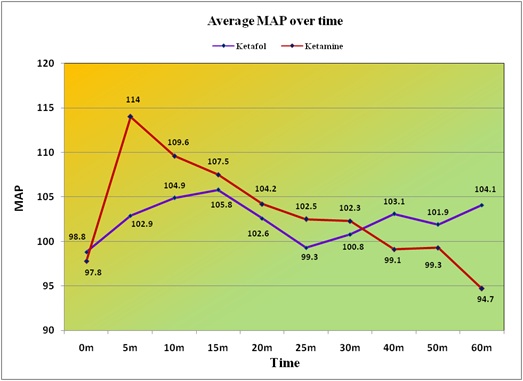 Figure 10: The average MAP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patients’ up to 30 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group from 40 minutes after treatment.
Figure 10: The average MAP of the patients given Ketamine is more than the average for the Ketafol patients’ up to 30 minutes and the average is lower than the Ketafol group from 40 minutes after treatment.
Just 4 (8%) patients given Ketofol experienced post procedural adverse events compared with 26 (52%) given Ketamine experienced post procedural adverse events (Table 7). During PSA, visual analogue pain scaleis summarized in (Table 8), revealing 82% of Ketofol patients and 72% Ketamine patients showing zero visual analogue scales. Patient satisfaction score (0=unsatisfied; 10=satisfied) 90% of the Ketofol patients gave a ten score for satisfaction, and 56% of the Ketamine patients gave a ten score for satisfaction.
|
Adverse Events |
Treatment group |
Size effect |
||
|
Ketofol |
Ketamine |
|||
|
Hypoxia |
21.60% |
34% |
0.26(0.12_0.66) |
|
|
Emergency reaction |
6.00% |
20.00% |
0.4 (0.23_0.81) |
|
|
Drowsiness |
0.00% |
14.00% |
0.56(0.16_0.96) |
|
|
Vomiting |
2.00% |
10.00% |
0.29 (0.99_0.68) |
|
|
Muscular hypertonicity |
0.00% |
4.00% |
0.28 (-0.10_0.67) |
|
Table 7: Adverse Events Table.
|
Visual analog scale |
Treatment group |
Total |
||
|
Ketafol |
Ketamine |
|||
|
No pain |
41, 82.0% |
36,72.0% |
77, 77.0% |
|
|
Slight |
4, 8.0% |
8,16.0% |
12, 12.0% |
|
|
Mild |
5, 10.0% |
3,6.0% |
8,8.0% |
|
|
Moderate |
0, 0% |
2,4.0% |
2, 4.0% |
|
|
Sever |
0,.0% |
1,2.0% |
1, 2.0% |
|
|
Horrible |
0,.0% |
0,.0% |
0, .0% |
|
|
Total |
50, 100% |
50, 100% |
100, 100.0% |
|
|
Interpretation: 82% of Ketofol patients while 72% of Ketamine patients felt no pain. |
||||
Table 8: Visual analog scale by Treatment group.
Limitations of the Study
It was a single-center study in which patients were enrolled as a convenience sample according to predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The paediatric population was not included in the study as PSA requirement is more in this age group. The sample size was near minimum for adequate power (95%) with a confidence interval (10%).The study did not contain a Propofol only arm, and thus we are unable to comment on whether Ketofol has any advantage over Propofol alone.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first prospective randomized controlled study comparing single-shot sub-dissociative dose ketofol versus Ketamine alone for adults’ procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department setting. The typical PSA should provide credible onset with an expected depth of sedation, a short duration of action and rapid, uneventful recovery.
The total sedation time and full physiological recovery (SRT) of Ketofol group were significantly faster than in the Ketamine group, but how far it is of clinical value? So if we compare the recovery times from procedural sedation and analgesia induced by intravenous ketamine range between 50 – 110 minutes [21], to that induced by Ketofol range between 8-15 minutes [1, 12, 22]. As a result, we had hypothesized a 10-minutes difference as clinically meaningful, shown in (Figure 3), where the number of patients discharged overtime is 10 minutes more in the Ketofol group than the ketamine group.
The incidence of hypoxia in Ketofol group was 21.6% which was acceptable compared to the incidence of hypoxia with 3-arm randomized trial done by Miner et al [23]. They report the incidence as Propofol alone was 29%, Ketofol formulation: 1:1 was 19%, and 1:4 was 32%. Higher incidence of hypoxia in the ketamine group (34%), Miner et al [23] detected a higher rate of subclinical respiratory depression in patients sedated with Ketamine than in patients sedated with Propofol. It is well known that rapid intravenous infusion of Ketamine has the potential to cause apnea [24]. Ketamine is an attractive PSA drug, especially in paediatric age group but in massive doses or combined with other sedative agents; however, respiratory depression and apnea can occur [25-27]. Independent idiosyncratic effects seen after iatrogenic administration include laryngospasm, hypersalivation, and bronchorrhea [28-30]. Generally, the average percentage of oxygen saturation of the patients given Ketofol is higher than the average for the Ketamine patients. It justified by rapid onset and extremely short half-life of Propofol and sub dissociative doses of Ketamine which do not have anaesthetic effects but rather has analgesic effects [30], except at 5 minutes when the maximum effect of the Propofol induces mild respiratory depression but of no significant clinically. In Fact, during PSA in adults’ breathing room air, desaturation detectable by pulse oximeter usually occurs before overt changes in capnometry are identified [31].
There were no reported cases of significant cardiovascular adverse events in this study in either treatment group. The average of the pulse rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial blood pressure is consistently normal more in Ketofol group than Ketamine patients. Indicates that the patients with Ketofol group are cardiovascular stable than Ketamine group except after 30 minutes when the patient of Ketofol group start wake up and probably feel of the pain there are an increase in pulse rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial blood pressure.
The adverse events of our trail show an effective synergy between Ketamine and Propofol agents. Patients in the Ketamine group exhibited nausea and vomiting in 10% of cases, the incidence of which is estimated to be between 5% and 15% in adults [24], compared with only 2% of cases in the Ketofol group similar finding in Shah et al. [18]. The incidence of problematic recovery agitation in adults receiving Ketamine is estimated to be between 10% and 20% [24].Our study was 20% in the Ketamine group compared to 6% in Ketofol group this difference confirm the blunting effect of the Propofol in inhibiting the emergence reaction of the Ketamine. The same blunting effect was justified about muscle hypertonicity during the Ketamine group PSA, which was 4% compared with nil in the Ketofol group.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when compared with Ketamine alone for adult procedural sedation and analgesia in emergency department setting, the Ketofol with rapid onset of action, faster recoveries with essential cardio respiratory stability, less adverse events, and more comfortable the patient during the procedure and better score of patient satisfaction.
References
- Willman EV, Andolfatto G (2007) A prospective evaluation of “ketofol” (ketamine/propofol combination) for procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med 49: 23-30.
- Sharieff GQ, Trocinski DR, Kanegaye JT, Fisher B, Harley JR (2007) Ketamine-propofol combination sedation for fracture reduction in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatric Emerg Care 23: 881-884.
- Mortero RF, Clark LD, Tolan MM, Metz RJ, Tsueda K, et al. (2001) The effects of small-dose Ketamine on propofol sedation: respiration, postoperative mood, perception, cognition, and pain. Anesth Analg 92: 1465-1469.
- Frizelle HP, Duranteau J, Samii K (1997) A comparison of Propofol with a Propofol- ketamine combination for sedation during spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg 84:1318-1322.
- Mace S (2006) Propofol. Agents for procedural sedation. In: Mace S, Ducharme J, Murphy M, eds. Pain Management and Sedation. Emergency Department Management. McGraw- Hill, New York 114Y120.
- Messenger DW, Murray HE, Dungey PE, Vlymen J, Sivilotti MLA (2008) Sub dissociative dose ketamine versus fentanyl for analgesia during propofol procedural sedation: a randomized clinical trial. Acad Emerg Med 15: 877-886.
- Guldner GT, Petinaux B, Clemens P, Foster S, Antoine S (2006) Ketamine for procedural sedation and analgesia by nonanesthesiologists in the field: a review for military health care providers. Mil Med 171: 484-490.
- Galinski MM, Dolveck FM, Combes XM, Limoges V, Smaïl N, et al. (2007) Management of severe acute pain in emergency settings: Ketamine reduces morphine consumption. Am J Emerg Med 25: 385-390.
- Strigo I, Duncan G, Bushnell C, Boivin M, Wainer I, et al. (2005) The effects of racemic Ketamine on painful stimulation of skin and viscera in human subjects. Pain 113: 255-264.
- Smith D, Mader TJ, Smithline HA (2001) Low dose intravenous ketamine as an analgesic: a pilot study using an experimental model of acute pain. Am J Emerg Med 19: 531-532.
- Badrinath S, Avramov MN, Shadrick M, Witt TR, Ivankovich AD (2000) The use of a ketamine-propofol combination during monitored anesthesia care. Anesth Analg 90: 858-862.
- Akin A, Guler G, Esmaoglu A, Bedirli N, Boyaci A (2005) A comparison of fentanyl-propofol with a Ketamine- propofol combination for sedation during endometrial biopsy. J Clin Anesth 17: 187-190.
- Erden IA, Pamuk AG, Akinci SB, Koseoglu A, Aypar U (2009) Comparison of propofol-fentanyl with propofol-fentanyl-ketamine combination in pediatric patients undergoing interventional radiology procedures. Paediatr Anaesth 19: 500-506.
- White PF, Way WL, Trevor AJ (1982) Ketamine-its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology 56: 119-136.
- Borgeat A, Wilder-Smith OH, Saiah M, Rifat K (1992) Subhypnotic doses of Propofol possess direct antiemetic properties. Anesth Analg 74: 539-541.
- Smith I, Monk TG, White PF, Ding Y (1994) Propofol infusion during regional anesthesia: sedative, amnestic, and anxiolytic properties. Anesth Analg 79: 313-319.
- Shah A, Mosdossy G, McLeod S, Lehnhardt K, Peddle M, et al. (2011) A blinded, randomized controlled trial to evaluate ketamine-propofol versus Ketamine alone for procedural sedation in children. Ann Emerg Med 57: 425-433.
- Bhatt M, Kennedy RM, Osmond MH, Krauss B, McAllister JD, et al. (2009) Consensus-based recommendations for standardizing terminology and reporting adverse events for emergency department procedural sedation and analgesia in children. Ann Emerg Med 53: 426-435.
- Donnelly RF, Willman E, Andolfatto G (2008) Stability of ketamine-propofol mixtures for procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department. Can J Hosp Pharm 61: 426–430.
- Green SM, Roback MG, Kennedy RM, Krauss B (2011) Clinical Practice Guideline for Emergency Department Ketamine Dissociative Sedation: 2011 Update. Ann Emerg Med. 57: 449-461.
- Andolfatto G, Abu-Laban RB, Zed PJ, Staniforth SM, Stackhouse S, et al. (2012) Ketamine-propofol combination (ketofol) versus Propofol alone for emergency department procedural sedation and analgesia: a randomized double-blind trial. Ann Emerg Med 59: 504-512.
- Miner JR, Gray RO, Bahr J, Patel R, McGill JW (2010) Randomized clinical trial of Propofol versus Ketamine for procedural sedation in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 17: 604-611.
- Strayer RJ, Nelson LS (2008) Adverse events associated with Ketamine for procedural sedation in adults. Am J Emerg Med 26: 985-1028.
- Green SM, Clark R, Hostetler MA, Cohen M, Carlson D, et al. (1999) Inadvertent ketamine overdose in children: clinical manifestations and outcome. Ann Emerg Med 1999; 34: 492-497.
- Dillon JB (1969) Clinical experience with repeated ketamine administration for procedures requiring anesthesia. In: Ketamine, Kreuscher H. (edn.), Spring-Verlag, Berlin.
- Smith JA, Santer LJ (1993) Respiratory arrest following intramuscular ketamine injection in a 4-year-old child. Ann Emerg Med 22: 613.
- Reich DL, Silvay G (1989) Ketamine: an update on the first twenty-five years of clinical experience. Can J Anaestha 36:186.
- Green SM, Rothrock SG, Lynch EL, Ho M, Harris T, et al. (1998) Intramuscular Ketamine for pediatric sedation in the emergency department: safety profile in 1,022 cases. Ann Emerg Med 31: 688-697.
- Murphy JL Jr (1993) Hypertension and pulmonary oedema associated with ketamine administration in a patient with a history of substance abuse. Can J Anaesth 40: 160.
- Pandey CK, Mathur N, Singh N, Chandola HC (2000) Fulminant pulmonary edema after intramuscular Ketamine. Can J Anaesth 47: 894-896.
- Green SM (2007) Research advances in procedural sedation and analgesia. Ann Emerg Med 49: 31-36.
- Sivilotti MLA, Messenger DW, Vlymen JV, Dungey PE, Murray HE (2010) A comparative evaluation of capnometry versus pulse oximetry during procedural sedation and analgesia on room air. CJEM 12: 397-404.
Citation: Al-Sheikh S, Ahmad MJ, Khan ZM, Mohammadiih MR, Al Tabatabai M, et al. (2021) Single-Shot Sub-Dissociative Dose Ketofol versus Ketamine Alone for Emergency Department Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in Adult. J Emerg Med Trauma Surg Care 8: 058
Copyright: © 2021 Shihab AL Sheikh, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

